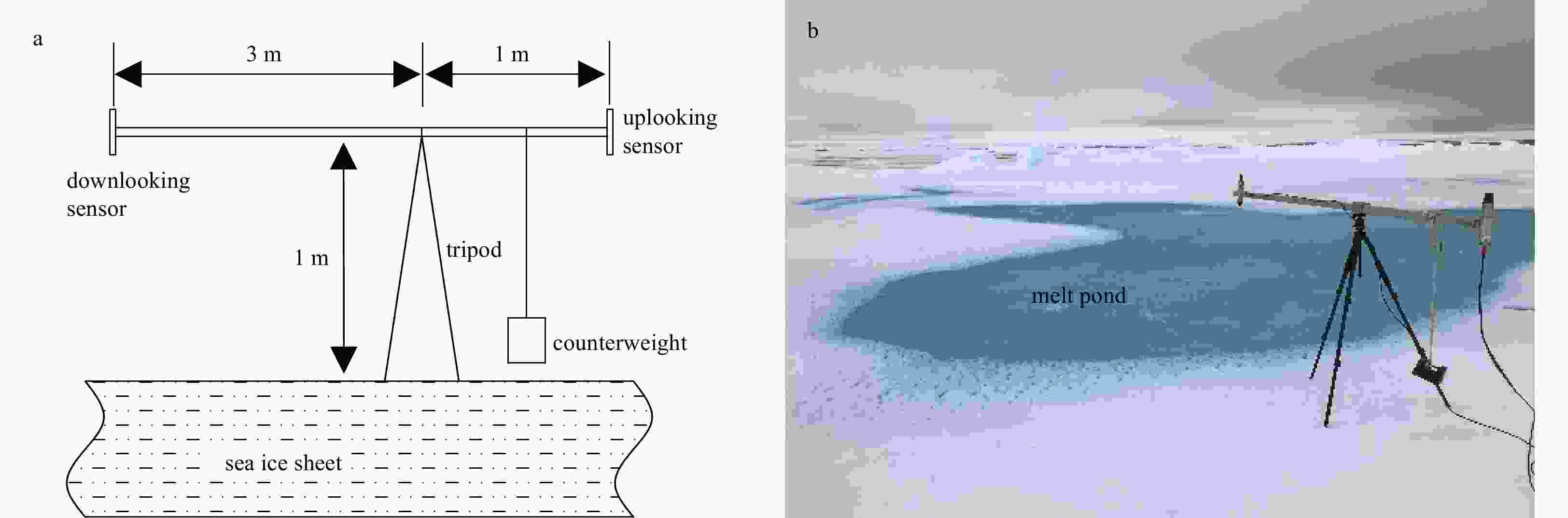
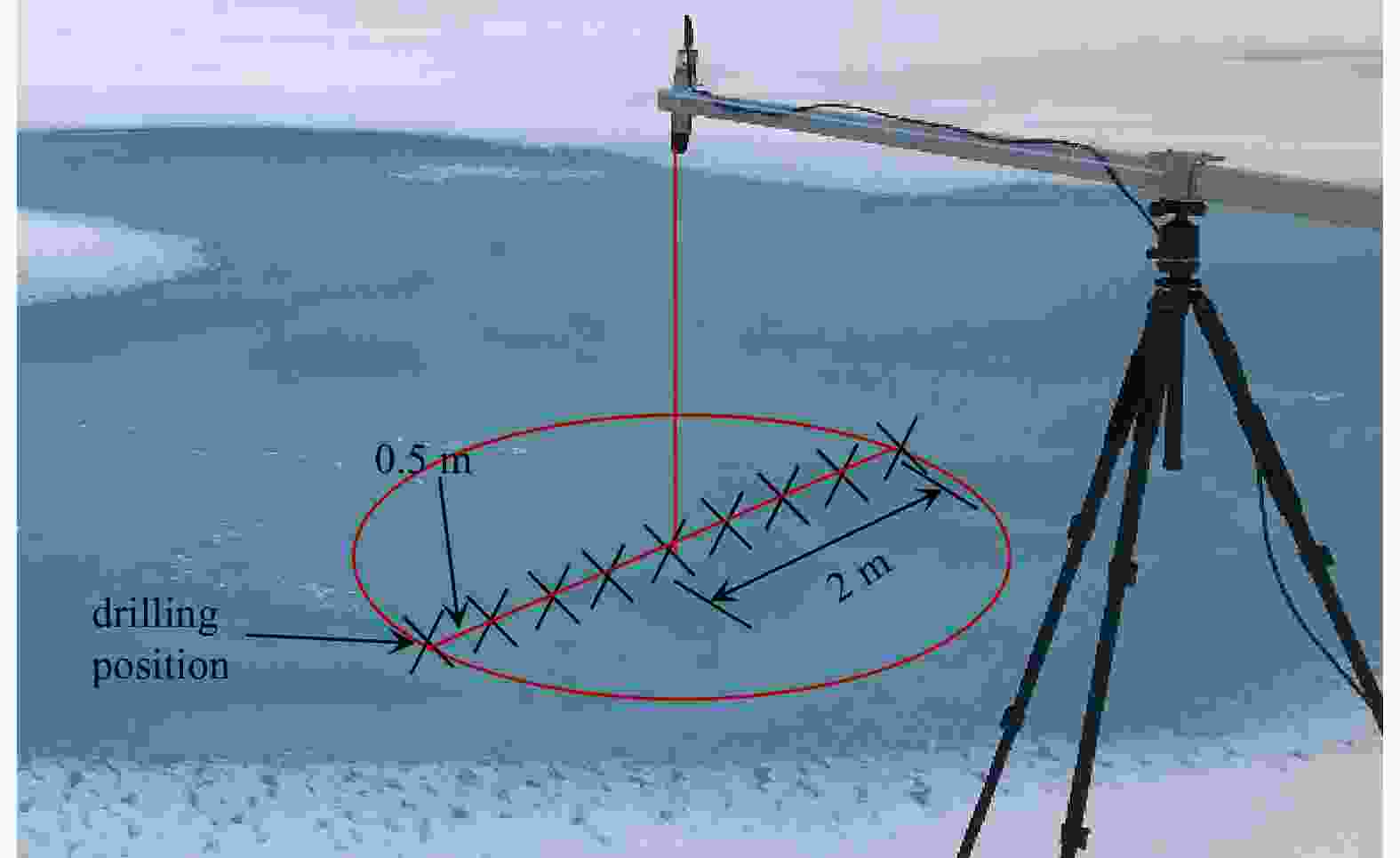
Physical and optical characteristics of sea ice in the Pacific Arctic Sector during the summer of 2018
-
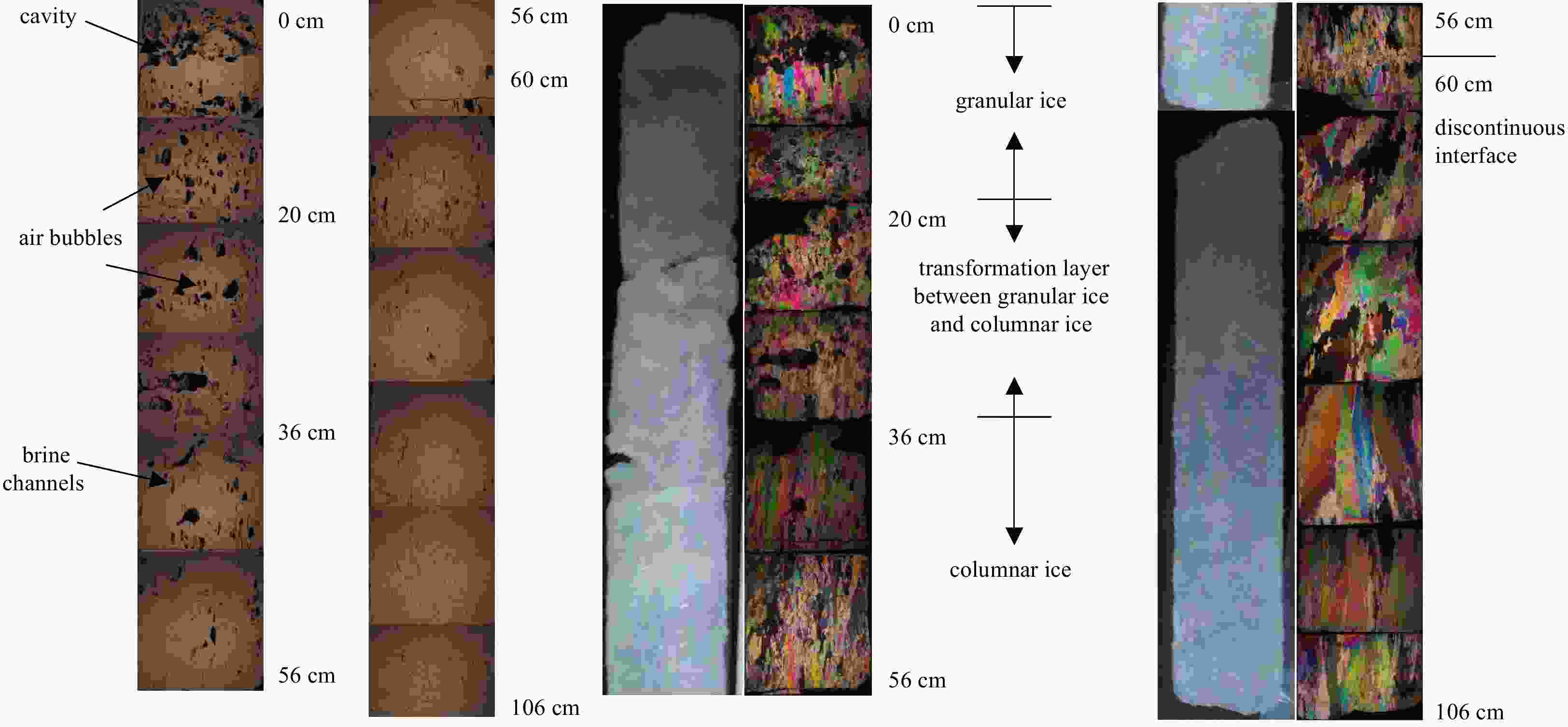
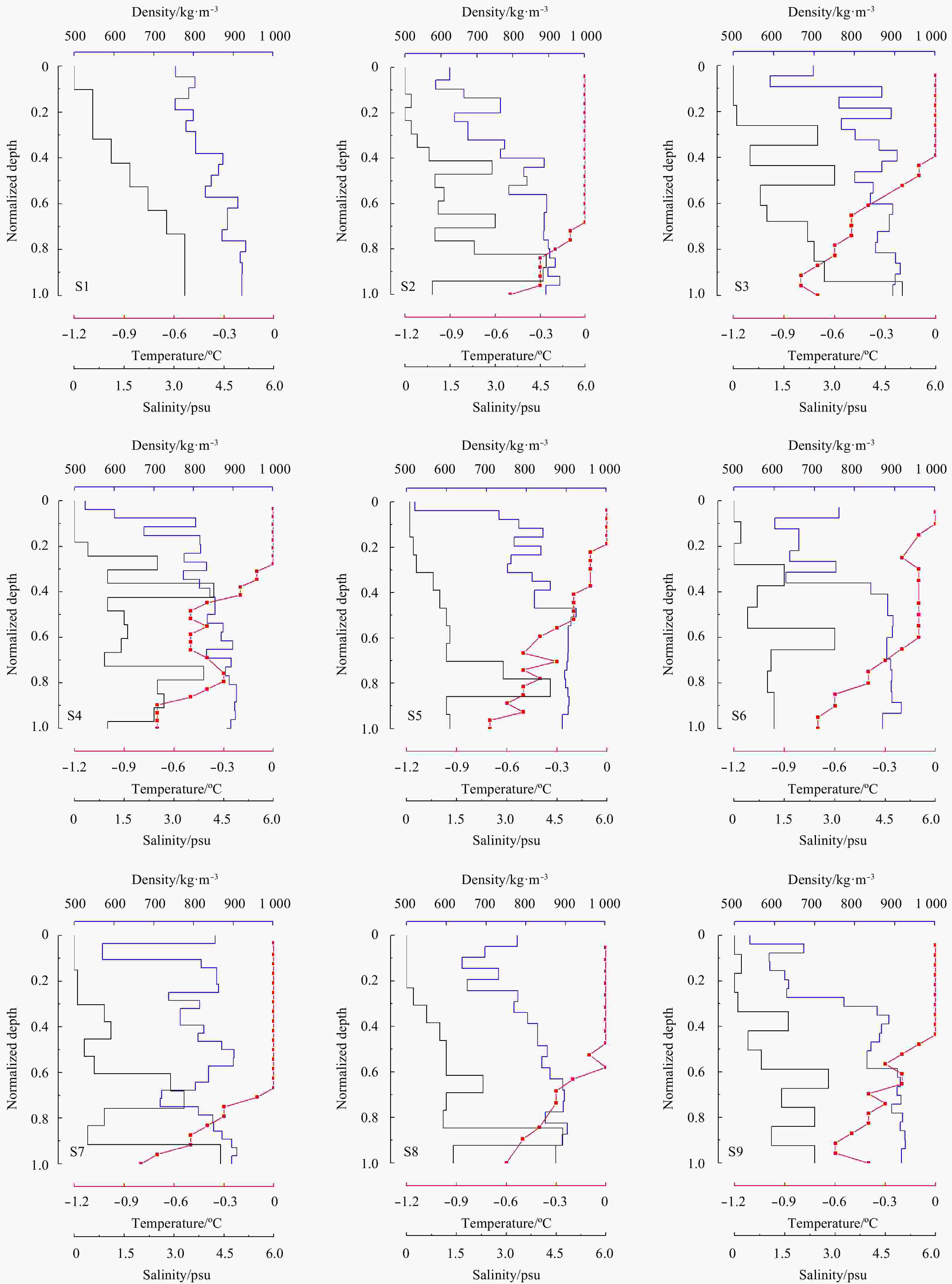
Abstract: The reduction in Arctic sea ice in summer has been reported to have a significant impact on the global climate. In this study, Arctic sea ice/snow at the end of the melting season in 2018 was investigated during CHINARE-2018, in terms of its temperature, salinity, density and textural structure, the snow density, water content and albedo, as well as morphology and albedo of the refreezing melt pond. The interior melting of sea ice caused a strong stratification of temperature, salinity and density. The temperature of sea ice ranged from –0.8°C to 0°C, and exhibited linear cooling with depth. The average salinity and density of sea ice were approximately 1.3 psu and 825 kg/m3, respectively, and increased slightly with depth. The first-year sea ice was dominated by columnar grained ice. Snow cover over all the investigated floes was in the melt phase, and the average water content and density were 0.74% and 241 kg/m3, respectively. The thickness of the thin ice lid ranged from 2.2 cm to 7.0 cm, and the depth of the pond ranged from 1.8 cm to 26.8 cm. The integrated albedo of the refreezing melt pond was in the range of 0.28–0.57. Because of the thin ice lid, the albedo of the melt pond improved to twice as high as that of the mature melt pond. These results provide a reference for the current state of Arctic sea ice and the mechanism of its reduction.
-
Key words:
- sea ice /
- snow /
- refreezing melt pond /
- physical properties /
- albedo
-
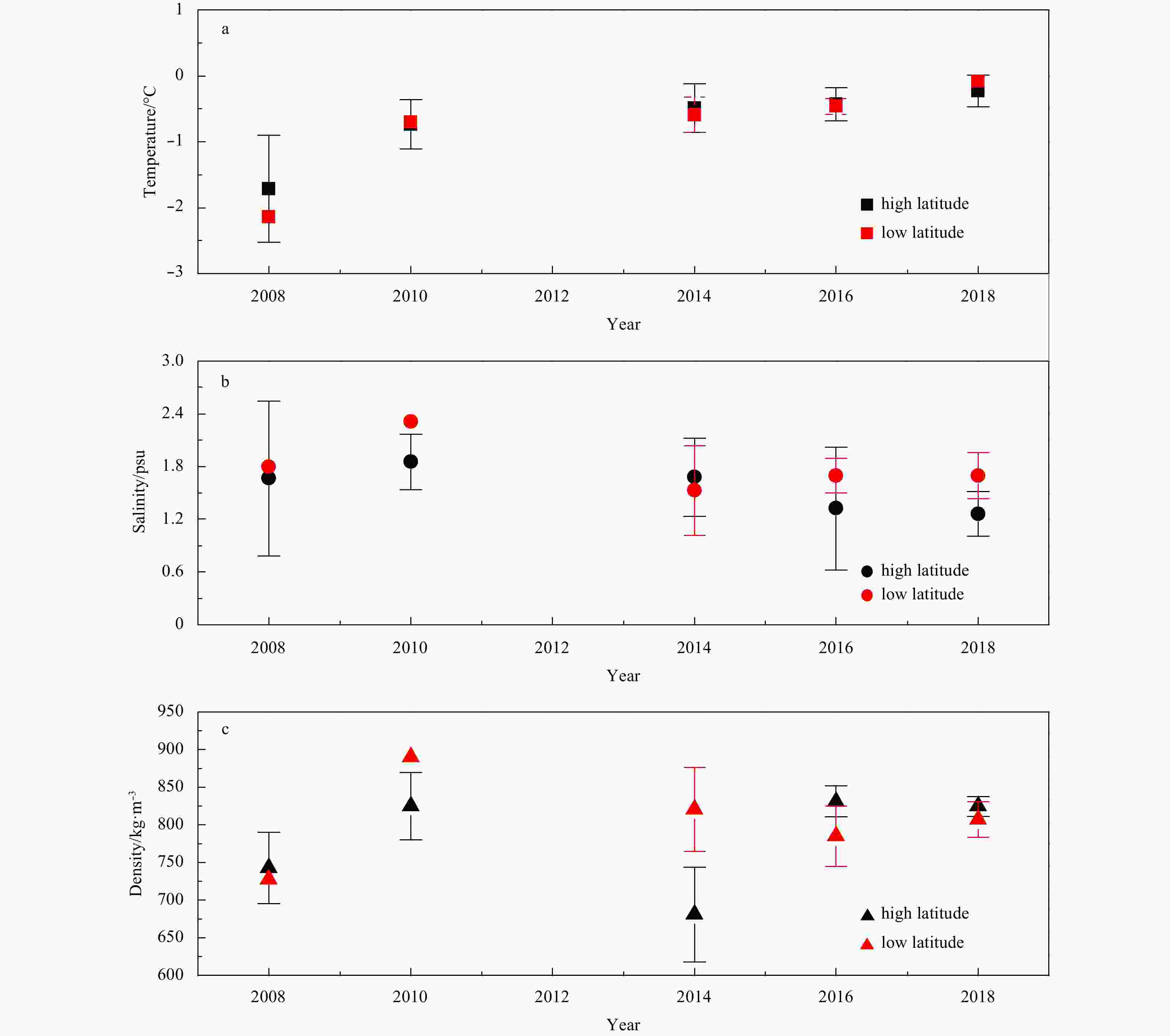
Figure 14. The average and standard deviation of the Arctic sea ice temperature (a), salinity (b) and density (c) in the past ten years (data collected by Lei et al., 2012a; Huang et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2018).
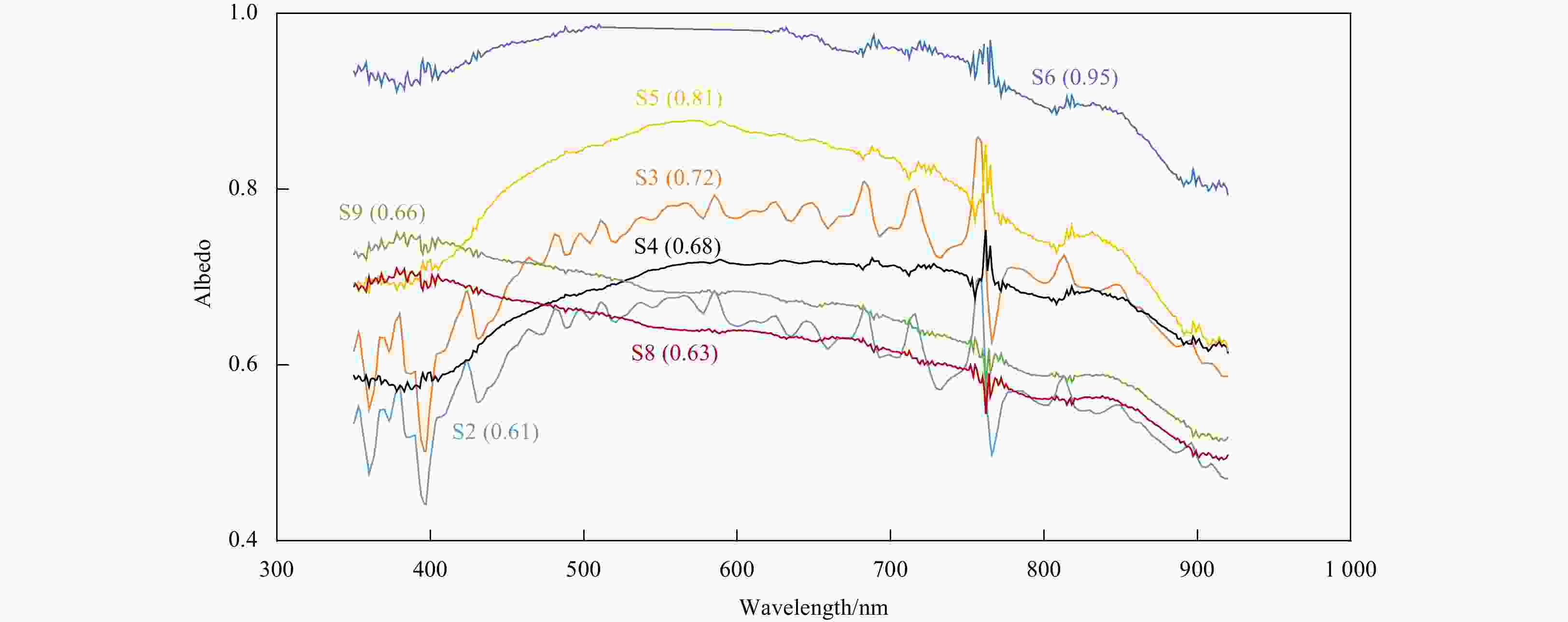
Figure 15. The Arctic sea ice albedo at different surface conditions, and the refreezing melt pond was the average and scope in this observation (the data of the new snow and autumn freeze up from Nicolaus et al. (2010a) and the melting snow, early seasonal melt pond and mature melt pond from Grenfell and Maykut (1977)).
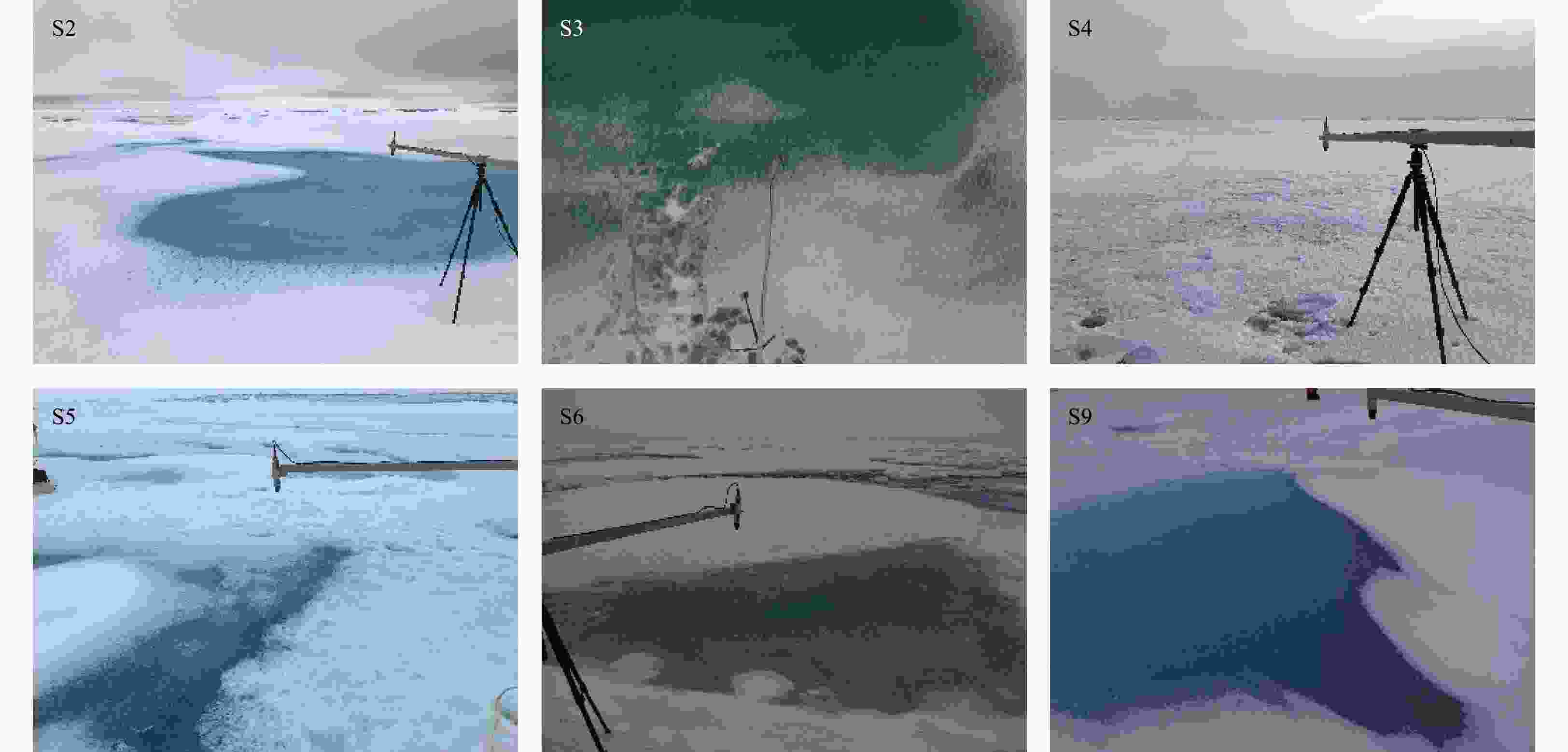
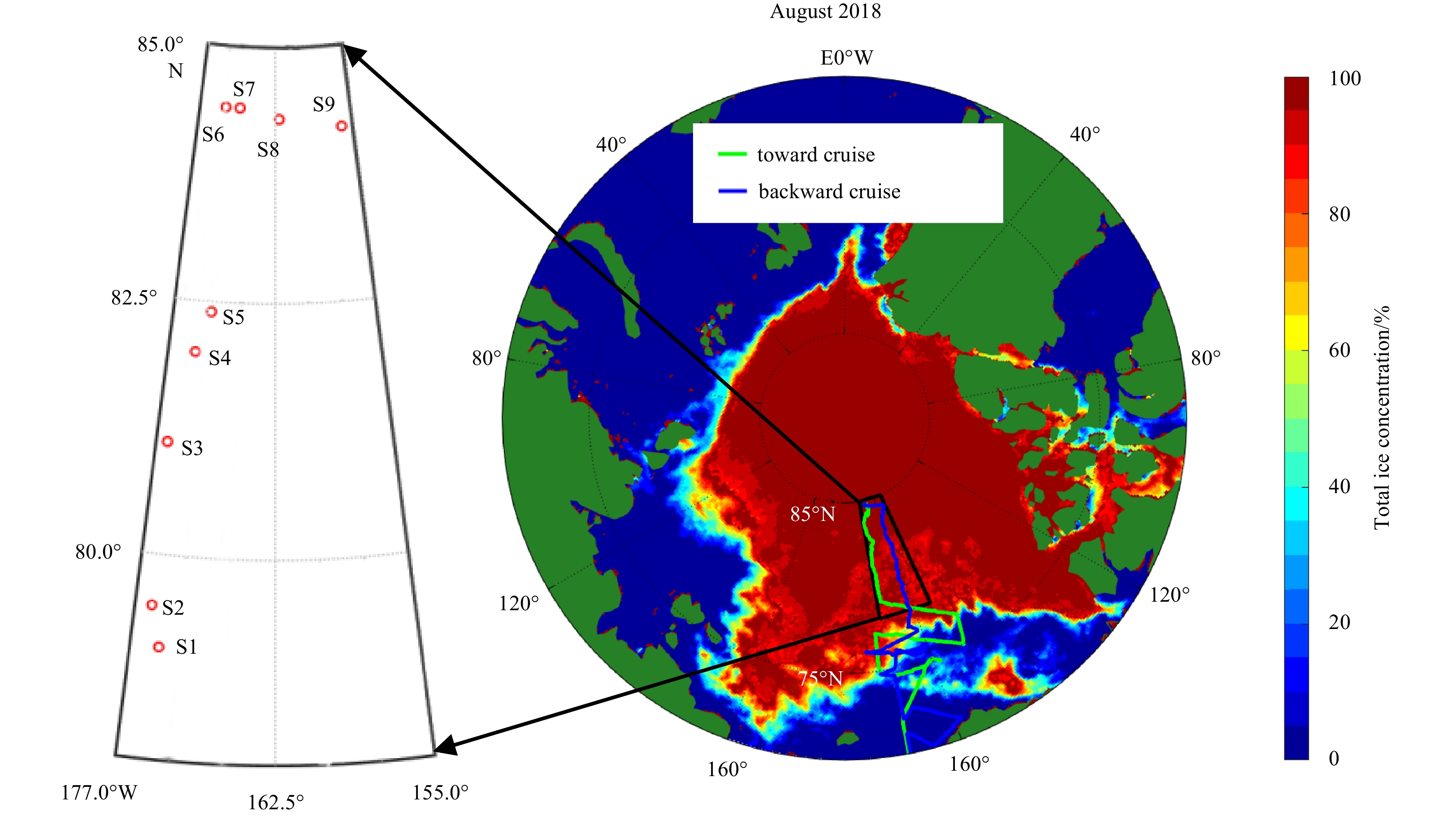
Table 1. The observational contents of each short-term ice station
Station Date and
time (UTC)Physical properties Albedo Ice Snow Melt pond Snow S1 10 Aug. 23:00–3:00 ○ × × × S2 12 Aug. 02:00–6:00 ○ ○ ○ ○ S3 13 Aug. 02:00–05:00 ○ ○ ○ ○ S4 14 Aug. 03:00–07:00 ○ ○ ○ ○ S5 14 Aug. 23:00–05:00 ○ × ○ × S6 20 Aug. 07:00–12:00 ○ × ○ ○ S7 21 Aug. 09:30–13:30 ○ × × × S8 23 Aug. 01:00–05:00 ○ × × ○ S9 24 Aug. 23:00–04:00 ○ ○ ○ ○ Note: ○ means measurement, and × means “no”. Table 2. Snow physical properties over short-term ice station
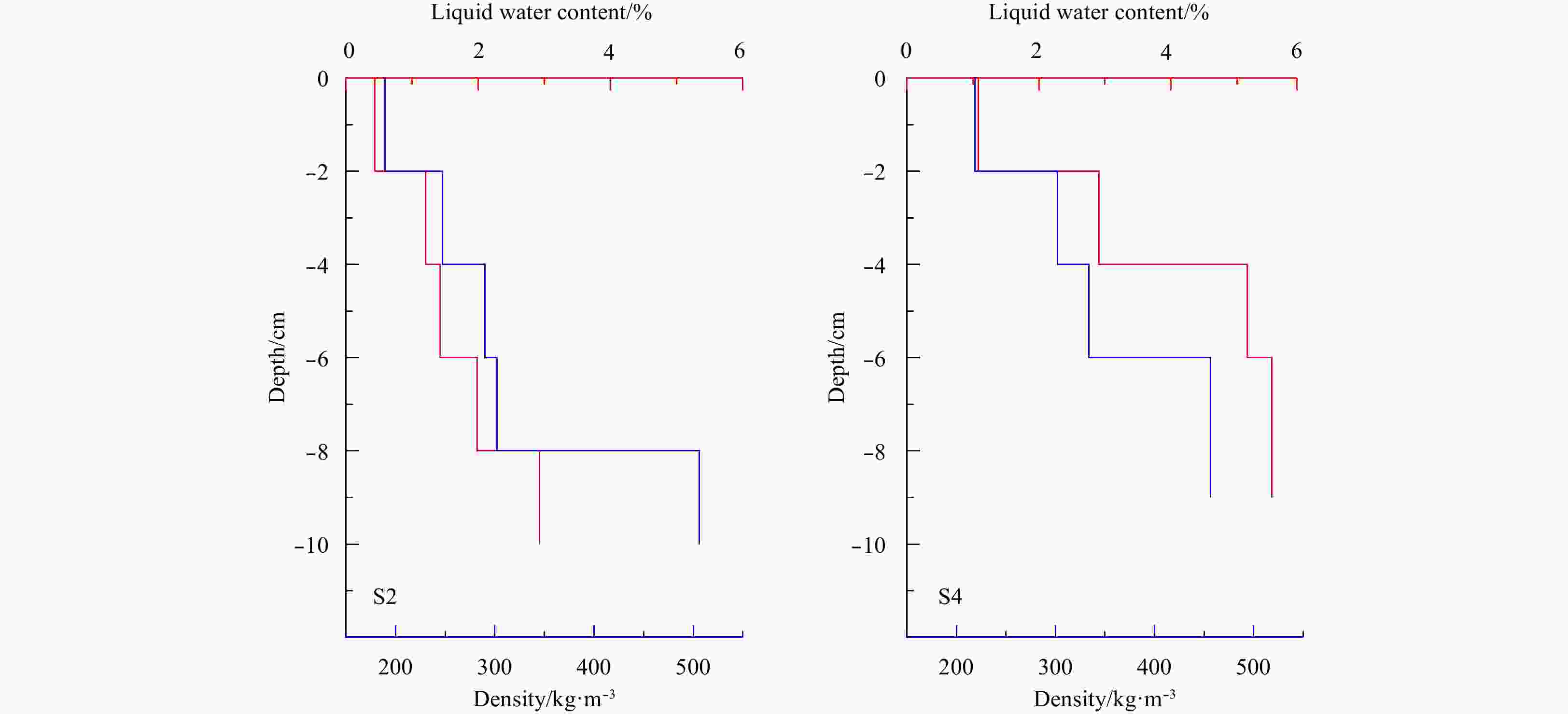
Station Snow thickness/mm Average water
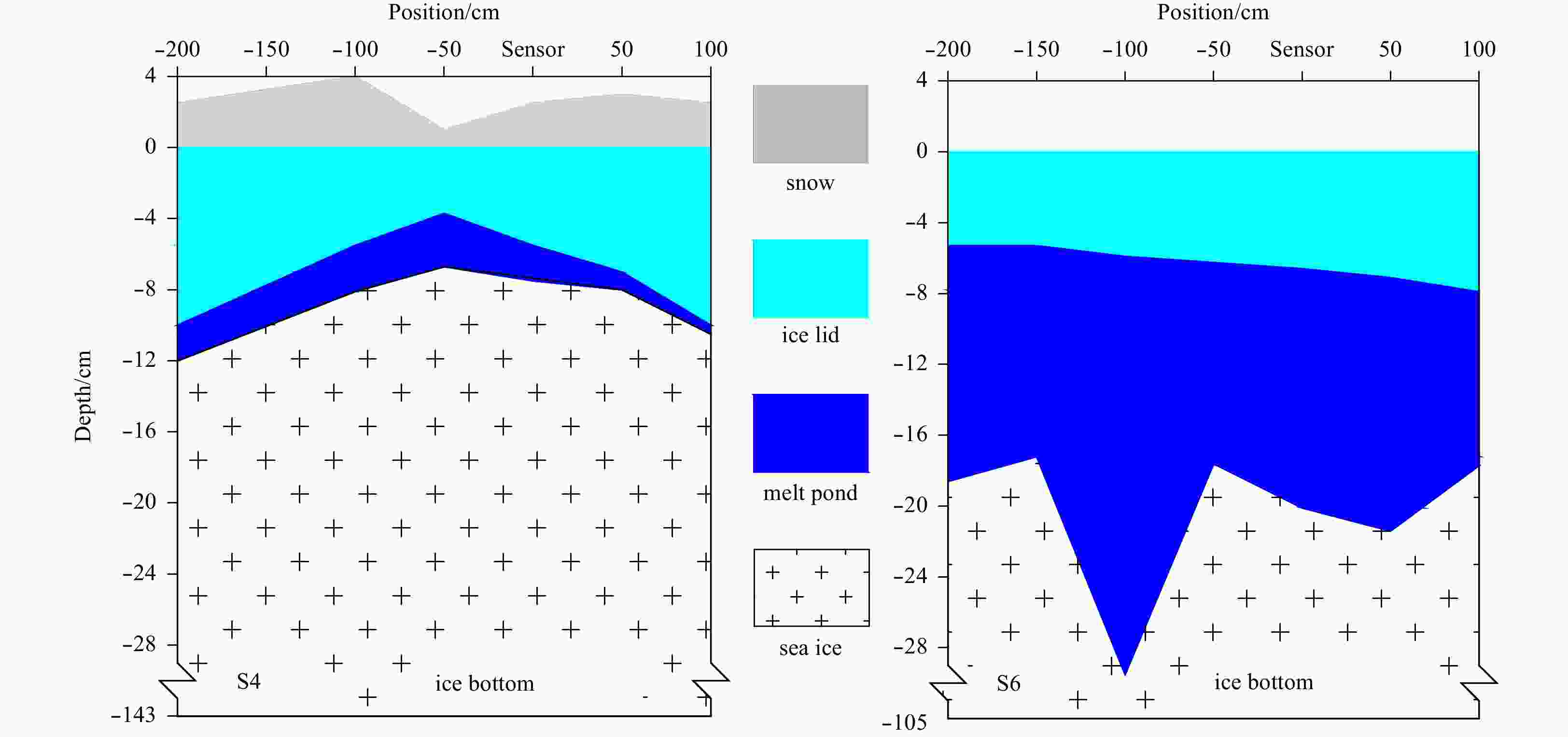
content/%Average density/kg·m–3 S2 100 1.59 307 S3 90 3.37 218 S4 67 0.31 185 S9 120 1.38 254 Table 3. The average thicknesses of the melt pond and snow
Station Melt pond/cm Snow/cm Hs Hl Hp Hi Hs Hi S2 0 2.2 12.4 – 10.2 – S3 0 3.8 4.3 117 6.0 116 S4 2.6 7.0 1.8 160 2.5 – S5 3.5 3.9 6.1 116 3.5 127 S6 0 5.5 11.9 105 3.0 – S8 – – – – 3.8 180 S9 0 5.7 26.8 149 8.0 168 Note: – means no data. Table 4. Dates and positions of in-situ measurements of Arctic sea ice in the last 10 years
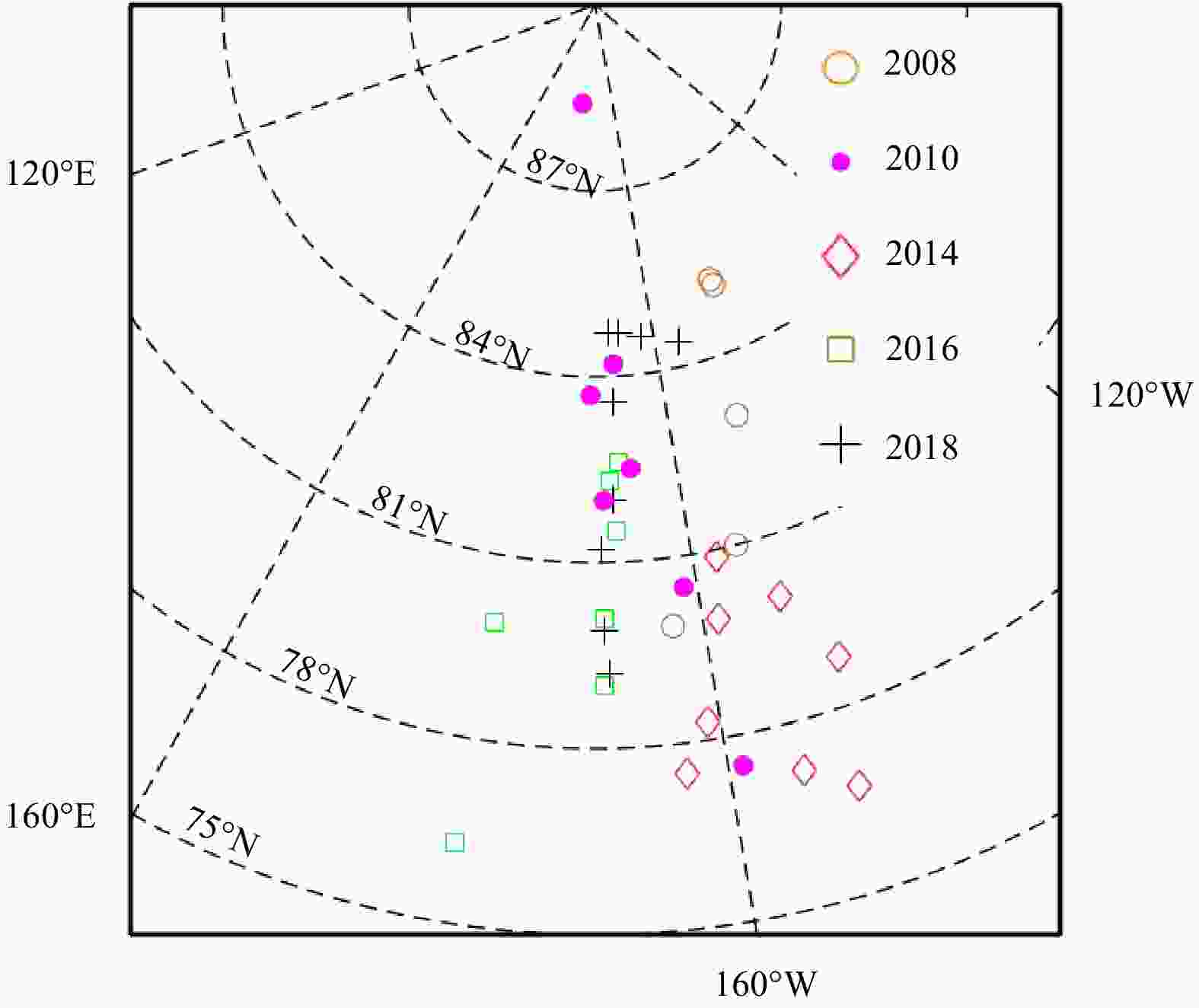
Year Date Ice station
numberPosition Latitude (N) Longitude (W) 2008 27 Aug.–2 Sep. 5 79.9º–85.2º 147.1º–162.8º 2010 30 Jul.–23 Aug. 7 77.5º–88.4º 158.9º–177.2º 2014 10 Aug.–28 Aug. 8 76.7º–80.9º 149.4º–163.1º 2016 4 Aug.–20 Aug. 7 76.3º–82.3º 167.0º–179.6º 2018 10 Aug.–24 Aug. 9 79.2º–84.7º 156.1º–169.4º -
[1] Aoki T, Hachikubo A, Hori M. 2003. Effects of snow physical parameters on shortwave broadband albedos. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(D19): 4616. doi: 10.1029/2003JD003506 [2] Berni J A J, Zarco-Tejada P J, Suarez L, et al. 2009. Thermal and narrowband multispectral remote sensing for vegetation monitoring from an unmanned aerial vehicle. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 47(3): 722–738. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2008.2010457 [3] Cheng Bin, Zhang Zhanhai, Vihma T, et al. 2008. Model experiments on snow and ice thermodynamics in the Arctic Ocean with CHINARE 2003 data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113(C9): C09020. doi: 10.1029/2007jc004654 [4] Comiso J C. 2012. Large decadal decline of the Arctic multiyear ice cover. Journal of Climate, 25(4): 1176–1193. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00113.1 [5] Comiso J C, Parkinson C L, Gersten R, et al. 2008. Accelerated decline in the arctic sea ice cover. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(1): L01703. doi: 10.1029/2007gl031972 [6] Curry J A, Schramm J L, Perovich D K, et al. 2001. Applications of sheba/fire data to evaluation of snow/ice albedo parameterizations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106(D14): 15345–15355. doi: 10.1029/2000jd900311 [7] Eicken H, Lensu M, Leppäranta M, et al. 1995. Thickness, structure, and properties of level summer multiyear ice in the Eurasian sector of the Arctic Ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research, 100(D11): 22697–22710. doi: 10.1029/95JC02188 [8] Flocco D, Feltham D L, Bailey E, et al. 2015. The refreezing of melt ponds on Arctic sea ice. Journal of Geophysical Research, 120(2): 647–659. doi: 10.1002/2014JC010140 [9] Galley R J, Trachtenberg M, Langlois A, et al. 2009. Observations of geophysical and dielectric properties and ground penetrating radar signatures for discrimination of snow, sea ice and freshwater ice thickness. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 57(1): 29–38. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2009.01.003 [10] Grenfell T C, Maykut G A. 1977. The optical properties of ice and snow in the Arctic Basin. Journal of Glaciology, 18(80): 445–463. doi: 10.3189/S0022143000021122 [11] Grenfell T C, Perovich D K. 1984. Spectral albedos of sea ice and incident solar irradiance in the southern Beaufort Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89(C3): 3573–3580. doi: 10.1029/jc089ic03p03573 [12] Han Hongwei, Li Zhijun, Huang Wenfeng, et al. 2015. The uniaxial compressive strength of the Arctic summer sea ice. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(1): 129–136. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0598-7 [13] Hohenegger C, Alali B, Steffen K R, et al. 2012. Transition in the fractal geometry of Arctic melt ponds. The Cryosphere, 6(5): 1157–1162. doi: 10.5194/tc-6-1157-2012 [14] Honda M, Inoue J, Yamane S. 2009. Influence of low Arctic sea-ice minima on anomalously cold Eurasian winters. Geophysical Research Letters, 36(8): L08707. doi: 10.1029/2008GL037079 [15] Huang Wenfeng, Lei Ruibo, Han Hongwei, et al. 2016. Physical structures and interior melt of the central Arctic sea ice/snow in summer 2012. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 124: 127–137. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2016.01.005 [16] Huang Wenfeng, Lei Ruibo, Ilkka M, et al. 2013. The physical structures of snow and sea ice in the Arctic section of 150o-180oW during the summer of 2010. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 32(5): 57–67. doi: 10.1007/s13131-013-0314-4 [17] Johannessen O M, Bengtsson L, Miles M W, et al. 2004. Arctic climate change: observed and modelled temperature and sea-ice variability. Tellus A: Dynamic Meteorology and Oceanography, 56(5): 559–560. doi: 10.3402/tellusa.v56i5.14599 [18] Keilin D, Hartree E F. 1949. Effect of low temperature on the absorption spectra of haemoproteins; with observations on the absorption spectrum of oxygen. Nature, 164(4163): 254–259. doi: 10.1038/164254a0 [19] Kwok R. 2018. Arctic sea ice thickness, volume, and multiyear ice coverage: losses and coupled variability (1958–2018). Environmental Research Letters, 13(10): 105005. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aae3ec [20] Lei Ruibo, Cheng Bin, Heil P, et al. 2018. Seasonal and interannual variations of sea ice mass balance from the central Arctic to the Greenland Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 123(4): 2422–2439. doi: 10.1002/2017jc013548 [21] Lei Ruibo, Leppäranta M, Erm A, et al. 2011. Field investigations of apparent optical properties of ice cover in Finnish and Estonian lakes in winter 2009. Estonian Journal of Earth Sciences, 60(1): 50–64. doi: 10.3176/earth.2011.1.05 [22] Lei Ruibo, Li Zhijun, Li Na, et al. 2012a. Crucial physical characteristics of sea ice in the Arctic section of 143°-180°W during August and early September 2008. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 31(4): 65–75. doi: 10.1007/s13131-012-0221-0 [23] Lei Ruibo, Zhang Zhanhai, Matero I, et al. 2012b. Reflection and transmission of irradiance by snow and sea ice in the central Arctic Ocean in summer 2010. Polar Research, 31(1): 17325. doi: 10.3402/polar.v31i0.17325 [24] Lindsay R, Schweiger A. 2015. Arctic sea ice thickness loss determined using subsurface, aircraft, and satellite observations. The Cryosphere, 9(1): 269–283. doi: 10.5194/tc-9-269-2015 [25] López-Moreno J I, Fassnacht S R, Heath J T, et al. 2013. Small scale spatial variability of snow density and depth over complex alpine terrain: Implications for estimating snow water equivalent. Advances in Water Resources, 55: 40–52. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.08.010 [26] Lu P, Cao X, Wang Q, et al. 2018a. Impact of a surface ice lid on the optical properties of melt ponds. Journal of Geophysical Research, 123(11): 8313–8328. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014161 [27] Lu Peng, Cheng Bin, Leppäranta M, et al. 2018b. Partitioning of solar radiation in Arctic sea ice during melt season. Oceanologia, 60(4): 464–477. doi: 10.1016/j.oceano.2018.03.002 [28] Lu Peng, Leppäranta M, Cheng Bin, et al. 2016. Influence of melt-pond depth and ice thickness on Arctic sea-ice albedo and light transmittance. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 124: 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2015.12.010 [29] Maykut G A, Untersteiner N. 1971. Some results from a time-dependent thermodynamic model of sea ice. Journal of Geophysical Research, 76(6): 1550–1575. doi: 10.1029/JC076i006p01550 [30] Martin S. 1979. A field study of brine drainage and oil entrainment in first-year sea ice. Journal of Glaciology, 22(88): 473–502. doi: 10.3189/S0022143000014477 [31] Morassutti M P, Ledrew E F. 1996. Albedo and depth of melt ponds on sea-ice. International Journal of Climatology, 16(7): 817–838. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0088(199607)16:7<817::aid-joc44>3.0.co;2-5 [32] Mundy C J, Ehn J K, Barber D G, et al. 2007. Influence of snow cover and algae on the spectral dependence of transmitted irradiance through Arctic landfast first-year sea ice. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112(C3): C03007. doi: 10.1029/2006JC003683 [33] Nicolaus M, Gerland S, Hudson S R, et al. 2010a. Seasonality of spectral albedo and transmittance as observed in the Arctic transpolar drift in 2007. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(C11): C11011. doi: 10.1029/2009JC006074 [34] Nicolaus M, Hudson S R, Gerland S, et al. 2010b. A modern concept for autonomous and continuous measurements of spectral albedo and transmittance of sea ice. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 62(1): 14–28. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2010.03.001 [35] Nicolaus M, Katlein C, Maslanik J, et al. 2012. Changes in Arctic sea ice result in increasing light transmittance and absorption. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(24): L24501. doi: 10.1029/2012GL053738 [36] Perovich D K. 1996. The optical properties of sea ice. Hanover: Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory [37] Perovich D K, Grenfell T C, Light B, et al. 2002. Seasonal evolution of the albedo of multiyear Arctic sea ice. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107(C10): 8044. doi: 10.1029/2000JC000438 [38] Perovich D K, Grenfell T C, Light B, et al. 2009. Transpolar observations of the morphological properties of Arctic sea ice. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114(C1): C00A04. doi: 10.1029/2008JC004892 [39] Perovich D K, Polashenski C. 2012. Albedo evolution of seasonal Arctic sea ice. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(8): L08501. doi: 10.1029/2012GL051432 [40] Petrich C, Eicken H. 2009. Growth, structure and properties of sea ice. In: Thomas D N, Dieckmann G S, eds. Sea Ice. 2nd ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell [41] Polashenski C, Perovich D, Courville Z. 2012. The mechanisms of sea ice melt pond formation and evolution. Journal of Geophysical Research, 117(C1): C01001. doi: 10.1029/2011JC007231 [42] Renner A H H, Gerland S, Haas C, et al. 2014. Evidence of Arctic sea ice thinning from direct observations. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(14): 5029–5036. doi: 10.1002/2014GL060369 [43] Stroeve J C, Kattsov V, Barrett A, et al. 2012. Trends in Arctic sea ice extent from CMIP5, CMIP3 and observations. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(16): L16502. doi: 10.1029/2012GL052676 [44] Timco G W, Frederking R M W. 1996. A review of sea ice density. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 24(1): 1–6. doi: 10.1016/0165-232X(95)00007-X [45] Timco G W, Weeks W F. 2010. A review of the engineering properties of sea ice. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 60(2): 107–129. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2009.10.003 [46] Tucker III W B, Gow A J, Meese D A, et al. 1999. Physical characteristics of summer sea ice across the arctic ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104(C1): 1489–1504. doi: 10.1029/98jc02607 [47] Wang Qingkai, Li Zhijun, Lei Ruibo, et al. 2018. Estimation of the uniaxial compressive strength of Arctic sea ice during melt season. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 151: 9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.03.002 [48] Webster M A, Rigor I G, Perovich D K, et al. 2015. Seasonal evolution of melt ponds on Arctic sea ice. Journal of Geophysical Research, 120(9): 5968–5982. doi: 10.1002/2015JC011030 [49] Weeks W F, Ackley S F. 1986. The growth, structure, and properties of sea ice. In: Untersteiner N, ed. The Geophysics of Sea Ice. Boston, MA: Springer, 9–164, doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-5352-0_2 -




 下载:
下载: