Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the elements in ferromanganese nodules from the Northwest Pacific
-
Abstract: To explore the geochemical characteristics and genesis of the elements in ferromanganese nodules from the Northwest Pacific, this study analyses the mineral composition, elemental content, occurrence phase and genetic mechanisms of samples by X-ray diffraction (XRD), inductively coupled plasma‒optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), inductively coupled plasma‒mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and phase analysis methods. The results show that ferromanganese nodules are mainly hydrogenetic, and Mn/Fe ratio ranges from 0.95 to 2.05. The major minerals are vernadite (δ-MnO2) and amorphous ferric oxyhydroxide (FeOOH), and the secondary minerals include todorokite, birnessite, quartz and plagioclase. Ferromanganese nodules contain high contents of Co (0.24%~0.42%), Cu (0.23%~0.73%), Ni (0.33%~0.86%) and rare earth elements (REEs,
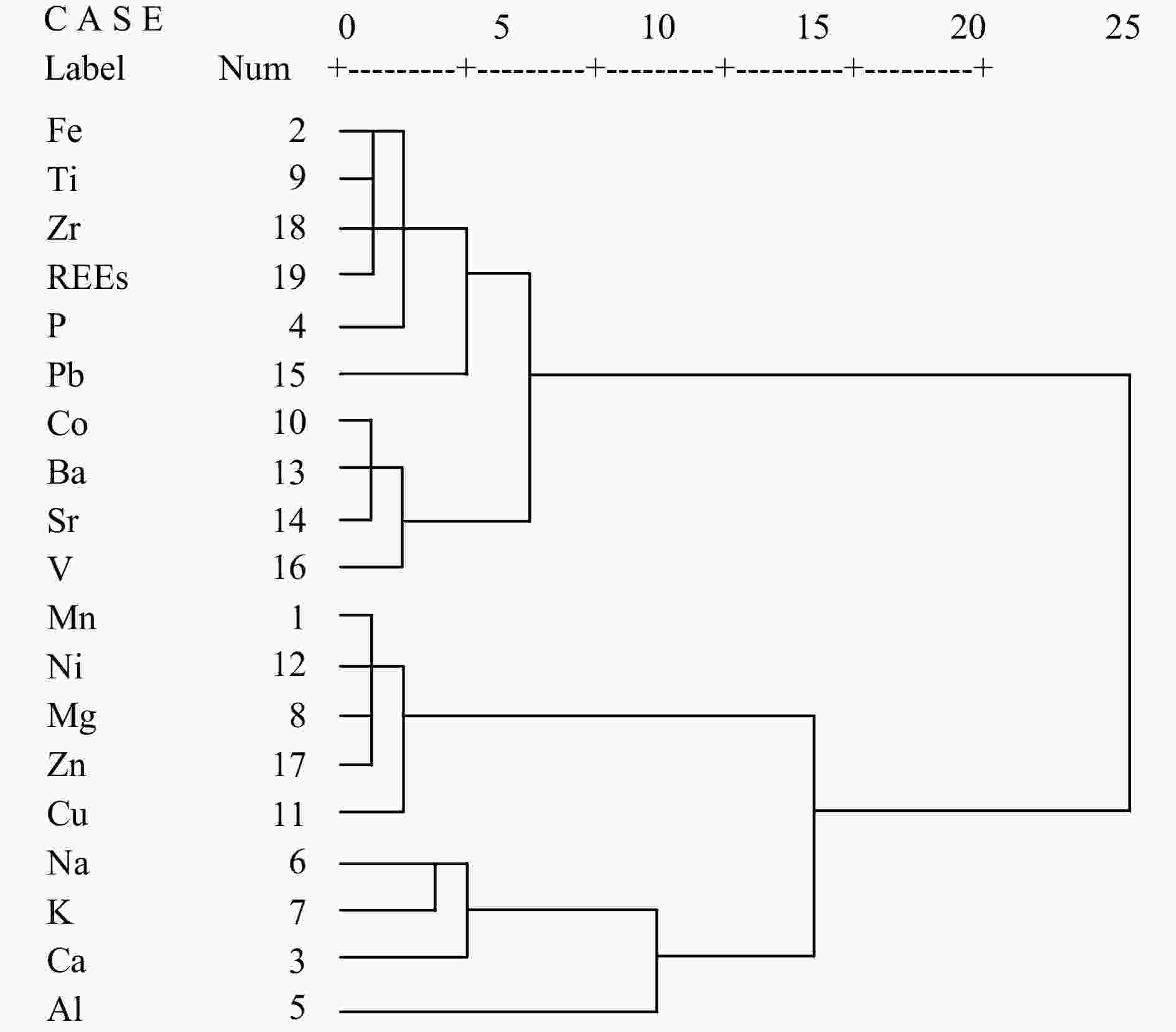
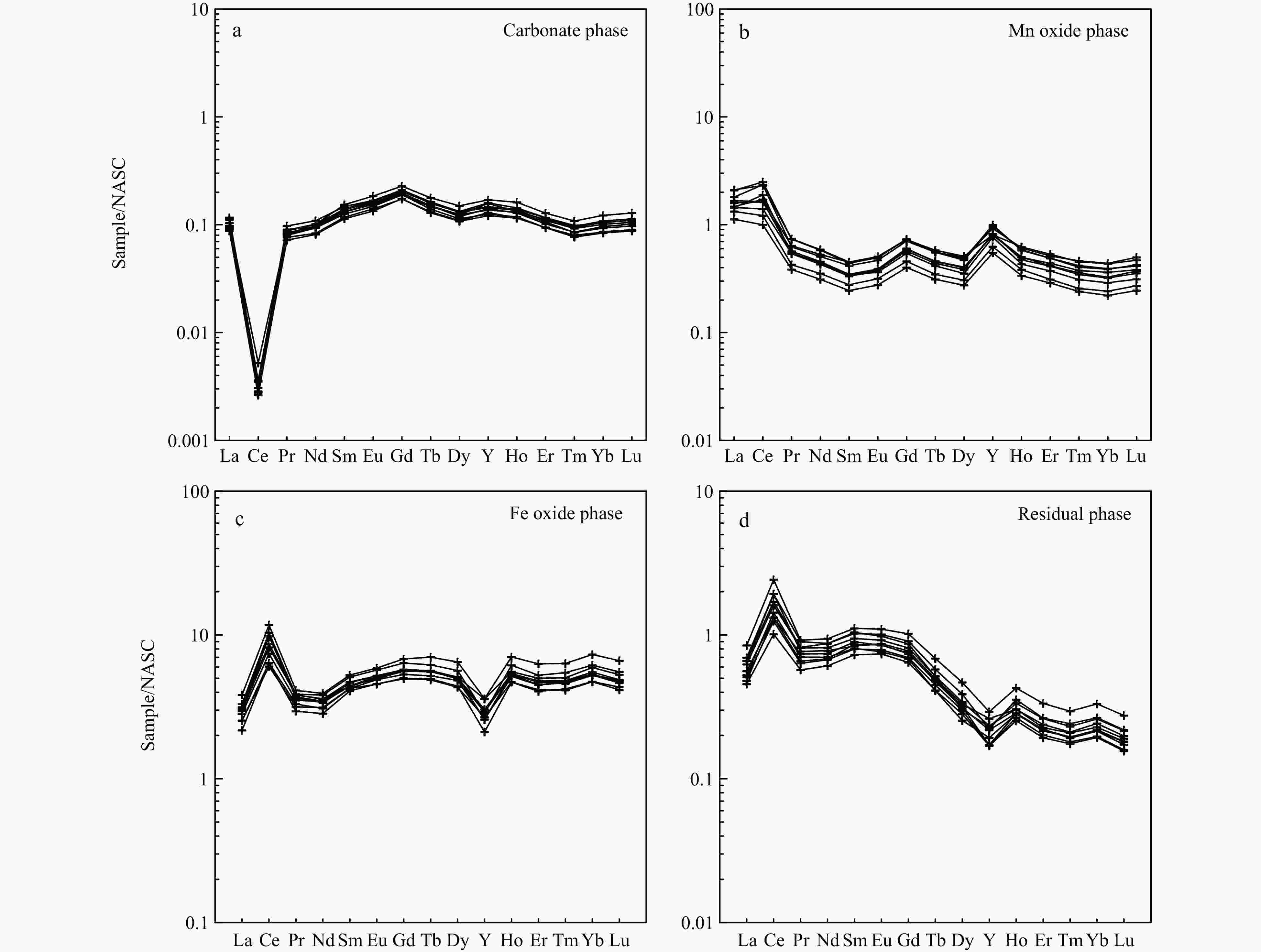
1192 µg/g~1990 µg/g), which have positive Ce and negative Y anomalies but no Eu anomaly. A cluster analysis suggests that the elements in ferromanganese nodules can be divided into three groups: hydrogenetic components, including Fe, Ti, Zr, P, Pb, Co, Ba, Sr, V and REEs; diagenetic components, including Mn, Ni, Mg, Zn and Cu; and detrital components, including Al, Na, K and Ca. According to chemical leaching, ferromanganese nodules can be divided into four phases: Na, Ca, Mg and Sr are mainly enriched in the carbonate phase; Mn, Co, Ni and Ba are mainly enriched in the Mn-oxide phase; Fe, P, Ti, Cu, Pb, V, Zn, Zr and REEs are mainly enriched in the Fe-oxide phase; and Al and K are mainly enriched in the residual phase. A combination of the two different methods reveal selective enrichment of metal elements from seawater by ferromanganese nodules, featuring multisource mineralization. Moreover, through ion exchange and adsorption, approximately 71.2% of REEs are enriched in the Fe-oxide phase, 15.4% in the Mn-oxide phase and 12.4% in the residual phase, while REE contents in the carbonate phase are relatively low. In addition, under the oxic conditions of seawater, the oxidation of soluble Ce3+ to insoluble CeO2 together with Fe-Mn minerals results in Ce enrichment in ferromanganese nodules. This study provides a reference for the metallogenesis of ferromanganese nodules from the Northwest Pacific.-
Key words:
- Northwest Pacific /
- ferromanganese nodules /
- REEs /
- occurrence phase /
- genesis
-
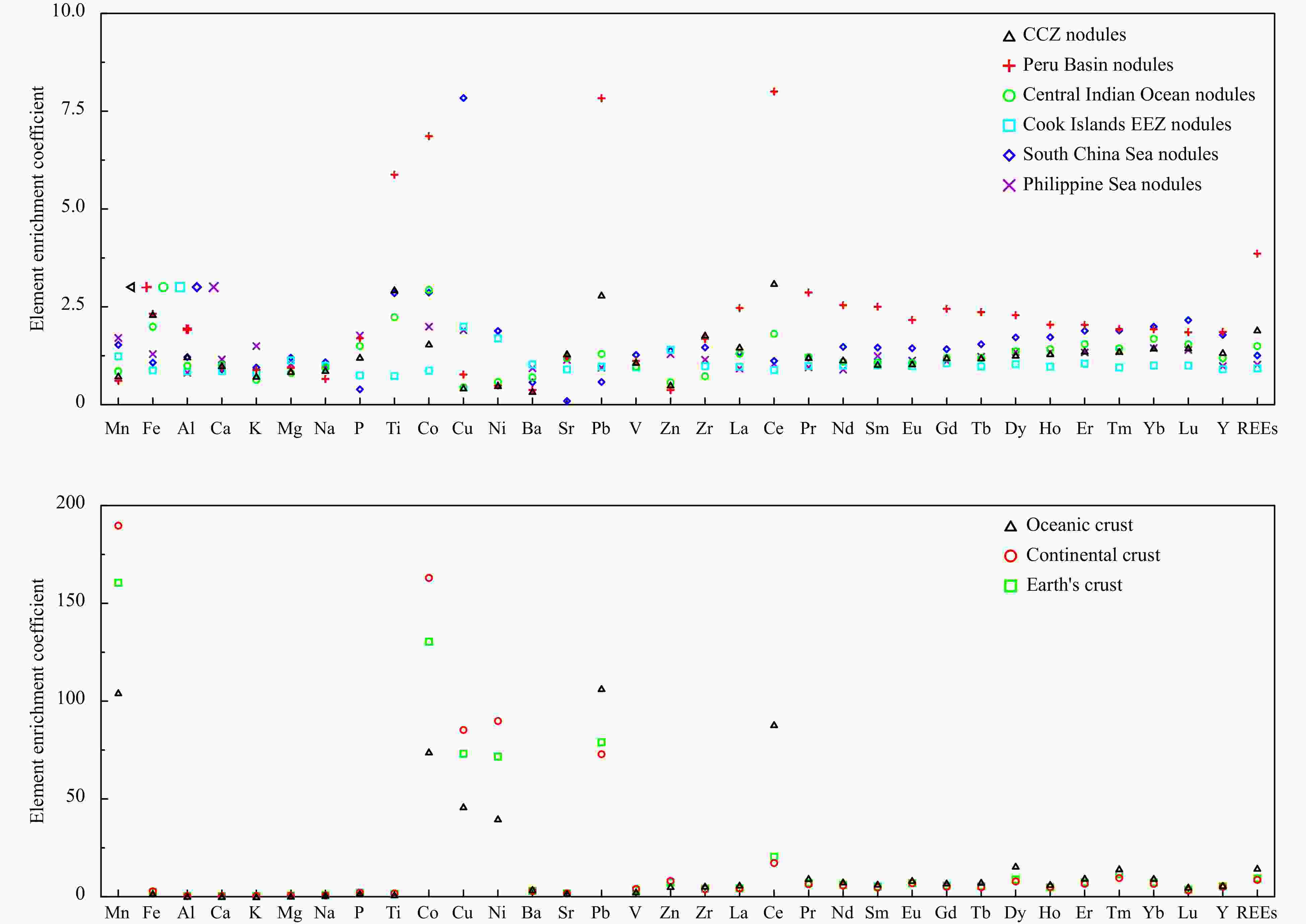
Figure 4. Element enrichment coefficients of ferromanganese nodules and other samples: Nodule data sources: CCZ, Peru Basin and Central Indian Ocean Basin (Hein et al., 2013), Cook Islands EEZ (Hein et al., 2015), South China Sea (Yin et al., 2019), Philippine Sea (Zhou et al., 2022), oceanic crust and continental crust (Li, 1984), Earth’s crust (Li, 1976).
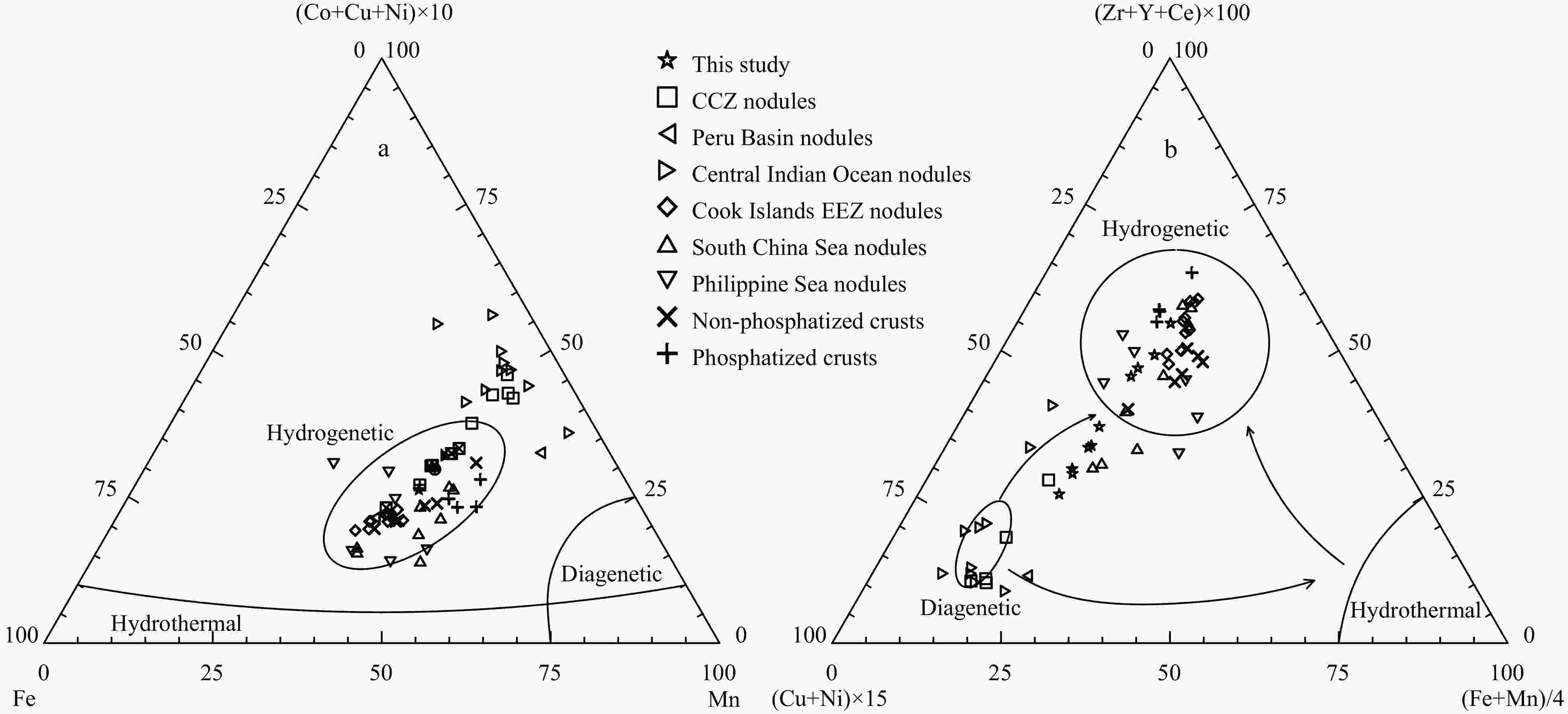
Figure 5. Ternary diagram of ferromanganese nodules: a. Fe-(Co+Cu+Ni)×10-Mn; b. (Cu+Ni)×15-(Zr+Y+Ce)×100- (Fe+Mn)/4. Nodule data sources: CCZ (Reykhard and Shulga, 2019), Peru Basin (Hein et al., 2013), Central Indian Ocean Basin (Sensarma et al., 2021), Cook Islands EEZ (Hein et al., 2015), South China Sea (Zhong et al., 2017a), Philippine Sea (Zhou et al., 2022), non-phosphatized and phosphatized crusts (Gao et al., 2022).
Figure 6. Elemental correlation diagram of ferromanganese nodules: a. δCe vs Nd, b. δCe vs YN/HoN. δCe=2CeN/(LaN+PrN), LaN, CeN, PrN, YN and HoN are normalized to the NASC. NASC data are from Wang et al. (1989). Nodule data sources: CCZ (Reykhard and Shulga, 2019), Peru Basin (Hein et al., 2013), Central Indian Ocean Basin (Sensarma et al., 2021), Cook Islands EEZ (Hein et al., 2015), South China Sea (Zhong et al., 2017a), Philippine Sea (Zhou et al., 2022), non-phosphatized and phosphatized crusts (Gao et al., 2022).
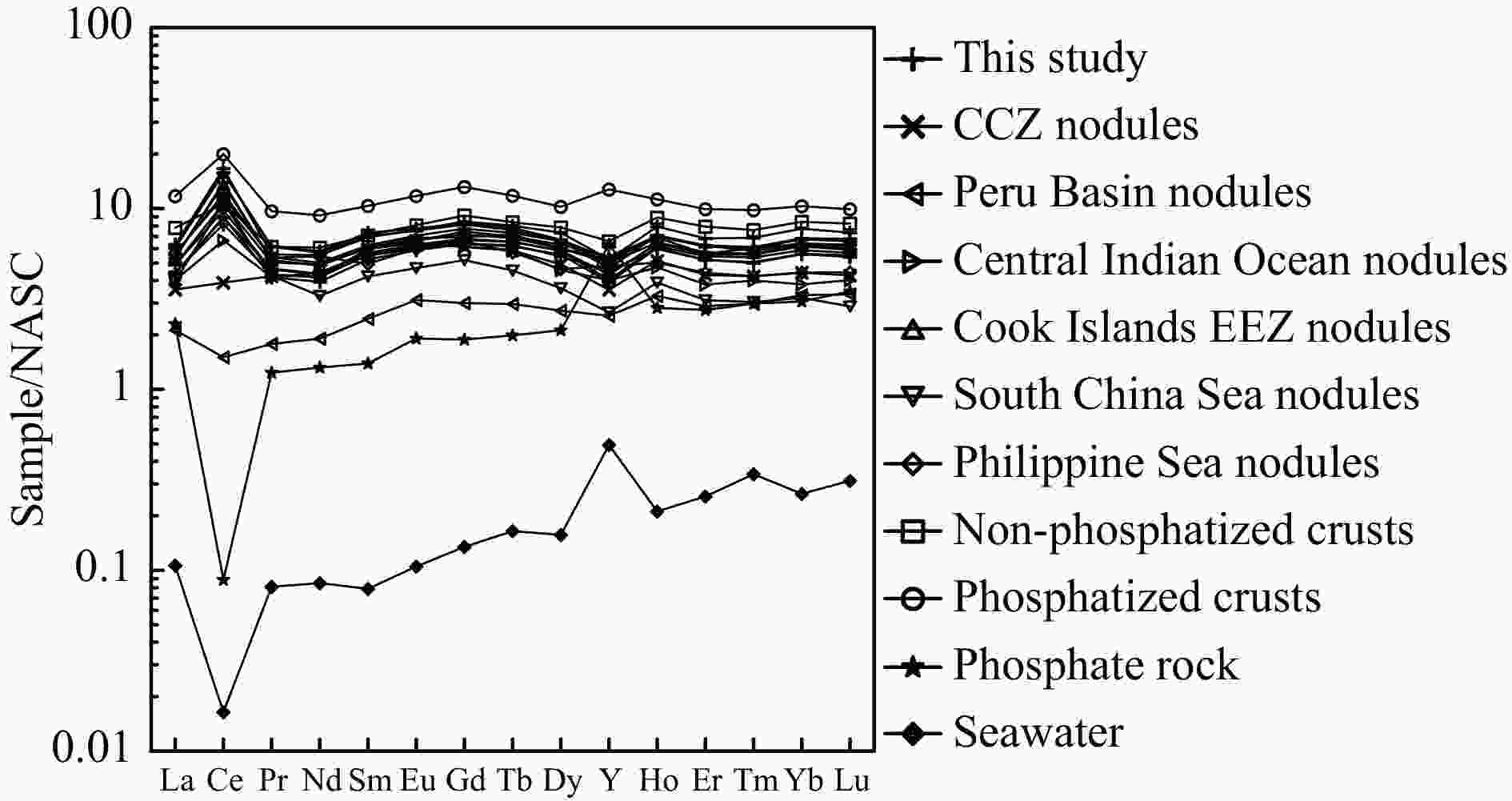
Figure 7. NASC-normalized REE distribution patterns of ferromanganese nodules: REE data of seawater are multiplied by 106. NASC and seawater data are from Wang et al. (1989), and the phosphate rock data are from this study. Nodule data sources: CCZ, Peru Basin and Central Indian Ocean Basin (Hein et al., 2013), Cook Islands EEZ (Hein et al., 2015), South China Sea (Yin et al., 2019), Philippine Sea (Zhou et al., 2022), non-phosphatized crusts (Gao et al., 2023), phosphatized crusts (Gao et al., 2022),
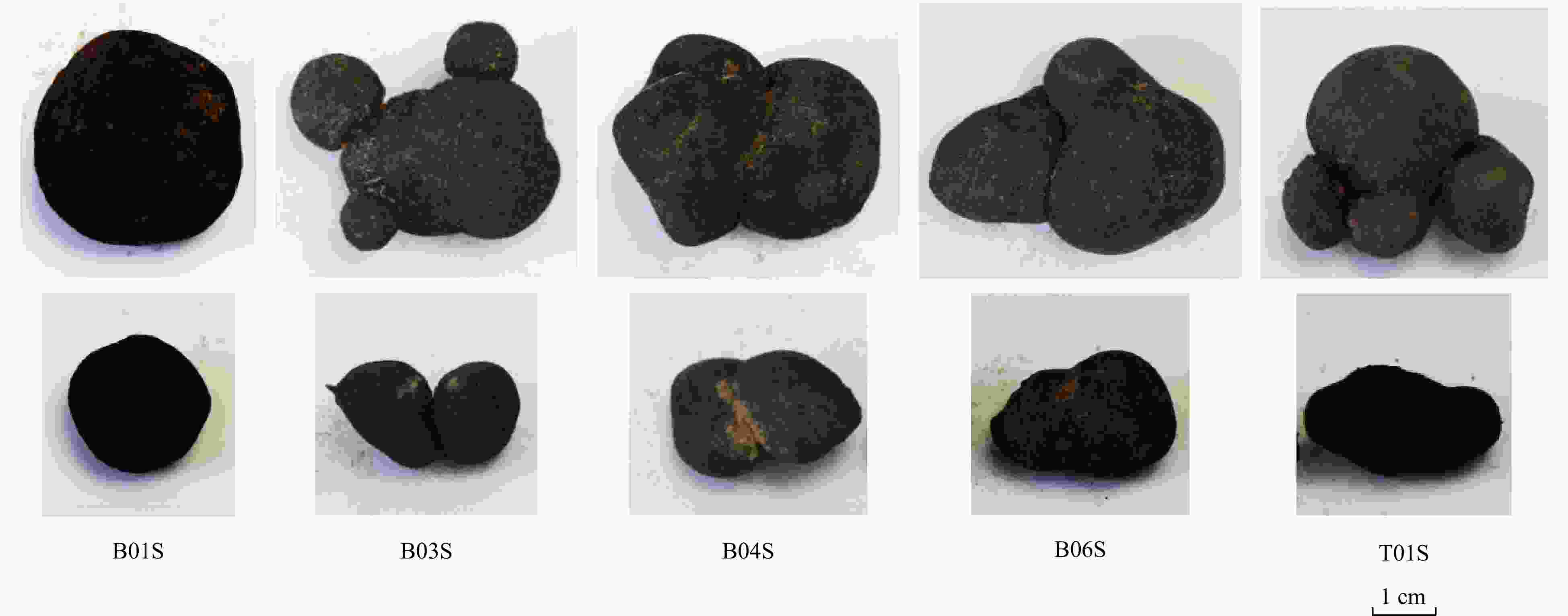
Table 1. Description of ferromanganese nodule samples
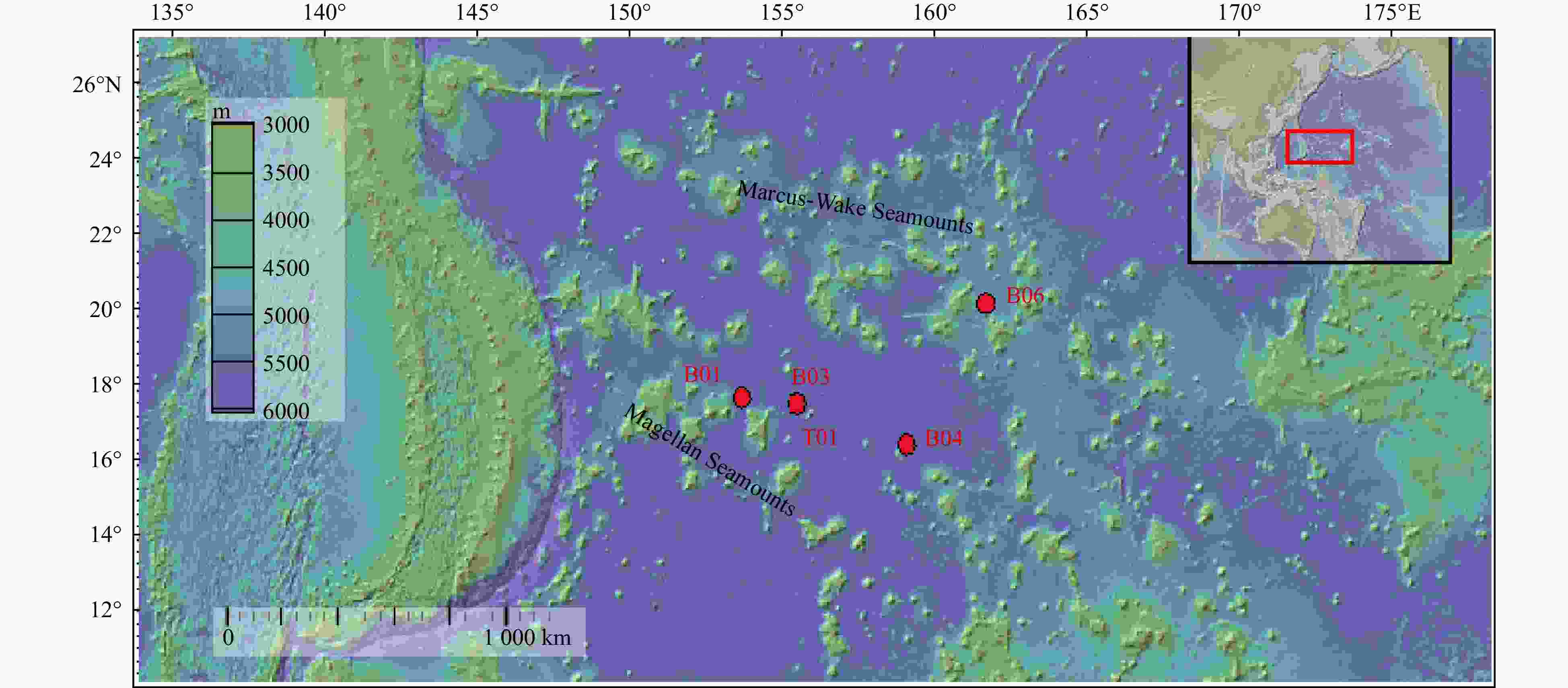
Station Longitude/°E Latitude/°N Number Type Diameter/cm Water depth/m Sampling B01 153.695282 17.807557 B01M Middle spherical nodules 3×3 5694 boxing B01S Small spherical nodules 2×2 5694 boxing B03 155.464373 17.640543 B03M Middle conjunctive nodules 4×3 5698 boxing B03S Small conjunctive nodules 3×2 5698 boxing B04 159.093026 16.549205 B04M Middle conjunctive nodules 4×3 5790 boxing B04S Small conjunctive nodules 3×2 5790 boxing B06 161.702904 20.310552 B06M Middle conjunctive nodules 4×3 5140 boxing B06S Small conjunctive nodules 3×2 5140 boxing T01 155.492477 17.656095 T01M Middle conjunctive nodules 4×3 5689 dredging T01S Small conjunctive nodules 3×2 5689 dredging Table 2. Major and trace element contents of ferromanganese nodules
Element Unit Spherical nodules Conjunctive nodules B01M B01S Average B06M B06S B03M B03S T01M T01S B04M B04S Average Mn % 16.55 17.36 16.96 20.99 20.44 21.26 23.22 21.99 23.19 18.79 24.94 21.85 Fe % 17.40 16.78 17.09 15.37 15.14 13.49 12.35 14.19 13.01 12.29 12.19 13.50 Al % 2.91 3.37 3.14 2.45 2.58 2.68 2.64 2.83 2.96 3.67 2.86 2.83 Ca % 1.58 1.60 1.59 1.74 1.79 1.68 1.56 1.70 1.67 2.07 1.62 1.73 K % 0.66 0.67 0.66 0.74 0.75 0.67 0.69 0.72 0.73 0.81 0.78 0.74 Mg % 1.24 1.41 1.32 1.55 1.45 1.62 1.81 1.74 1.91 1.48 1.89 1.68 Na % 1.50 1.55 1.53 1.70 1.73 1.69 1.69 1.81 1.84 2.12 1.83 1.80 P % 0.28 0.29 0.28 0.28 0.27 0.26 0.22 0.26 0.24 0.22 0.22 0.25 Ti % 1.38 1.33 1.35 1.05 1.08 0.87 0.73 0.87 0.75 0.71 0.64 0.84 Co % 0.37 0.35 0.36 0.42 0.41 0.32 0.28 0.33 0.29 0.24 0.26 0.32 Cu % 0.23 0.30 0.27 0.32 0.30 0.47 0.59 0.55 0.59 0.53 0.73 0.51 Ni % 0.33 0.38 0.36 0.62 0.55 0.68 0.84 0.71 0.83 0.58 0.86 0.71 Ba % 0.12 0.12 0.12 0.14 0.14 0.12 0.11 0.12 0.12 0.10 0.10 0.12 Sr % 0.09 0.09 0.09 0.10 0.10 0.08 0.07 0.09 0.08 0.08 0.07 0.08 Pb % 0.12 0.11 0.11 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.09 0.09 0.09 0.08 0.10 V µg/g 498 458 478 529 530 473 456 494 480 432 474 483 Zn µg/g 505 553 529 654 599 697 844 697 820 624 905 730 Zr µg/g 681 657 669 639 637 524 463 508 473 465 420 516 Mn/Fe - 0.95 1.03 0.99 1.37 1.35 1.58 1.88 1.55 1.78 1.53 2.05 1.63 Ca/P - 5.68 5.60 5.64 6.13 6.59 6.42 7.00 6.50 6.84 9.59 7.23 7.04 La µg/g 201 170 186 203 193 179 156 156 140 139 143 164 Ce µg/g 1216 1017 1117 1154 1150 877 713 779 648 656 597 822 Pr µg/g 44.0 40.6 42.3 48.8 48.5 42.5 36.2 39.9 36.8 32.9 34.2 40.0 Nd µg/g 182 160 171 191 188 165 143 161 144 130 137 158 Sm µg/g 39.5 34.3 36.9 41.8 40.0 35.7 31.9 34.6 31.3 29.8 31.7 34.6 Eu µg/g 9.44 8.22 8.83 9.62 9.35 8.78 7.85 8.28 7.42 7.29 7.62 8.28 Gd µg/g 44.1 38.8 41.4 43.1 42.4 40.2 35.3 37.3 33.2 33.1 34.8 37.4 Tb µg/g 6.82 5.95 6.38 6.65 6.46 6.22 5.57 5.84 5.33 5.24 5.55 5.86 Dy µg/g 42.7 36.7 40.0 39.0 38.1 38.4 33.9 34.9 31.6 32.3 34.0 35.3 Ho µg/g 8.26 7.27 7.77 7.40 7.25 7.37 6.43 6.74 6.22 6.30 6.67 6.80 Er µg/g 23.3 21.3 22.3 21.2 21.2 20.9 18.5 19.5 17.7 17.7 18.9 19.4 Tm µg/g 3.45 3.06 3.25 3.01 2.92 3.06 2.68 2.81 2.50 2.52 2.78 2.79 Yb µg/g 24.0 21.2 22.6 21.1 19.9 20.9 18.2 19.5 17.3 17.4 19.2 19.2 Lu µg/g 3.53 3.26 3.40 3.16 3.02 3.17 2.73 2.88 2.58 2.64 2.84 2.88 Y µg/g 141 147 144 142 137 126 109 135 122 105 116 124 REEs µg/g 1990 1716 1853 1935 1907 1575 1320 1444 1246 1218 1192 1480 LREE µg/g 1693 1431 1562 1648 1629 1308 1088 1179 1007 995 950 1226 HREE µg/g 297 285 291 287 278 266 232 265 239 223 241 254 LREE/HREE – 5.69 5.03 5.36 5.75 5.86 4.91 4.69 4.45 4.22 4.47 3.94 4.78 Y/Ho – 17.1 20.2 18.7 19.2 18.9 17.1 16.9 20.1 19.7 16.8 17.4 18.3 δCe – 2.81 2.67 2.74 2.53 2.59 2.19 2.06 2.15 1.97 2.11 1.86 2.18 δEu – 0.99 0.98 0.99 0.99 0.99 1.01 1.02 1.01 1.01 1.01 1.00 1.01 δY – 0.68 0.82 0.75 0.76 0.75 0.68 0.67 0.80 0.79 0.67 0.70 0.73 Note: LREEs=La+Ce+Pr+Nd+Sm+Eu, HREEs=Gd+Tb+Dy+Ho+Er+Tm+Yb+Lu+Y, δCe=2CeN/(LaN+PrN), δEu=2EuN/(SmN+GdN), δY=2YN/(DyN+HoN), and LaN, CeN, PrN, SmN, EuN, GdN, YN, DyN and HoN are normalized to North American shale (NASC). NASC data are from Wang et al. (1989). Table 3. Elemental correlation coefficient matrix of ferromanganese nodules
Element Mn Fe Ca P Al Na K Mg Ti Co Cu Ni Ba Sr Pb V Zn Zr REEs Mn 1 Fe –0.763* 1 Ca –0.186 –0.296 1 P –0.632* 0.930** –0.249 1 Al –0.448 –0.064 0.467 –0.200 1 Na 0.350 –0.755* 0.797** –0.708* 0.423 1 K 0.344 –0.567 0.734* –0.562 0.261 0.866** 1 Mg 0.947** –0.782** –0.202 –0.663* –0.236 0.390 0.276 1 Ti –0.813** 0.989** –0.286 0.904** –0.009 –0.767** –0.599 –0.827** 1 Co –0.393 0.789** –0.187 0.872** –0.539 –0.624 –0.357 –0.546 0.747* 1 Cu 0.826** –0.908** 0.025 –0.874** 0.082 0.611 0.453 0.891** –0.927** –0.827** 1 Ni 0.971** –0.867** –0.081 –0.745* –0.319 0.470 0.364 0.966** –0.903** –0.538 0.888** 1 Ba –0.235 0.670* –0.141 0.791** –0.585 –0.498 –0.247 –0.377 0.611 0.965** –0.709* –0.378 1 Sr –0.362 0.643* 0.127 0.770** –0.417 –0.332 –0.083 –0.516 0.600 0.936** –0.760* –0.484 0.950** 1 Pb –0.768** 0.791** –0.315 0.717* –0.081 –0.775** –0.778** –0.777** 0.848** 0.580 –0.838** –0.780** 0.396 0.395 1 V 0.021 0.484 –0.175 0.581 –0.745* –0.391 –0.082 –0.186 0.397 0.858** –0.484 –0.151 0.917** 0.827** 0.161 1 Zn 0.954** –0.820** –0.234 –0.756* –0.262 0.357 0.302 0.960** –0.845** –0.594 0.905** 0.964** –0.466 –0.599 –0.750* –0.228 1 Zr –0.757* 0.959** –0.163 0.927** –0.155 –0.700* –0.484 –0.828** 0.961** 0.878** –0.979** –0.857** 0.765** 0.779** 0.807** 0.563 –0.846** 1 REEs –0.622 0.886** –0.179 0.886** –0.382 –0.701* –0.459 –0.765** 0.876** 0.939** –0.939** –0.742* 0.833** 0.830** 0.768** 0.709* –0.759* 0.960** 1 Note: Elemental correlation coefficient is simple pearson (n=10). ** marked P=99%, * marked P=95%. Table 4. Principal component analysis of ferromanganese nodules
Element Main factor F1 F2 F3 Mn –0.995 0.0570 0.0170 Ni –0.984 –0.102 0.0800 Zn –0.967 –0.206 – 0.0530 Mg –0.958 –0.150 – 0.0200 Cu –0.850 –0.474 0.173 Ti 0.835 0.339 –0.398 Zr 0.790 0.541 –0.265 Fe 0.788 0.418 –0.381 Pb 0.762 0.138 –0.539 P 0.674 0.570 –0.338 V 0.0270 0.974 – 0.0750 Ba 0.287 0.935 –0.118 Sr 0.423 0.881 0.116 Co 0.444 0.867 –0.211 Al 0.424 –0.746 0.393 REEs 0.658 0.682 –0.270 Ca 0.192 – 0.0870 0.950 K –0.322 – 0.0290 0.895 Na –0.362 –0.323 0.865 Eigenvalue 8.86 5.71 3.57 Variance/% 46.6 30.1 18.8 Accumulative
variance/%46.6 76.7 95.5 Table 5. Results of elemental occurrence phases in ferromanganese nodules
Number Phase Mn
%Fe
%Al
%Ca
%K
%Mg
%Na
%P
%Ti
%Co
%Cu
µg/gNi
µg/gBa
µg/gSr
µg/gPb
µg/gV
µg/gZn
µg/gZr
µg/gREEs
µg/gB01M Carbonate phase 0.002 0.01 0.14 1.41 0.22 1.02 1.62 0.002 0.0002 0.0001 75.48 41.76 7.61 411 0.06 0.0001 32.68 0.16 12.77 Mn-Oxide phase 16.41 0.45 0.001 0.41 0.22 0.58 0.05 0.0001 0.001 0.29 255 2386 590 354 0.96 115 124 0.0001 290 Fe-Oxide phase 0.61 15.44 2.58 0.03 0.01 0.10 0.001 0.59 1.83 0.06 2089 1014 510 8.20 1155 358 335 657 1413 Residual phase 0.03 2.21 2.82 0.35 0.32 0.40 0.32 0.06 0.33 0.002 101 49.27 154 46.36 30.94 37.67 29.37 49.75 270 B01S Carbonate phase 0.01 0.01 0.24 1.45 0.23 1.13 1.65 0.002 0.0003 0.0001 141 86.15 8.19 463 0.03 0.14 51.64 0.11 15.36 Mn-Oxide phase 16.92 0.52 0.002 0.31 0.19 0.64 0.05 0.0001 0.001 0.28 532 2827 558 282 1.19 98.05 155 0.0001 236 Fe-Oxide phase 0.61 14.23 3.00 0.09 0.05 0.11 0.04 0.57 1.70 0.06 2224 814 443 30.48 855 311 305 533 1251 Residual phase 0.05 3.10 2.79 0.30 0.31 0.37 0.33 0.08 0.45 0.002 168 34.17 240 41.60 75.06 46.37 42.35 64.95 116 B06M Carbonate phase 0.002 0.004 0.09 1.40 0.23 1.16 1.65 0.001 0.0002 0.0001 106 75.91 9.50 465 0.02 0.08 51.37 0.0001 14.57 Mn-Oxide phase 18.64 0.62 0.0001 0.38 0.13 0.65 0.02 0.0001 0.0004 0.32 691 4480 828 292 1.71 122 223 0.0001 301 Fe-Oxide phase 0.61 12.51 1.60 0.01 0.02 0.06 0.01 0.54 1.32 0.04 2058 854 358 8.45 1105 323 283 503 1170 Residual phase 0.02 1.49 1.69 0.16 0.28 0.21 0.29 0.03 0.21 0.001 75.37 23.29 85.62 21.66 41.10 26.10 25.56 34.32 168 B06S Carbonate phase 0.002 0.01 0.10 1.46 0.22 1.16 1.65 0.001 0.0003 0.0001 117 93.89 8.52 481 0.02 0.0001 54.56 0.0001 15.42 Mn-Oxide phase 18.94 0.59 0.001 0.38 0.15 0.59 0.03 0.0001 0.0004 0.33 609 4071 821 318 4.52 119 198 0.0001 314 Fe-Oxide phase 0.66 13.23 1.60 0.02 0.02 0.05 0.01 0.55 1.46 0.05 2140 925 417 9.95 1142 356 289 547 1216 Residual phase 0.02 1.57 2.15 0.24 0.32 0.26 0.37 0.03 0.22 0.001 77.49 21.49 101 32.20 37.68 25.80 25.80 35.65 222 B03M Carbonate phase 0.003 0.01 0.12 1.41 0.17 1.12 1.65 0.002 0.0002 0.0001 139 79.6 4.97 399 0.06 0.0001 51.83 0.23 15.01 Mn-Oxide phase 20.52 0.52 0.0005 0.43 0.20 1.03 0.03 0.0002 0.001 0.25 1328 5221 745 296 1.36 127 243 0.0001 226 Fe-Oxide phase 0.72 13.14 2.21 0.01 0.0001 0.08 0.001 0.60 1.30 0.05 3471 1283 375 10.49 1187 339 374 522 1123 Residual phase 0.01 1.29 2.47 0.30 0.34 0.33 0.34 0.02 0.15 0.001 74.96 27.19 102 35.21 16.87 21.38 22.69 25.17 47.96 B03S Carbonate phase 0.004 0.005 0.13 1.30 0.14 1.15 1.77 0.002 0.0002 0.0001 132 78.79 3.24 357 0.06 0.0001 52.87 0.19 14.20 Mn-Oxide phase 22.25 0.46 0.0003 0.44 0.24 1.26 0.03 0.002 0.001 0.22 2069 6242 717 278 0.99 120 292 0.0001 172 Fe-Oxide phase 0.64 11.69 2.24 0.01 0.0001 0.09 0.002 0.50 1.03 0.05 3818 1636 323 8.58 1036 324 453 448 983 Residual phase 0.01 1.37 2.45 0.23 0.37 0.36 0.29 0.02 0.16 0.001 83.01 46.38 83.08 27.53 16.04 23.44 25.82 27.85 29.04 T01M Carbonate phase 0.004 0.01 0.15 1.43 0.22 1.22 1.83 0.002 0.0003 0.0001 226 97.90 7.43 446 0.02 0.0001 69.05 0.0001 16.67 Mn-Oxide phase 20.38 0.64 0.001 0.35 0.17 0.89 0.03 0.002 0.0004 0.26 1782 5316 655 252 1.25 118 247 0.0001 223 Fe-Oxide phase 0.59 12.21 2.14 0.02 0.02 0.07 0.01 0.53 1.17 0.03 3122 1004 418 10.03 895 316 308 427 1062 Residual phase 0.01 1.26 2.00 0.25 0.28 0.26 0.29 0.02 0.16 0.001 87.54 35.72 88.19 27.61 13.05 19.63 22.23 23.30 27.09 T01S Carbonate phase 0.004 0.004 0.13 1.25 0.18 1.19 1.80 0.002 0.0002 0.0001 155 80.28 4.91 375 0.01 0.0001 55.15 0.04 13.18 Mn-Oxide phase 20.71 0.61 0.0004 0.37 0.18 1.08 0.02 0.003 0.0004 0.22 2180 6139 702 239 1.49 124 303 0.0001 198 Fe-Oxide phase 0.55 10.55 2.13 0.02 0.01 0.07 0.01 0.48 0.94 0.03 2997 1054 315 8.15 807 281 345 383 871 Residual phase 0.01 1.27 2.26 0.25 0.32 0.31 0.30 0.02 0.16 0.001 96.06 57.14 69.34 28.25 12.31 20.66 24.72 24.48 25.06 B04M Carbonate phase 0.01 0.004 0.13 1.18 0.16 0.96 1.67 0.002 0.0002 0.0001 198 88.95 3.45 335 0.03 0.0001 61.14 0.17 14.87 Mn-Oxide phase 17.68 0.71 0.001 0.31 0.23 0.86 0.04 0.001 0.0005 0.20 1844 4634 434 221 1.72 130 253 0.04 231 Fe-Oxide phase 0.58 10.44 1.87 0.02 0.01 0.07 0.001 0.45 0.94 0.03 3151 818 408 10.27 884 270 256 421 829 Residual phase 0.02 1.96 3.58 1.16 0.49 0.41 0.96 0.04 0.21 0.002 178 63.38 184 127 24.64 30.16 32.76 45.93 26.61 B04S Carbonate phase 0.005 0.01 0.16 1.36 0.14 1.11 1.78 0.002 0.0002 0.0001 172 96.28 2.46 337 0.05 0.0001 63.00 0.18 16.32 Mn-Oxide phase 23.31 0.51 0.0002 0.41 0.31 1.31 0.04 0.003 0.001 0.20 2962 6258 479 261 0.90 124 317 0.0001 145 Fe-Oxide phase 0.58 10.96 2.36 0.02 0.01 0.09 0.001 0.48 0.85 0.05 4245 1609 489 9.19 929 320 454 396 853 Residual phase 0.01 1.51 2.54 0.20 0.38 0.38 0.28 0.02 0.18 0.002 127 105 119 27.17 18.70 25.82 30.45 32.46 26.31 -
Bai Zhimin, Wang Yingbin, Jiang Bo, et al. 2004. Occurrence modes of REE in the Pacific cobalt-rich crusts. Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese), 11(2): 387–392 Bau M, Koschinsky A. 2009. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts. Geochemical Journal, 43(1): 37–47, doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0005 Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. 2014. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium. Chemical Geology, 381: 1–9, doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.004 Bonatti E, Kraemer T, Rydell H S. 1972. Classification and genesis of submarine iron-manganese deposits. In: Horn D R, ed. Ferromanganese Deposits on the Ocean Floor. New York: Columbia University, 149–166 (查阅网上资料, 不确定文献类型及格式是否正确, 请确认) Byrne R H. 2002. Inorganic speciation of dissolved elements in seawater: the influence of pH on concentration ratios. Geochemical Transactions, 2002,3: 11–16 Cao Dekai, Ren Xiangwen, Shi Xuefa. 2017. Genesis and grade control factors of polymetallic nodules in the East Mariana Basin of Pacific. Journal of Marine Sciences (in Chinese), 35(4): 76–86 Chen J C, Owen R M. 1989. The hydrothermal component in ferromanganese nodules from the Southeast Pacific Ocean. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53(6): 1299–1305, doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90064-1 Cheng Yulong, Xu Yonghang, Li Dongyi, et al. 2023a. Enrichment mechanism of critical metals and records of paleoenvironment in a polymetallic nodule from the Somali Basin. Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese), 39(9): 2778–2794, doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.09.14 Cheng Yulong, Xu Yonghang, Yi Liang, et al. 2023b. Chronology and critical metals enrichment mechanism of ferromanganese nodules from the Parece Vela Basin, Philippine Sea. Chemical Geology, 630: 121494, doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2023.121494 Cui Yingchun, Shi Xuefa, Liu Jihua, et al. 2012. Records of past 70 Ma dust activities in ferromanganese crusts from Pacific Ocean. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition) (in Chinese), 42(2): 393–399 Deng Xianze, He Gaowen, Xu Yue, et al. 2022. Oxic bottom water dominates polymetallic nodule formation around the Caiwei Guyot, northwestern Pacific Ocean. Ore Geology Reviews, 143: 104776, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104776 Deng Yinan, Ren Jiangbo, Guo Qingjun, et al. 2019. Trace elements geochemistry characteristics of seawater and porewater in deep-water basin, western Pacific. Earth Science (in Chinese), 44(9): 3101–3114 Fu Yazhou, Wen Hanjie. 2020. Variabilities and enrichment mechanisms of the dispersed elements in marine Fe-Mn deposits from the Pacific Ocean. Ore Geology Reviews, 121: 103470, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103470 Gao Jingjing, Liu Jihua, Zhang Hui, et al. 2022. Geochemistry and sources of rare earth elements in cobalt-rich crusts from the Caiwei and Xufu seamounts, West Pacific Ocean. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 42(3): 87–99 Gao Jingjing, Liu Jihua, Zhang Hui, et al. 2023. Geochemistry and occurrence phase of the elements in cobalt-rich crusts from the Magellan Seamounts. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 54(2): 424–435 Guan Yao, Ren Yingzhi, Sun Xiaoming, et al. 2019. Fine scale study of major and trace elements in the Fe-Mn nodules from the South China Sea and their metallogenic constraints. Marine Geology, 416: 105978, doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.105978 Guan Yao, Sun Xiaoming, Ren Yingzhi, et al. 2017. Mineralogy, geochemistry and genesis of the polymetallic crusts and nodules from the South China Sea. Ore Geology Reviews, 89: 206–227, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.06.020 Halbach P, Scherhag C, Hebisch U, et al. 1981. Geochemical and mineralogical control of different genetic types of deep-sea nodules from the Pacific Ocean. Mineralium Deposita, 16(1): 59–84 He Gaowen, Sun Xiaoming, Yang Shengxiong, et al. 2011. A comparison of REE geochemistry between polymetallic nodules and cobaltrich crusts in the Pacific Ocean. Geology in China (in Chinese), 38(2): 462–472 Hein J R, Conrad T A, Frank M, et al. 2012. Copper-nickel-rich, amalgamated ferromanganese crust-nodule deposits from Shatsky Rise, NW Pacific. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 13(10): Q10022 Hein J R, Koschinsky A. 2014. Deep-ocean ferromanganese crusts and nodules. Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition), 13: 273–291 Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Kuhn T. 2020. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 1(3): 158–169 Hein J R, Kosschinsky A, Bau M, et al. 2000. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts in the Pacific. In: Cronan D S, ed. Handbook of Marine Mineral Deposits. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 239–280 Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, et al. 2013. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: Comparison with land-based resources. Ore Geology Reviews, 51: 1–14, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.12.001 Hein J R, Spinardi F, Okamoto N, et al. 2015. Critical metals in manganese nodules from the Cook Islands EEZ, abundances and distributions. Ore Geology Reviews, 68: 97–116, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.12.011 Heller C, Kuhn T, Versteegh G J M, et al. 2018. The geochemical behavior of metals during early diagenetic alteration of buried manganese nodules. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 142: 16–33., doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2018.09.008 Huang Wei, Hu Bangqi, Xu Lei, et al. 2021. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the ferromanganese nodules in the middle western margin of the Parece Vela Basin. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 41(1): 199–209 Jiang Xuejun, Lin Xuehui, Yao De, et al. 2011. Enrichment mechanisms of rare earth elements in marine hydrogenic ferromanganese crusts. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(2): 197–203, doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4070-4 Josso P, Pelleter E, Pourret O, et al. 2017. A new discrimination scheme for oceanic ferromanganese deposits using high field strength and rare earth elements. Ore Geology Reviews, 87: 3–15, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.003 Kawabe M, Fujio S, Yanagimoto D. 2003. Deep-water circulation at low latitudes in the western North Pacific. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 50(5): 631–656, doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(03)00040-2 Khanchuk A I, Mikhailik P E, Mikhailik E V, et al. 2015. Peculiarities of the distribution of rare-earth elements and yttrium in mineral phases of the ferromanganese crusts from the Detroit Guyot (Pacific Ocean). Doklady Earth Sciences, 465(2): 1243–1247, doi: 10.1134/S1028334X15120016 Knaack D R, Leybourne M L, Layton-Matthews D, et al. 2023. The role of depositional environment and chemical composition on the triple oxygen isotope ratios of ferromanganese precipitates and their endmember components. Chemical Geology, 642: 121785, doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2023.121785 Koppers A A P, Staudigel H, Pringle M S, et al. 2003. Short-lived and discontinuous intraplate volcanism in the South Pacific: Hot spots or extensional volcanism? Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 4(10): 1089 Koschinsky A, Halbach P. 1995. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: genetic implications. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(24): 5113–5132, doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00358-4 Koschinsky A, Hein J R. 2003. Uptake of elements from seawater by ferromanganese crusts: Solid-phase associations and seawater speciation. Marine Geology, 198(3–4): 331–351, doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00122-1 Koschinsky A, Hein J R, Kraemer D, et al. 2020. Platinum enrichment and phase associations in marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules based on a multi-method approach. Chemical Geology, 539: 119426, doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119426 Kuhn T, Wegorzewski A, Rühlemann C, et al. 2017. Composition, formation, and occurrence of polymetallic nodules. In: Sharma R, ed. Deep-Sea Mining: Resource Potential, Technical and Environmental Considerations. Cham: Springer, 23–63 Li Tong. 1976. Chemical element abundances in the Earth and it's major shells. Geochimica (in Chinese), 5(3): 167–174 Li Tong. 1984. Abundance of Chemical elements in oceanic and Continental crust. Geotectonica et Metallogenia (in Chinese), 8(1): 19–27 Li Dengfeng, Fu Yu, Sun Xiaoming, et al. 2020. Critical metal enrichment mechanism of deep-sea hydrogenetic nodules: Insights from mineralogy and element mobility. Ore Geology Reviews, 118: 103371, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103371 Li Kang, Zeng Zhigang, Yin Xuebo, et al. 2009. Mode of element occurrence in surface sediments from East Pacific Rise near 13°N and the equator. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 29(3): 53–60 Liang Yongjia, Sun Xiaoming, Li Dengfeng, et al. 2024. Effects of phosphate on REY adsorption by goethite: Insights into REY enrichment and release in marine iron oxyhydroxides during early diagenesis. Chemical Geology, 649: 121966, doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2024.121966 Luo Shuaijie, Ren Jiangbo, He Gaowen, et al. 2023. Geochemical characteristics of polymetallic nodules and adjacent sediments in the western Pacific Ocean: effects of sedimentary environments on nodules. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 43(3): 119–131 Machida S, Fujinaga K, Ishii T, et al. 2016. Geology and geochemistry of ferromanganese nodules in the Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone around Minamitorishima Island. Geochemical Journal, 50(6): 539–555, doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0419 Menendez A, James R H, Lichtschlag A, et al. 2019. Controls on the chemical composition of ferromanganese nodules in the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone, eastern equatorial Pacific. Marine Geology, 409: 1–14, doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.12.004 Mikhailik P E, Mikhailik E V, Zarubina N V, et al. 2017. Distribution of rare-earth elements and yttrium in hydrothermal sedimentary ferromanganese crusts of the sea of Japan (from phase analysis results). Russian Geology and Geophysics, 58(12): 1530–1542, doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2017.11.013 Mohwinkel D, Kleint C, Koschinsky A. 2014. Phase associations and potential selective extraction methods for selected high-tech metals from ferromanganese nodules and crusts with siderophores. Applied Geochemistry, 43: 13–21, doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.01.010 Müller R D, Sdrolias M, Gaina C, et al. 2008. Age, spreading rates, and spreading asymmetry of the world's ocean crust. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 9(4): Q04006 Nakamura K, Horinouchi K, Shimomura R, et al. 2024. Geochemical insights into secular changes in the depositional environment of ferromanganese nodules in the western north Pacific. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 203: 104227, doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2023.104227 Ren Jiangbo, Deng Yinan, Lai Peixin, et al. 2021. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the polymetallic nodules in the Pacific survey area. Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese), 28(2): 412–425 Ren Jiangbo, He Gaowen, Deng Xiguang, et al. 2022. Metallogenesis of Co-rich ferromanganese nodules in the northwestern Pacific: Selective enrichment of metallic elements from seawater. Ore Geology Reviews 143: 104778 Ren Jiangbo, He Gaowen, Yang Yong, et al. 2024. Ultraselective enrichment of trace elements in seawater by Co-rich ferromanganese nodules. Global and Planetary Change, 239: 104498, doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2024.104498 Ren Jiangbo, He Gaowen, Yao Huiqiang, et al. 2016. Geochemistry and significance of REE and PGE of the cobalt-rich crusts from west Pacific Ocean Seamounts. Earth Science (in Chinese), 41(10): 1745–1757 Ren Yingzhi, Sun Xiaoming, Guan Yao, et al. 2019. Distribution of rare earth elements plus yttrium among major mineral phases of marine Fe-Mn crusts from the South China Sea and Western Pacific Ocean: a comparative study. Minerals, 9(1): 8 Ren Jiangbo, Yao Huiqiang, Yang Yong, et al. 2023. Critical metal enrichment in atypical hydrogenetic ferromanganese nodules: a case study in the Central Basin Ridge of the West Philippine Basin. Chemical Geology, 615: 121224, doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2022.121224 Reykhard L Y, Shulga N A. 2019. Fe-Mn nodule morphotypes from the NE Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone, Pacific Ocean: comparison of mineralogy, geochemistry and genesis. Ore Geology Reviews, 110: 102933, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.102933 Sensarma S, Saha A, Hazra A. 2021. Implications of REE incorporation and host sediment influence on the origin and growth processes of ferromanganese nodules from Central Indian Ocean Basin. Geoscience Frontiers, 12(3): 101123, doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.11.017 Shen Fangyu, Shi Xuefa, Bi Dongjie, et al. 2024. Geochemical characteristics of a ferromanganese nodule with a tooth nucleus from the northwestern Pacific: Implications for element migration between Fe-Mn (oxyhydr)oxide and biogenic apatite. Ore Geology Reviews, 166: 105925, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2024.105925 Surya P L, Durbar R, Nagender N B, et al. 2020. Anomalous phase association of REE in ferromanganese crusts from Indian mid-oceanic ridges: evidence for large scale dispersion of hydrothermal iron. Chemical Geology, 549: 119679 (查阅网上资料, 作者信息不确定, 请确认) Wang Zhonggang, Yu Xueyuan, Zhao Zhenhua, et al. 1989. Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 1–535 (查阅网上资料, 未找到对应的英文翻译, 请确认) Wegorzewski A V, Kuhn T. 2014. The influence of suboxic diagenesis on the formation of manganese nodules in the Clarion Clipperton nodule belt of the Pacific Ocean. Marine Geology, 357: 123–138, doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.07.004 Wu Xiaoping, Zhao Guangtao, Xu Cuiling, et al. 2023. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics and genesis of subsurface buried manganese nudule from discol experiment area of Peru Basin in Southeastern Pacific. Periodical of Ocean University of China (in Chinese), 53(2): 94–106 Xu Zhaokai, Li Anchun, Yu Xinke, et al. 2008. Elemental occurrence Phases of the new-type ferromanganese crusts from the East Philippine Sea. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences (in Chinese), 33(3): 329–336, doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2008.043 Yang Kehong, Dong Yanhui, Li Zhenggang, et al. 2024. Geochemistry of buried polymetallic nodules from the eastern Pacific Ocean: Implication for the depth-controlled alteration process. Marine Geology, 467: 107190, doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2023.107190 Yin Zhengxin, Wang Haifeng, Han Jinsheng, et al. 2019. Comparison between the marginal-sea polymetallic nodules in South China Sea and ocean polymetallic nodules. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition) (in Chinese), 49(1): 261–277 Zhang Huan, Zhou Junming, Yuan Peng, et al. 2023. Highly positive Ce anomalies of hydrogenetic ferromanganese micronodules from abyssal basins in the NW and NE Pacific: implications for REY migration and enrichment in deep-sea sediments. Ore Geology Reviews, 154: 105324, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105324 Zhong Yi, Chen Zhong, González F J, et al. 2017a. Composition and genesis of ferromanganese deposits from the northern South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 138: 110–128, doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.02.015 Zhong Yi, Chen Zhong, González F J, et al. 2021. Insights into the origin of ferromanganese-rich deposits associated with South China Sea contourite depositional systems. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 133: 105257, doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105257 Zhong Yi, Chen Zhong, Mo Aibin, et al. 2017b. Genetic types and elemental occurrence phases of ferromanganese nodules in the northern South China Sea. Journal of Tropical Oceanography (in Chinese), 36(2): 48–59 Zhou Jiao, Cai Pengjie, Yang Chupeng, et al. 2022. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of ferromanganese nodules and crusts from the Central Rift Seamounts Group of the West Philippine Sea. Ore Geology Reviews, 145: 104923, doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104923 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 23
- HTML全文浏览量: 8
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: