Effects of rising temperature on growth and energy budget of juvenile Eogammarus possjeticus (Amphipoda: Anisogammaridae)
-
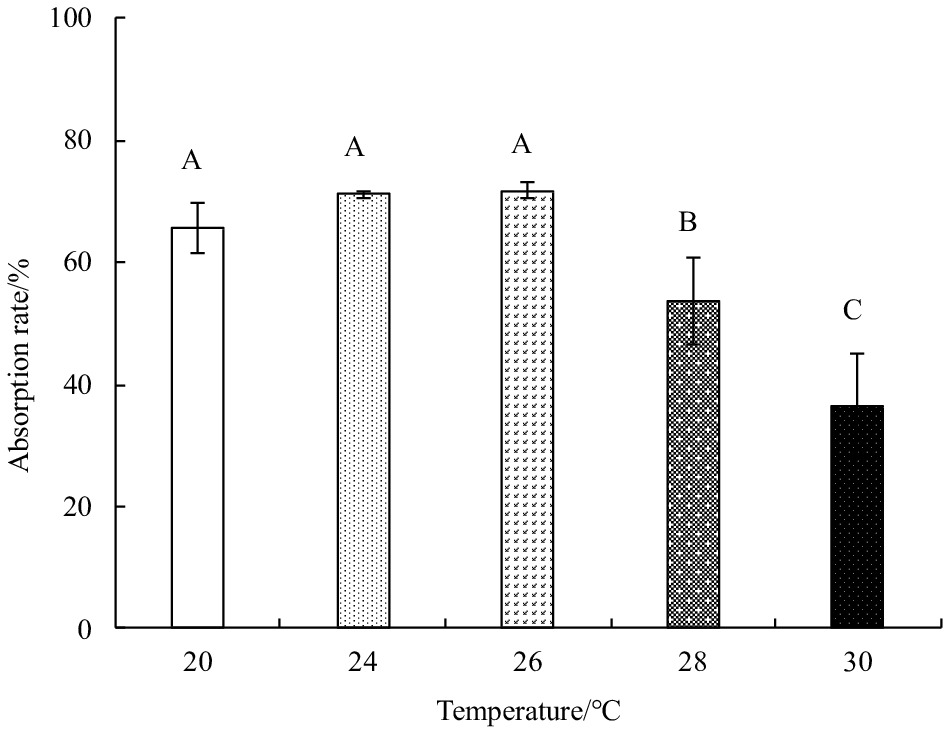
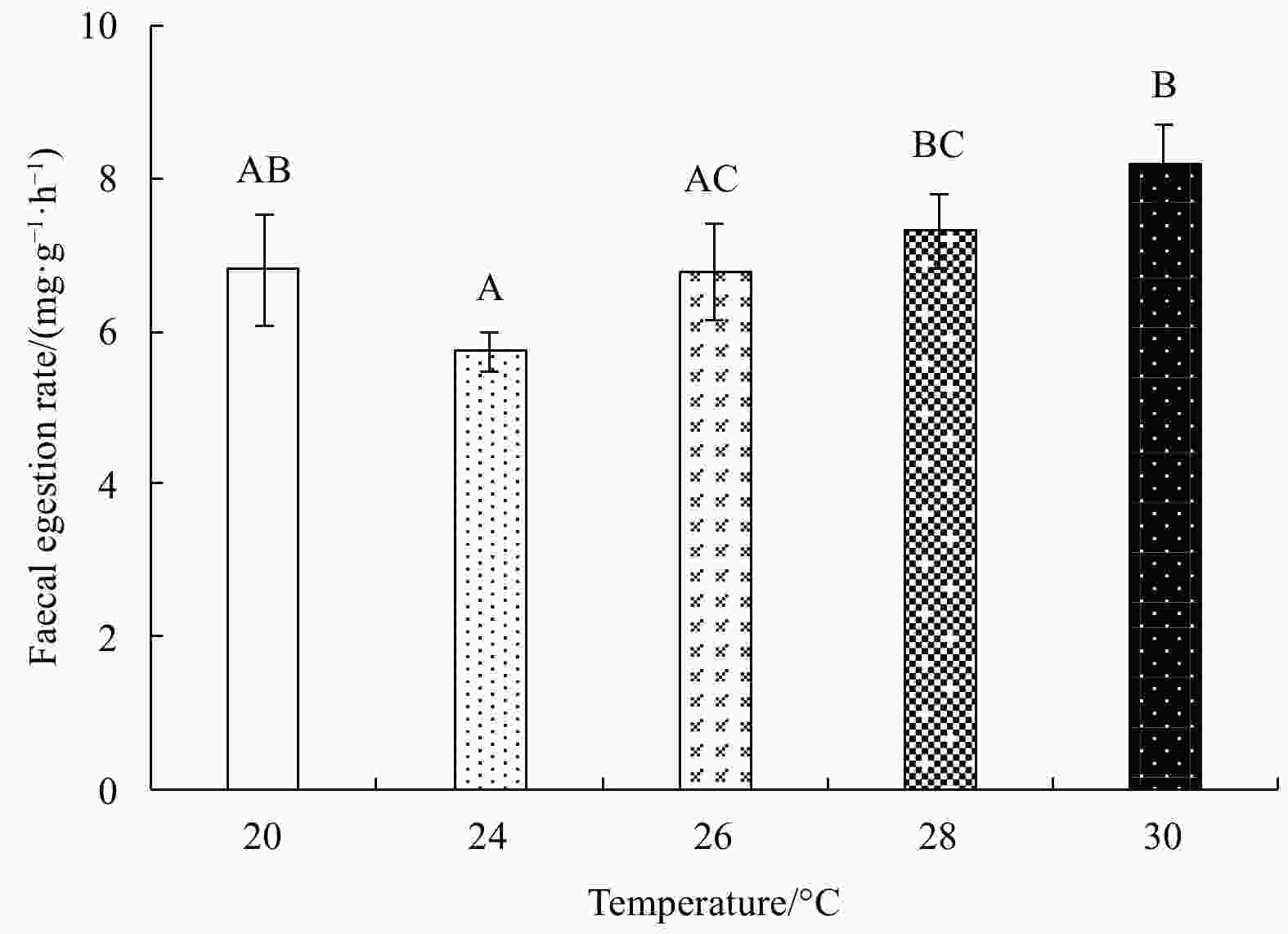
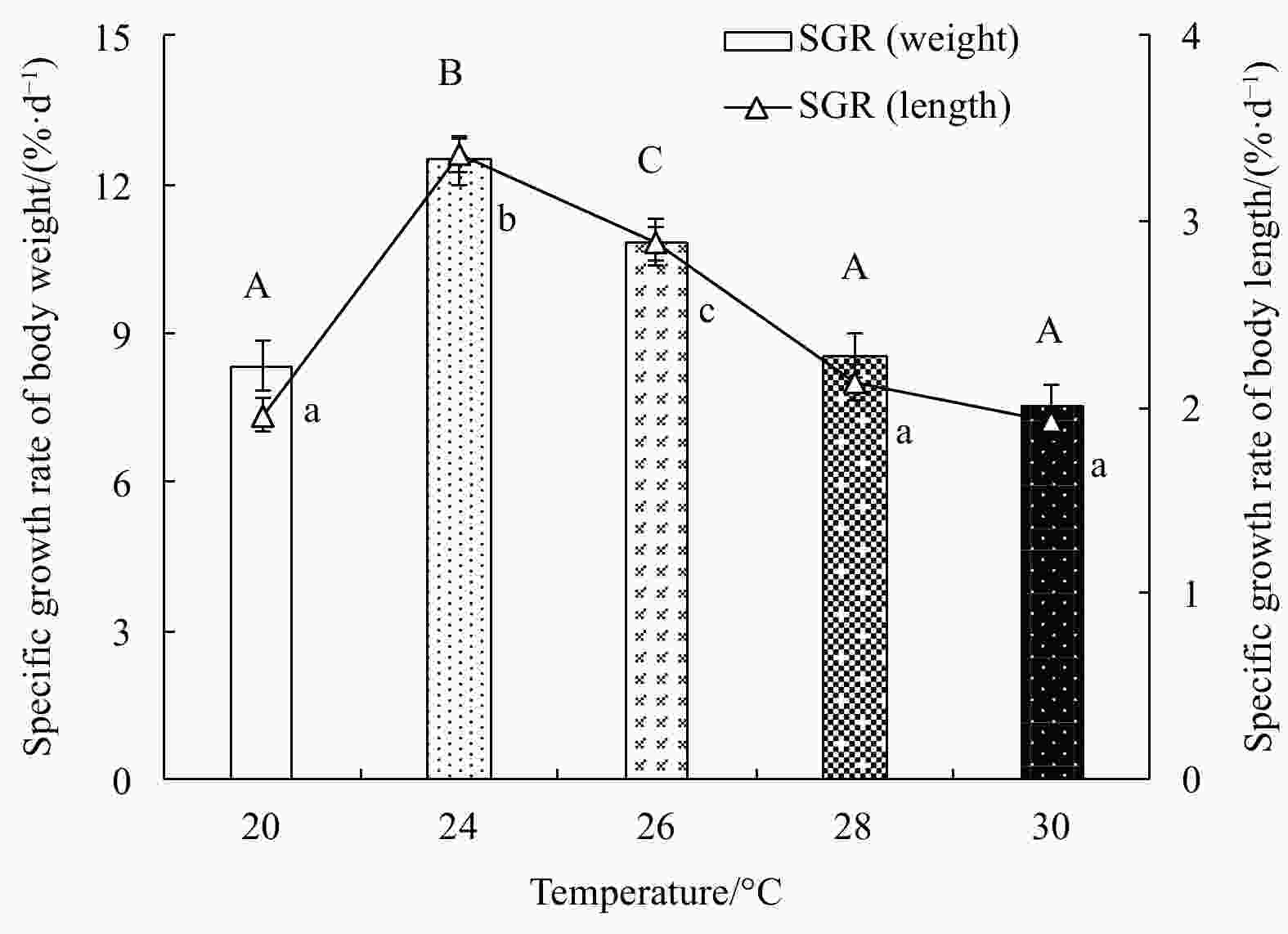
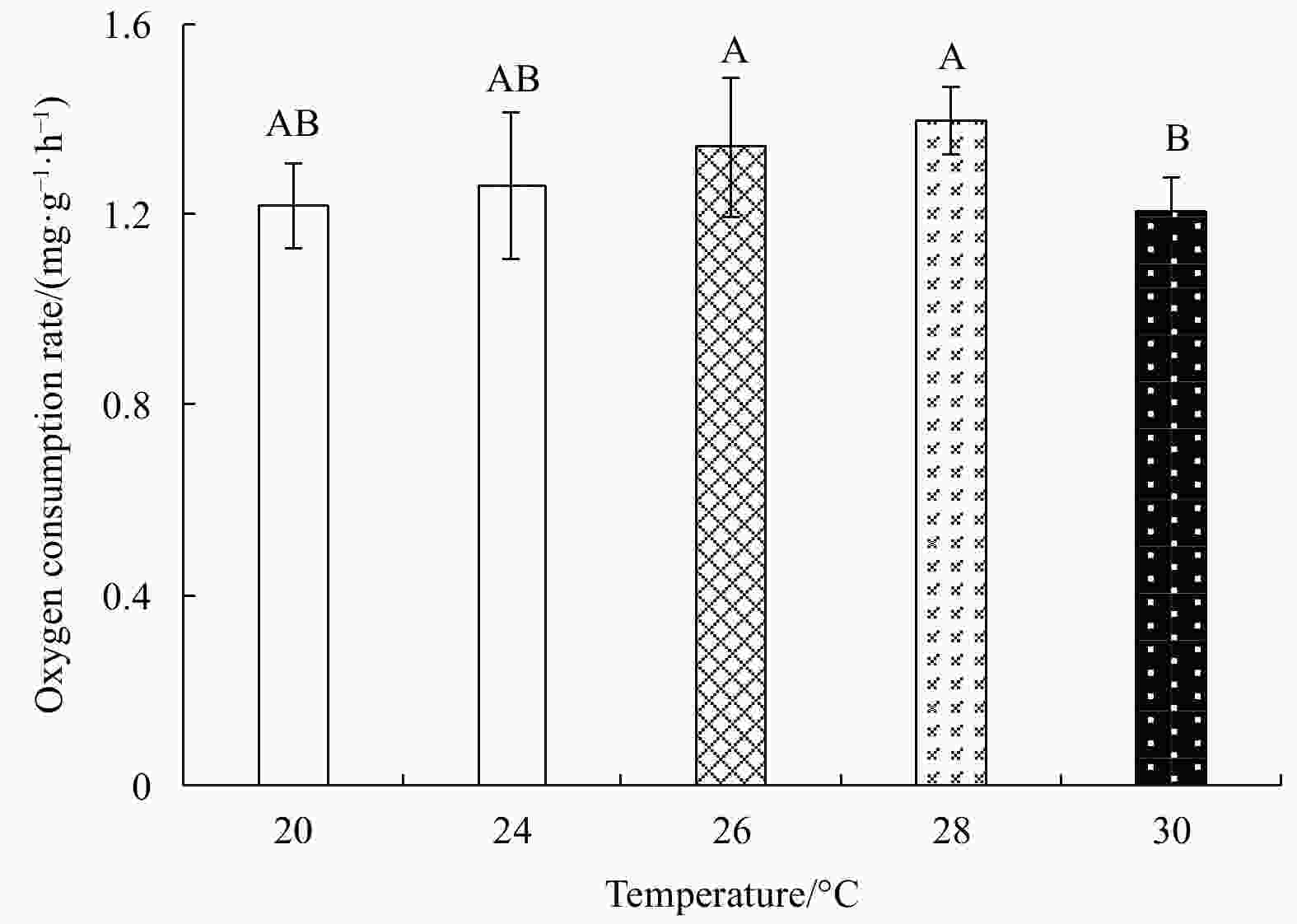
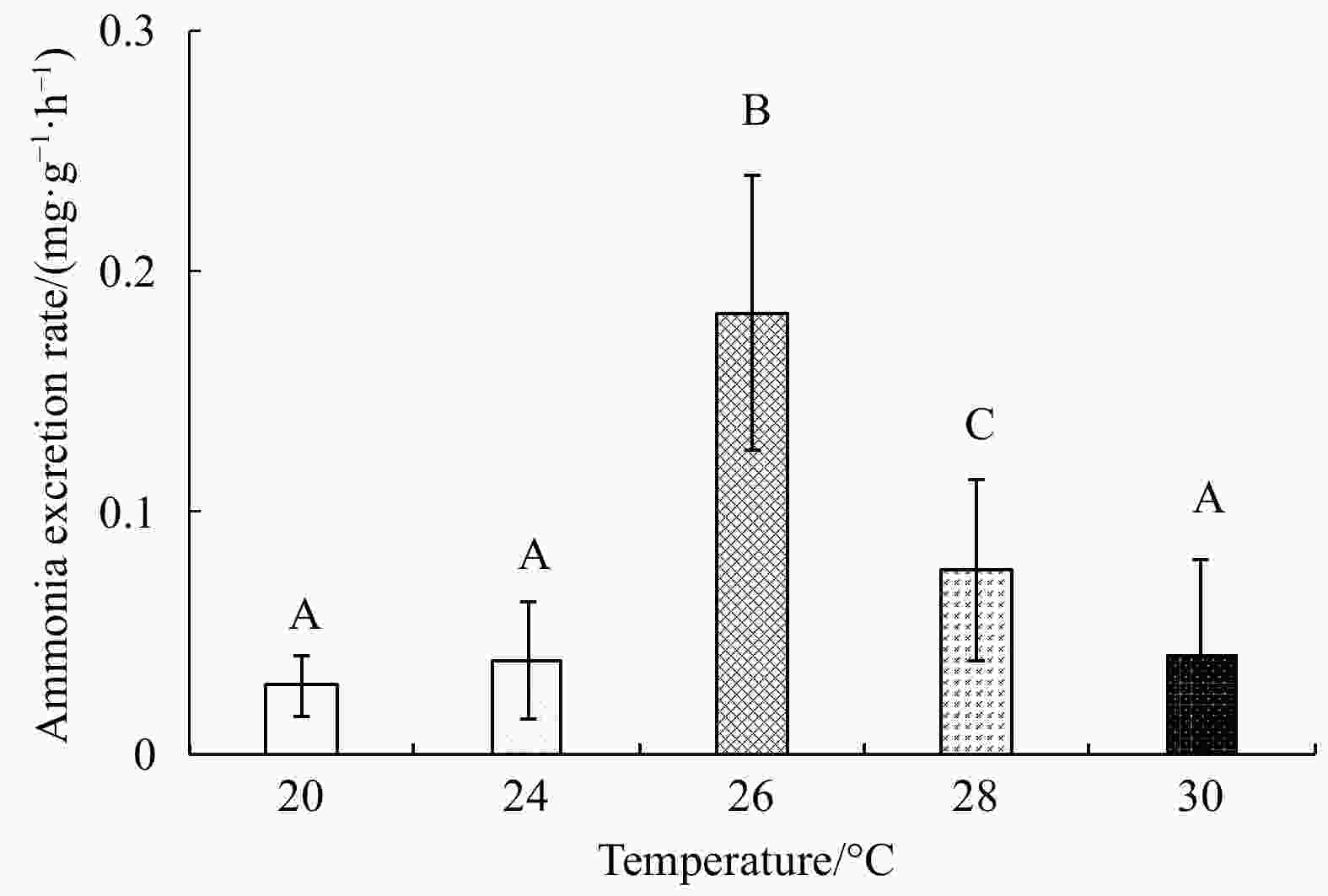
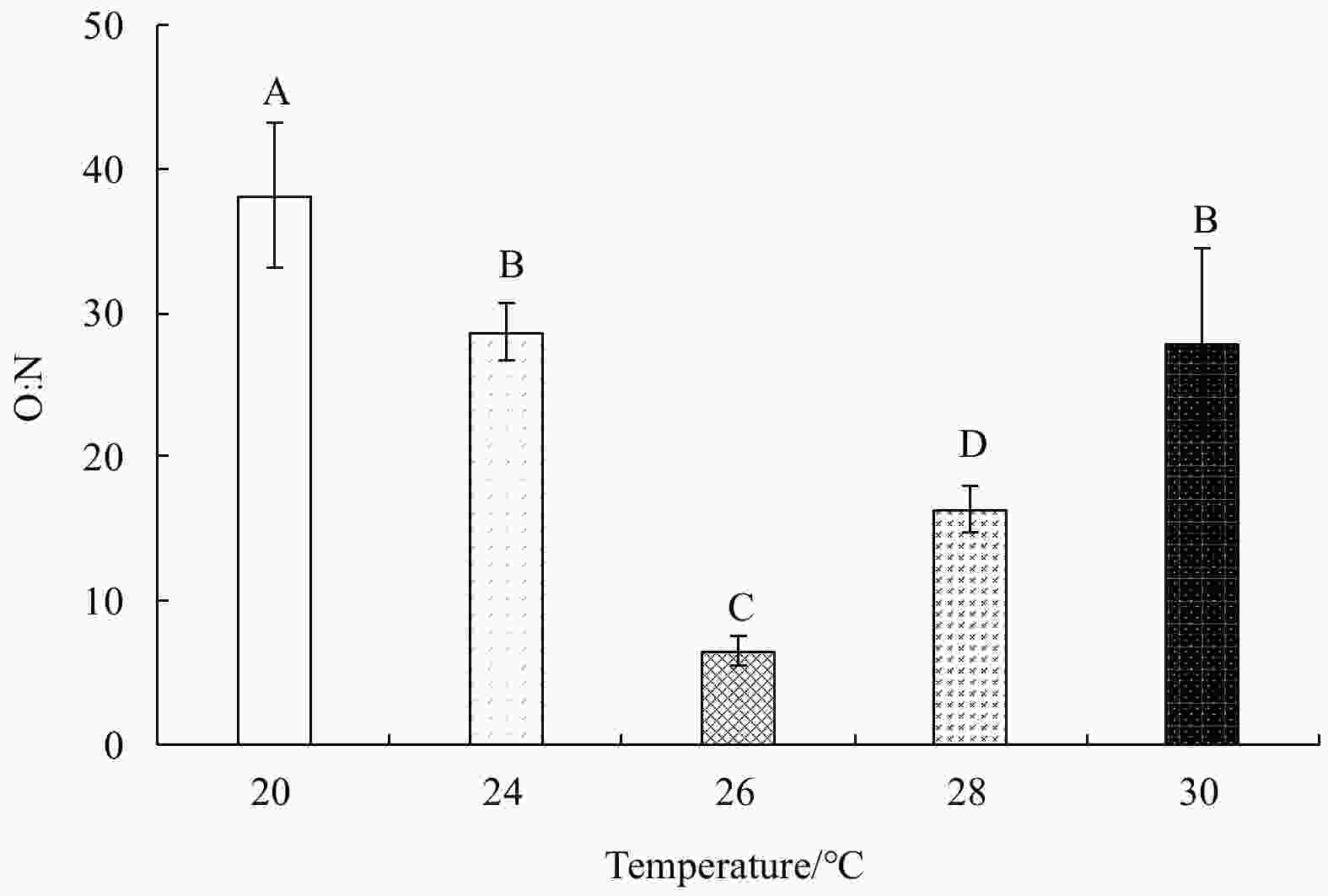
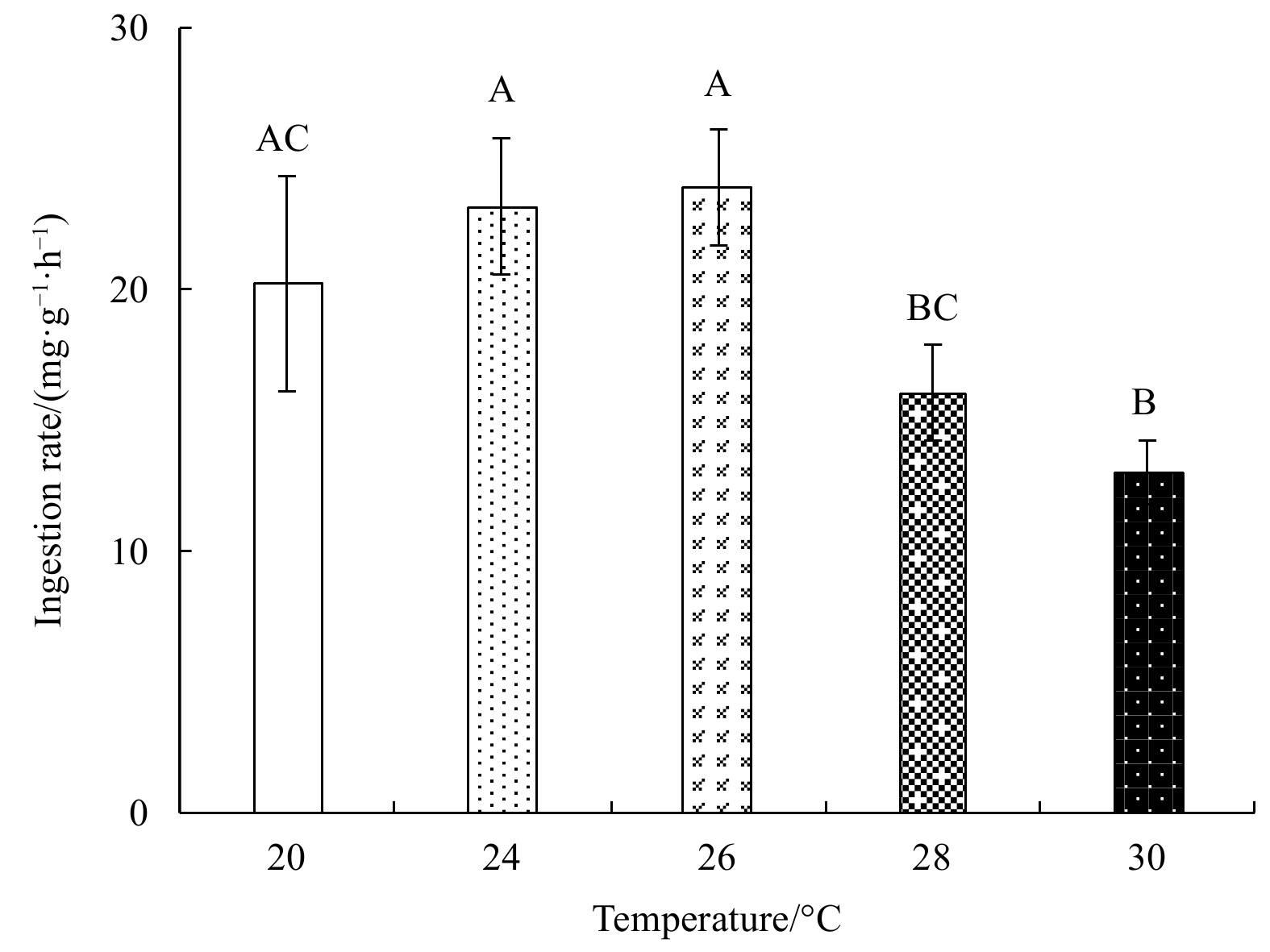
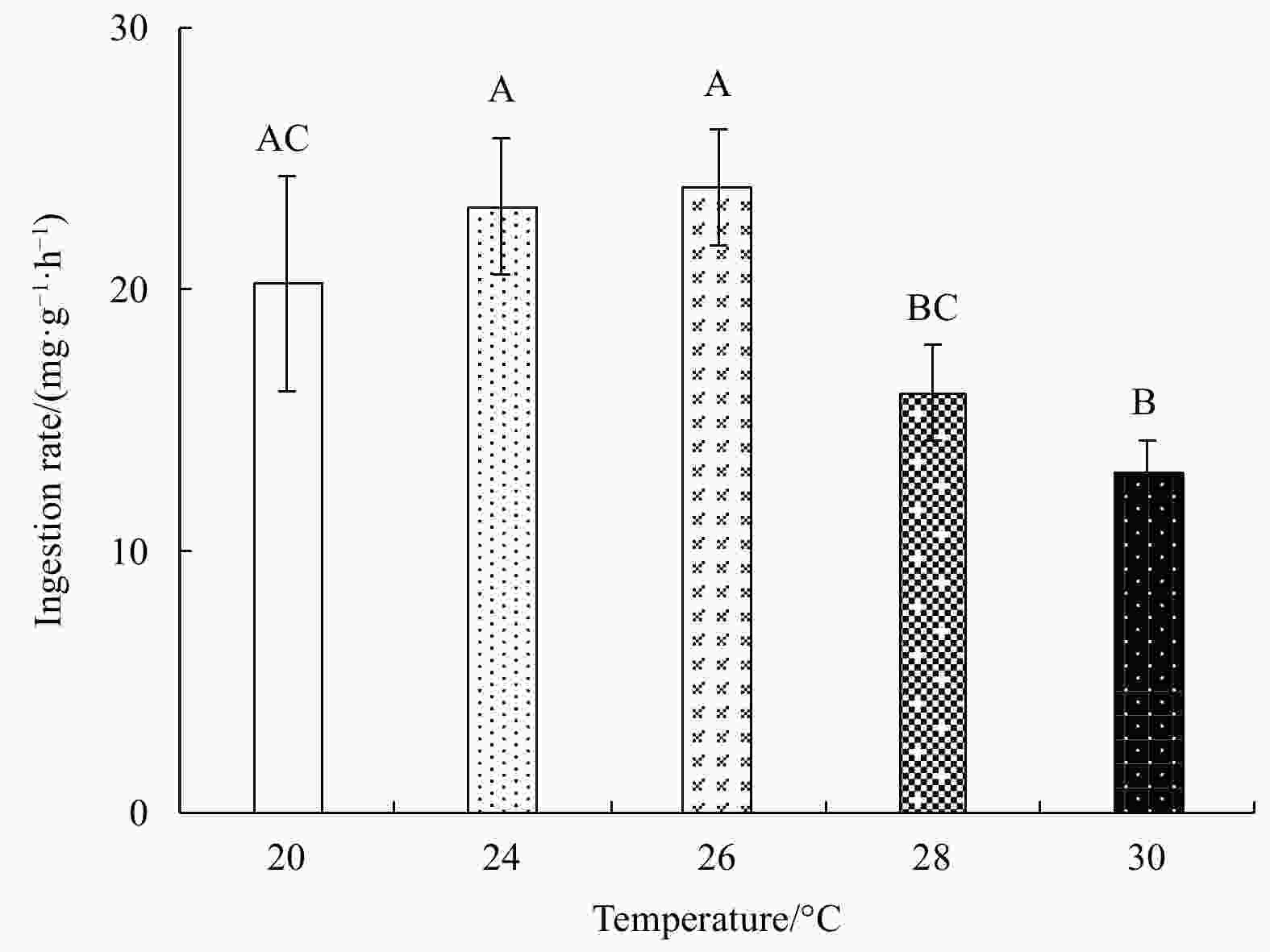
Abstract: Growth and energy budget of marine amphipod juvenile Eogammarus possjeticus at different temperatures (20°C, 24°C, 26°C, 28°C, 30°C, 32°C and 34°C) were investigated in this study. The results showed that the cumulative mortality rate increased significantly with rising temperature (p<0.01), and exceeded 50% after 24 h when temperature was above 30°C. With the temperature increasing from 20°C to 26°C, the ingestion rate and absorption rate increased, but decreased significantly above 28°C (p<0.01), indicating a decline in feeding ability at high temperatures. The specific growth rate increased with rising temperature, but decreased significantly (p<0.01) after reaching the maximum value at 24°C. Similarly, the oxygen consumption and ammonia emission rates also showed a trend of first increase and then decrease. However, the O:N ratio decreased first and then increased with rising temperature, indicating that the energy demand of E. possjeticus juvenile transferred from metabolism of carbohydrate and lipid to protein. In the energy distribution of amphipods, the proportion of each energy is different. With rising temperature, the ratio of the energy deposited for growth accounted for ingested gross energy showing a trend of decrease, while the energy lost to respiration, ammonia excretion, and feces accounted for ingested gross energy being showed a trend of increase. It seemed that rising temperature increased the metabolism and energy consumption of the amphipods and, meanwhile, decreased the energy used for growth, which may be an important reason for the slow growth and small body size of the amphipods during the summer high-temperature period.
-
Key words:
- Eogammarus possjeticus /
- rising temperature /
- growth /
- respiratory metabolism /
- energy budget
-
Table 1. The cumulative mortality rates of E. possjeticus juvenile under different temperatures
Temperature/°C Number/ind. Cumulative mortality rate/% 12 h 24 h 48 h 72 h 96 h 7 d 20 40 0.00 1.25 1.25 6.25 6.88 11.25 24 40 0.00 0.63 0.63 1.88 3.13 8.75 26 40 0.00 0.00 0.00 12.50 12.50 17.50 28 40 0.00 0.63 1.25 10.63 11.25 16.25 30 40 1.88 1.88 2.50 11.25 13.13 18.13 32 40 39.38 50.00 57.50 59.38 62.50 72.50 34 40 54.38 65.63 69.38 70.00 70.63 73.13 Table 2. The median lethal temperature (LT50) and 95% confidence interval of E. possjeticus juvenile
Time LT50/°C 95% confidence interval 12 h 32.66 32.03–33.30 24 h 31.96 31.33–32.60 48 h 31.61 31.00–32.23 72 h 30.53 29.78–31.30 96 h 30.31 29.55–31.09 7 d 29.32 28.52–30.14 Table 3. The Q10 coefficients under different temperature intervals for E. possjeticus juvenile
Temperature interval/°C Q10 coefficient 20–24 1.03 24–26 1.21 26–28 1.24 28–30 0.34 Table 4. Short-term energy budget of E. possjeticus juvenile at different temperatures
Temperature
/°CConsumption energy
/(J·g–1·h–1)Respiration energy
/(J·g–1·h–1)Excretion energy
/(J·g–1·h–1)Fecal energy
/(J·g–1·h–1)Growth energy
/(J·g–1·h–1)20 605.47±122.21a 62.68±4.69ab 2.55±0.31a 78.50±8.50ab 461.74±116.94a 24 679.49±76.76a 63.46±7.83ab 3.42±0.60a 65.05±2.87a 547.57±67.77a 26 690.93±64.46a 65.95±6.78ab 15.66±1.41b 75.36±7.03ab 533.95±53.82a 28 415.13±56.98b 68.84±3.55a 6.52±0.93c 72.76±6.21ab 267.01±53.01b 30 348.54±32.51b 55.35±3.35b 3.28±0.98a 84.44±5.30b 205.47±30.57b Note: Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences among treatments (p<0.05). Table 5. Energy budget equation of E. possjeticus juvenile at different temperatures
Temperature/°C Energy budget equation 20 100C=10.35R+0.42U+12.97F+76.26G 24 100C=9.34R+0.50U+9.57F+80.59G 26 100C=9.55R+2.27U+10.91F+77.28G 28 100C=16.58R+1.57U+17.53F+64.32G 30 100C=15.88R+0.94U+24.23F+58.95G Note: C, consumption energy; R, respiration energy; U, excretion energy; F, fecal energy; and G, growth energy. -
[1] Arfianti T, Wilson S, Costello M J. 2018. Progress in the discovery of amphipod crustaceans. PeerJ, 6: e5187. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5187 [2] Atkinson D. 1994. Temperature and organism size: A biological law for ectotherms?. Advances in Ecological Research, 25: 1–58. doi: 10.1016/s0065–2504(08)60212–3 [3] Atkinson D, Sibly R M. 1997. Why are organisms usually bigger in colder environments? Making sense of a life history puzzle. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 12(1): 235–239. doi: 10.1016/s0169–5347(97)01058–6 [4] Balloo N, Appadoo C. 2017. Effect of acidified seawater and high temperature on the survival and behaviour of supralittoral and sublittoral amphipods (Crustacea). Western Indian Ocean Journal of Marine Science, 16(2): 1–11 [5] Baudron A R, Needle C L, Rijnsdorp A D, et al. 2014. Warming temperatures and smaller body sizes: synchronous changes in growth of North Sea fishes. Global Change Biology, 2(4): 1023–1031. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12514 [6] Bayne B L. 1976. Aspects of reproduction in bivalve molluscs. In: Estuarine Processes. New York: Academic Press, 432–448, doi: 10.1016/b978–0-12–751801-5.50043–5 [7] Bedulina D S, Zimmer M, Timofeyev M A. 2010. Sub-littoral and supra-littoral amphipods respond differently to acute thermal stress. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 155(4): 413–418. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2010.01.004 [8] Bermudes M, Glencross B, Austen K, et al. 2010. The effects of temperature and size on the growth, energy budget and waste outputs of barramundi (Lates calcarifer). Aquaculture, 306(1–4): 160–166. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.05.031 [9] Brown J H, Gillooly J F, Allen A P, et al. 2004. Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology, 85(7): 1771–1789. doi: 10.1890/03–9000 [10] Cheung W W L, Sarmiento J L, Dunne J, et al. 2013. Shrinking of fishes exacerbates impacts of global ocean changes on marine ecosystems. Nature Climate Change, 3(3): 254–258. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1691 [11] Clarke A, Johnston N M. 1999. Scaling of metabolic rate with body mass and temperature in teleost fish. Journal of Animal Ecology, 68(5): 893–905. doi: 10.1046/j.1365–2656.1999.00337.x [12] Cottin D, Roussel D, Foucreau N, et al. 2012. Disentangling the effects of local and regional factors on the thermal tolerance of freshwater crustaceans. Naturwissenschaften, 99(4): 259–264. doi: 10.1007/s00114–012-0894–4 [13] Cui Yibo, Chen Shaolian, Wang Shaomei. 1995. Effect of temperature on the energy budget of the grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idellus Val. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 26(2): 169–174 [14] Cumillaf J P, Blanc J, Paschke K, et al. 2016. Thermal biology of the sub-polar–temperate estuarine crab Hemigrapsus crenulatus (Crustacea: Decapoda: Varunidae). Biology Open, 5(3): 220–228. doi: 10.1242/bio.013516 [15] Daufresne M, Lengfellner K, Sommer U. 2009. Global warming benefits the small in aquatic ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(31): 12788–12793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902080106 [16] Díaz Villanueva V, Albariño R, Canhoto C. 2011. Detritivores feeding on poor quality food are more sensitive to increased temperatures. Hydrobiologia, 678(1): 155–165. doi: 10.1007/s10750–011-0837–7 [17] Durant J M, Hjermann D Ø, Ottersen G, et al. 2007. Climate and the match or mismatch between predator requirements and resource availability. Climate Research, 33: 271–283. doi: 10.3354/cr033271 [18] Fang Jinghui, Tian Xiangli, Dong Shuanglin. 2010. The influence of water temperature and ration on the growth, body composition and energy budget of tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Aquaculture, 299(1–4): 106–114. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.11.026 [19] Fišer C, Robinson C T, Malard F. 2018. Cryptic species as a window into the paradigm shift of the species concept. Molecular Ecology, 27(3): 613–635. doi: 10.1111/mec.14486 [20] Foucreau N, Cottin D, Piscart C, et al. 2014. Physiological and metabolic responses to rising temperature in Gammarus pulex (Crustacea) populations living under continental or Mediterranean climates. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 168: 69–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.11.006 [21] Foucreau N, Piscart C, Puijalon S, et al. 2016. Effects of rising temperature on a functional process: consumption and digestion of leaf litter by a freshwater shredder. Fundamental and Applied Limnology, 187(4): 295–306. doi: 10.1127/fal/2016/0841 [22] Galic N, Forbes V E. 2017. Effects of temperature on the performance of a freshwater amphipod. Hydrobiologia, 785(1): 35–46. doi: 10.1007/s10750–016-2901–9 [23] Gardner J L, Peters A, Kearney M R, et al. 2011. Declining body size: a third universal response to warming?. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 26(6): 285–291. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2011.03.005 [24] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. 2008. GB 17378.4-2007 The specification for marine monitoring—Part 4: Seawater analysis (in Chinese). Beijing: Standards Press of China, 111–113 [25] Genner M J, Sims D W, Southward A J, et al. 2010. Body size-dependent responses of a marine fish assemblage to climate change and fishing over a century-long scale. Global Change Biology, 16(2): 517–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1365–2486.2009.02027.x [26] Gomes V, de Arruda Campos Rocha Passos M J, da Silva Rocha A J, et al. 2013. Metabolic rates of the antarctic amphipod Gondogeneia antarctica at different temperatures and salinities. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 61(4): 243–249. doi: 10.1590/S1679–87592013000400005 [27] Hochachka P W, Somero G N. 1984. Biochemical Adaptation. Princeton: Princeton University Press [28] Horton T, Lowry J, De Broyer C, et al. 2021. World Amphipoda Database. http://www.marinespecies.org/amphipoda [2021-06-23] [29] Huang Rui, Xu Fengkai. 2017. Study on the acute toxicity of rotenone to Lateolabrax japonicas and Chaeturichthys stigmatias Richardson. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology (in Chinese), (1): 96–101. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37–1141.2017.01.013 [30] Huang Jinfeng, Xu Qiyou, Chang Yumei. 2016. Effects of temperature and dietary protein on the growth performance and IGF-I mRNA expression of juvenile mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture Nutrition, 22(2): 283–292. doi: 10.1111/anu.12254 [31] IPCC. 2007. Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Contribution of working groups I, II and III to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Geneva, Switzerland: IPCC [32] Jadhav M, Bawane V, Gulave A. 2012. Size dependent variation in the rate of oxygen consumption, ammonia and O:N ratio of freshwater bivalve, Lamellidens marginalis from Godavari river during monsoon (M. S) India. Trends in Fisheries Research, 1(2): 22–26 [33] Jia Haibo, Sun Yao, Tang Qisheng. 2008. Effects of temperature on energy budget and ecological conversion efficiency of tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes. Marine Fisheries Research (in Chinese), 29(5): 39–46 [34] Kooijman S. 2010. Dynamic Energy Budget Theory for Metabolic Organisation. 3rd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press [35] Kozłowski J, Czarnołęski M, Dańko M. 2004. Can optimal resource allocation models explain why ectotherms grow larger in cold?. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 44(6): 480–493. doi: 10.1093/icb/44.6.480 [36] Machado G B O, Ferreira A P, Bueno M, et al. 2019. Effects of macroalgal host identity and predation on an amphipod assemblage from a subtropical rocky shore. Hydrobiologia, 836: 65–81. doi: 10.1007/s10750–019-3941–8 [37] Mas-Martí E, Muñoz I, Oliva F, et al. 2015. Effects of increased water temperature on leaf litter quality and detritivore performance: a whole-reach manipulative experiment. Freshwater Biology, 60(1): 184–197. doi: 10.1111/fwb.12485 [38] Millien V, Lyons S K, Olson L, et al. 2006. Ecotypic variation in the context of global climate change: revisiting the rules. Ecology Letters, 9(7): 853–869. doi: 10.1111/j.1461–0248.2006.00928.x [39] Moore M, Folt C. 1993. Zooplankton body size and community structure: effects of thermal and toxicant stress. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 8(5): 178–183. doi: 10.1016/0169–5347(93)90144-e [40] Naumenko S A, Logacheva M D, Popova N V, et al. 2017. Transcriptome-based phylogeny of endemic Lake Baikal amphipod species flock: fast speciation accompanied by frequent episodes of positive selection. Molecular Ecology, 26(2): 536–553. doi: 10.1111/mec.13927 [41] O’Connor M I, Gilbert B, Brown C J. 2011. Theoretical predictions for how temperature affects the dynamics of interacting herbivores and plants. The American Naturalist, 178(5): 626–638. doi: 10.1086/662171 [42] Ohlberger J. 2013. Climate warming and ectotherm body size—from individual physiology to community ecology. Functional Ecology, 27(4): 991–1001. doi: 10.1111/1365–2435.12098 [43] Pang Xu, Yuan Xingzhong, Cao Zhendong, et al. 2015. The effect of temperature on repeat swimming performance in juvenile qingbo (Spinibarbus sinensis). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 41: 19–29. doi: 10.1007/s10695–014-0002–0 [44] Parmesan C. 2006. Ecological and evolutionary responses to recent climate change. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 37(1): 637–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.37.091305.1101 [45] Parmesan C, Yohe G. 2003. A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature, 421(6918): 37–42. doi: 10.1038/nature01286 [46] Pauly D. 2010. Gasping Fish and Panting Squids: Oxygen, Temperature and the Growth of Water-Breathing Animals. Oldendorf/Luhe, Germany: International Ecology Institute [47] Pawar S, Dell A I, Savage V M, et al. 2016. Real versus artificial variation in the thermal sensitivity of biological traits. The American Naturalist, 187(2): E41–E52. doi: 10.1086/684590 [48] Peres H, Oliva-Teles A. 1999. Influence of temperature on protein utilization in juvenile European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture, 170(3–4): 337–348. doi: 10.1016/s0044–8486(98)00422–0 [49] Piscart C, Navel S, Maazouzi C, et al. 2011. Leaf litter recycling in benthic and hyporheic layers in agricultural streams with different types of land use. Science of the Total Environment, 409(20): 4373–4380. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.060 [50] Reading C J. 2007. Linking global warming to amphibian declines through its effects on female body condition and survivorship. Oecologia, 151(1): 125–131. doi: 10.1007/s00442–006-0558–1 [51] Ren Xianqiu. 2006. Fauna Sinica Invertebrate vol. 41 Crustacea Amphipoda Gammaridea (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 250–252 [52] Root T L, Price J T, Hall K R, et al. 2003. Fingerprints of global warming on wild animals and plants. Nature, 421(6918): 57–60. doi: 10.1038/nature01333 [53] Sandersfeld T, Davison W, Lamare M D, et al. 2015. Elevated temperature causes metabolic trade-offs at the whole-organism level in the Antarctic fish Trematomus bernacchii. Journal of Experimental Biology, 218: 2373–2381. doi: 10.1242/jeb.122804 [54] Saucedo P E, Ocampo L, Monteforte M, et al. 2004. Effect of temperature on oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion in the Calafia mother-of-pearl oyster, Pinctada mazatlanica (Hanley, 1856). Aquaculture, 229(1–4): 377–387. doi: 10.1016/s0044–8486(03)00327–2 [55] Sheridan J A, Bickford D. 2011. Shrinking body size as an ecological response to climate change. Nature Climate Change, 1: 401–406. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1259 [56] Shi Yonghai, Zhang Genyu, Liu Jianzhong, et al. 2011. Effects of temperature and salinity on oxygen consumption of tawny puffer Takifugu flavidus juvenile. Aquaculture Research, 42(2): 301–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1365–2109.2010.02638.x [57] Stenseth N C, Mysterud A, Ottersen G, et al. 2002. Ecological effects of climate fluctuations. Science, 297(5585): 1292–1296. doi: 10.1126/science.1071281 [58] Todd C D, Hughes S L, Marshall C T, et al. 2008. Detrimental effects of recent ocean surface warming on growth condition of Atlantic salmon. Global Change Biology, 14(5): 958–970. doi: 10.1111/j.1365–2486.2007.01522.x [59] Walther G R, Post E, Convey P, et al. 2002. Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature, 416(6879): 389–395. doi: 10.1038/416389a [60] Xue Suyan, Fang Jianguang, Zhang Jihong, et al. 2013. Effects of temperature and salinity on the development of the amphipod crustacean Eogammarus sinensis. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 31(5): 1010–1017. doi: 10.1007/s00343–013-2302–0 [61] Xue Suyan, Mao Yuze, Li Jiaqi, et al. 2018. Life history responses to variations in temperature by the marine amphipod Eogammarus possjeticus (Gammaridae) and their implications for productivity in aquaculture. Hydrobiologia, 814: 133–145. doi: 10.1007/s10750–018-3524–0 [62] Ye Le, Yang Shengyun, Zhu Xiaoming, et al. 2011. Effects of temperature on survival, development, growth and feeding of larvae of Yellowtail clownfish Amphiprion clarkii (Pisces: Perciformes). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(5): 241–245. doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2011.06.003 [63] Yom-Tov Y, Geffen E. 2011. Recent spatial and temporal changes in body size of terrestrial vertebrates: probable causes and pitfalls. Biological Reviews, 86(2): 531–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1469–185X.2010.00168.x [64] Yuan Xiutang. 2005. Studies on physio-ecology and bioremediation of the sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences [65] Yuan Xiutang, Yang Hongsheng, Wang Lili, et al. 2007. Effects of aestivation on the energy budget of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea). Acta Ecologica Sinica (in Chinese), 27(8): 3155–3161. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000–0933.2007.08.008 [66] Zhang Lei, Zhao Zhigang, Fan Qixue. 2017. Effects of water temperature and initial weight on growth, digestion and energy budget of yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco (Richardson, 1846). Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 33(6): 1108–1117. doi: 10.1111/jai.13465 -




 下载:
下载: