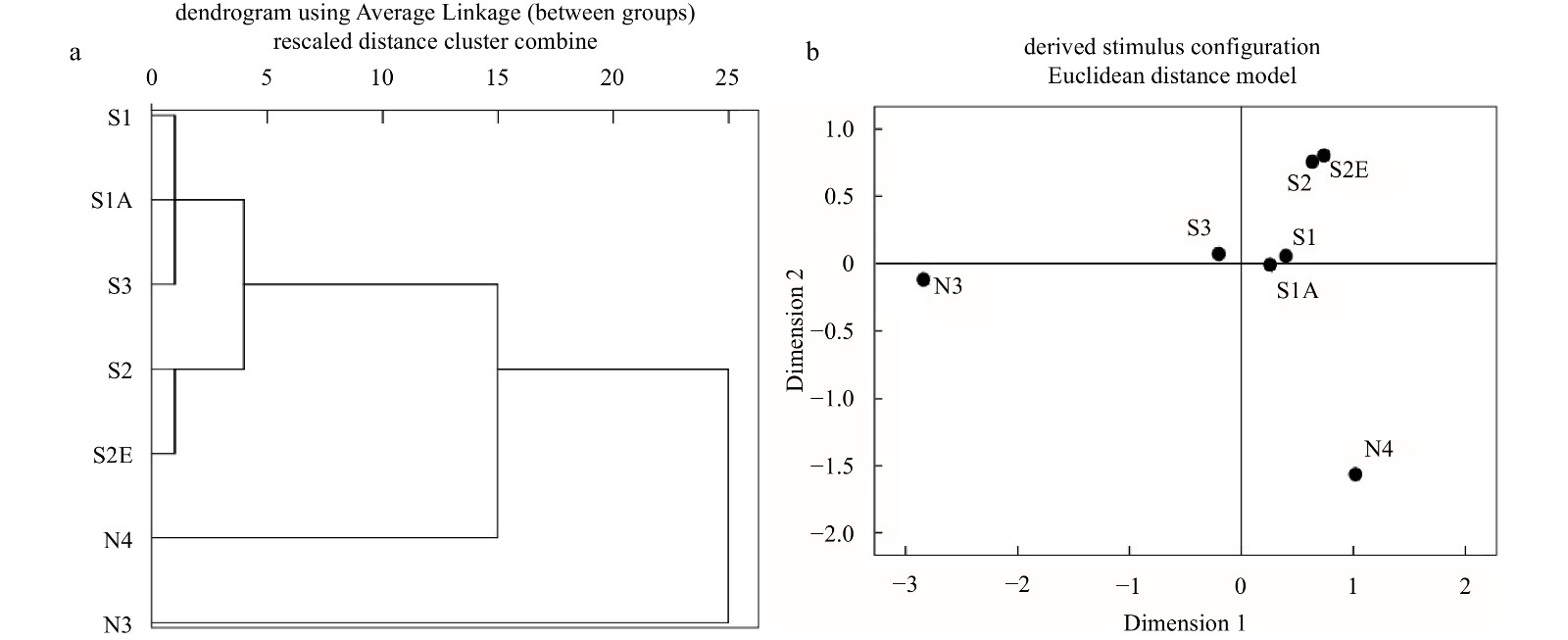
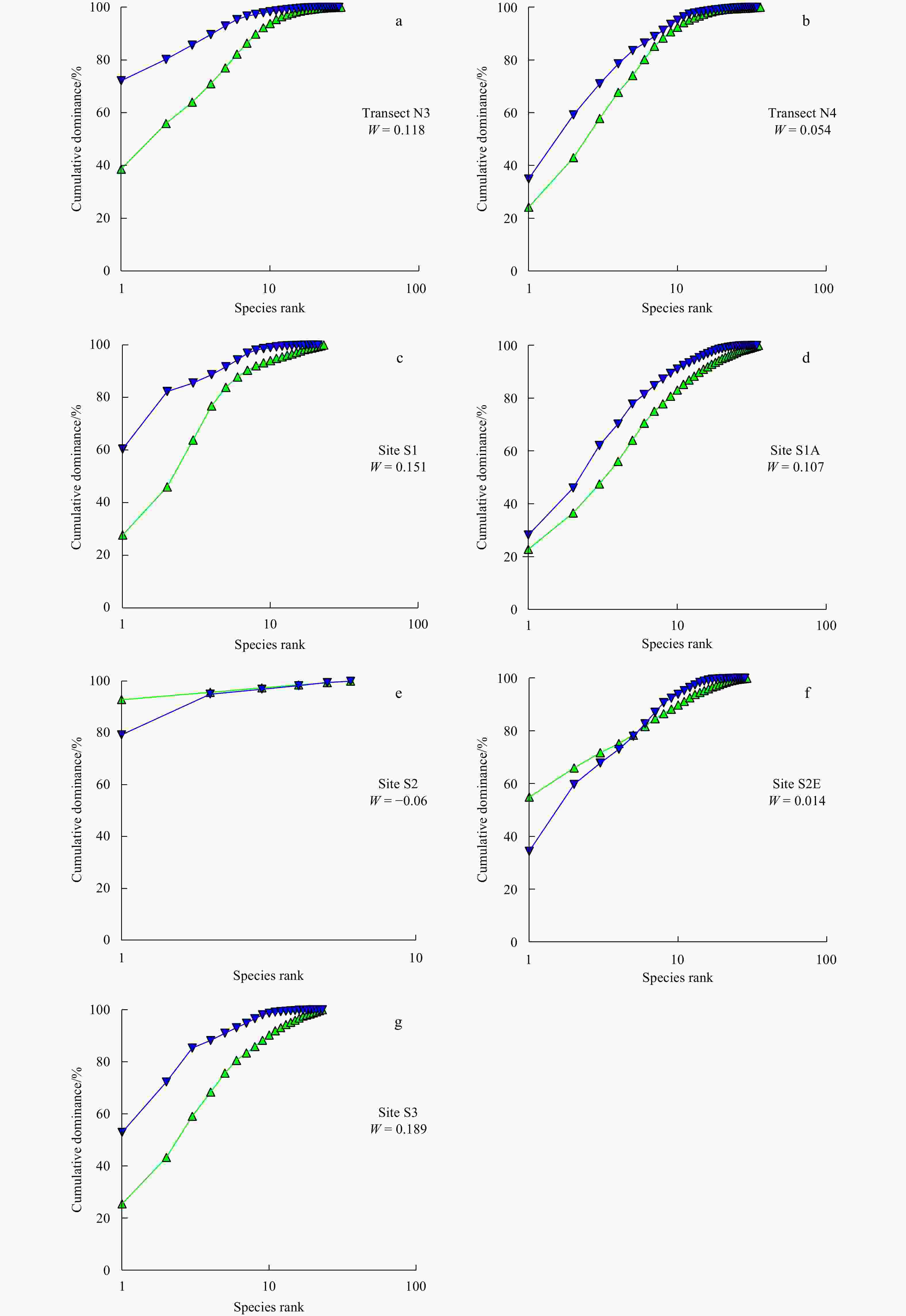
Assessment of macrobenthic community function and ecological quality after reclamation in the Changjiang (Yangtze) River Estuary wetland
-
Abstract: An ecological optimization project (semi-closed reclamation project) was implemented to control the invasion of Spartina alterniflora, and optimize the habitat of the Chongming Dongtan wetland, in the Changjiang (Yangtze) River Estuary. After project implementation, a macrobenthic ecological survey was conducted in a natural tidal flat and a semi-closed reclamation restoration area within the Chongming Dongtan wetland from 2019 to 2020. Compared with historical data before reclamation, findings showed that the groups, numbers, and species diversity of the macrobenthos increased significantly, and the ecological optimization project resulted in good ecological benefits. In addition, compared to the natural tidal flat, the number of collected macrobenthic phyla, and the macrobenthic density and biomass were significantly lower in the restoration area. Furthermore, the biodiversity index and functional redundancy of natural tidal flats were generally higher, indicating that the community composition and function of natural tidal flats were relatively more stable. Even though the species composition differed between a number of restoration areas and natural tidal flats, there was no difference in functional diversity, indicating that the effect of restoring ecological functions in restoration areas was optimal. Among them, the biodiversity and functional redundancy of Site S2 were significantly reduced, and the ecosystem function was extremely unstable. Habitat heterogeneity, vegetation community and decreasing salinity were the main factors that affected the ecological functions of macrobenthos. The ecological quality was also evaluated; the Transects N3 and N4 showed good quality. The overall ecological quality of the restoration area was generally high, but that of Site S2 was poor and that of Site S2E was merely good, which was mainly due to modifications of the ecological function of macrobenthos. It is suggested that reeds mowing and freshwater species release should be adopted in restoration areas to improve the community function and the environmental disturbance resistance of the macrobenthos.
-
Key words:
- macrobenthos /
- ecological optimization project /
- semi-closed reclamation /
- community restoration /
- functional diversity /
- ecological health
-
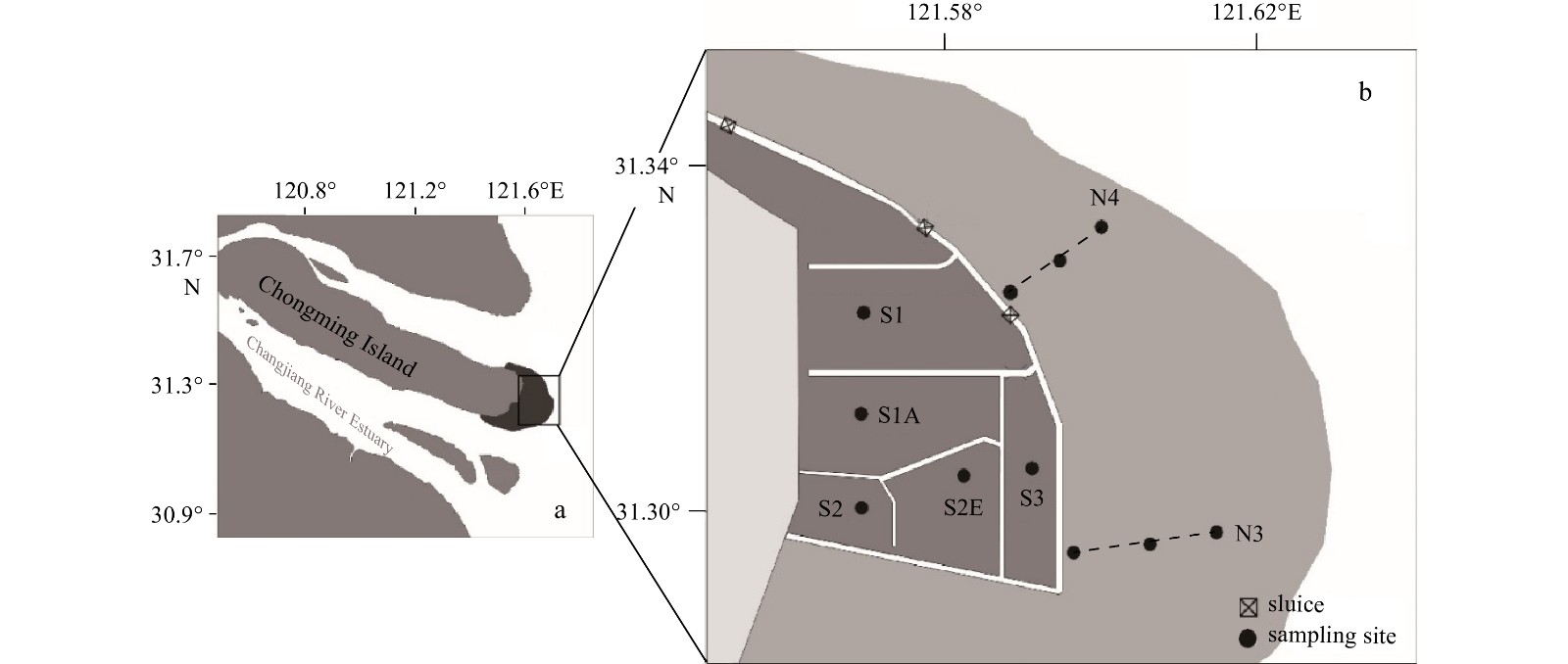
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of macrobenthic sampling in Chongming Dongtan wetland from 2019 to 2020. In b, the dark grey area represents the semi-closed reclamation restoration area, and the light grey area represents the natural tidal-flat area. The dots represent the sampling sites; the dash lines represent the Transects N3 and N4.
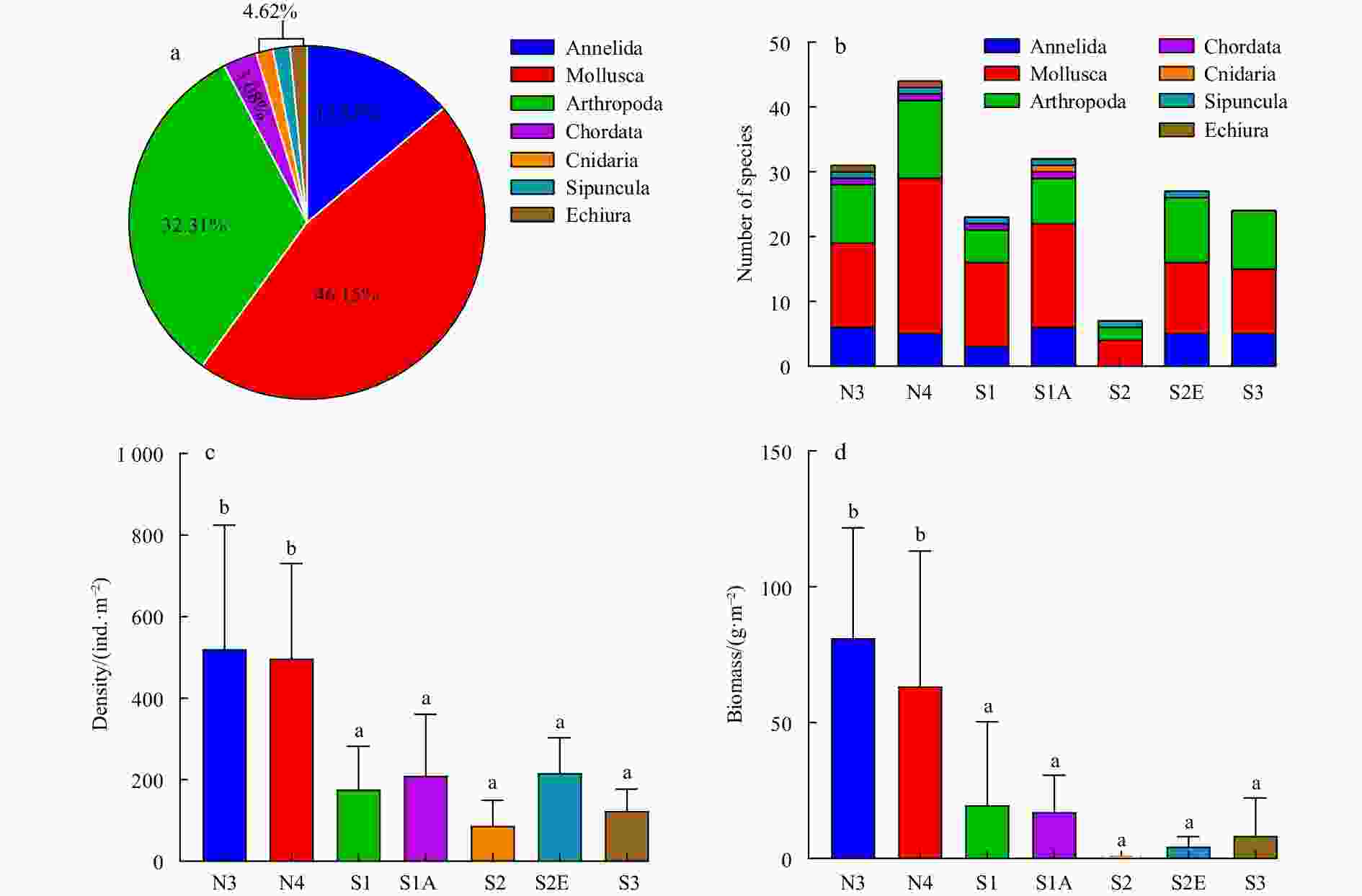
Figure 2. The species composition (a), number of species (b), density (c) and biomass (d) of macrobenthos in Chongming Dongtan wetland from 2019 to 2020. N3 and N4 are sampling transects; S1, S1A, S2, S2E and S3 are sampling sites. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences among sites.
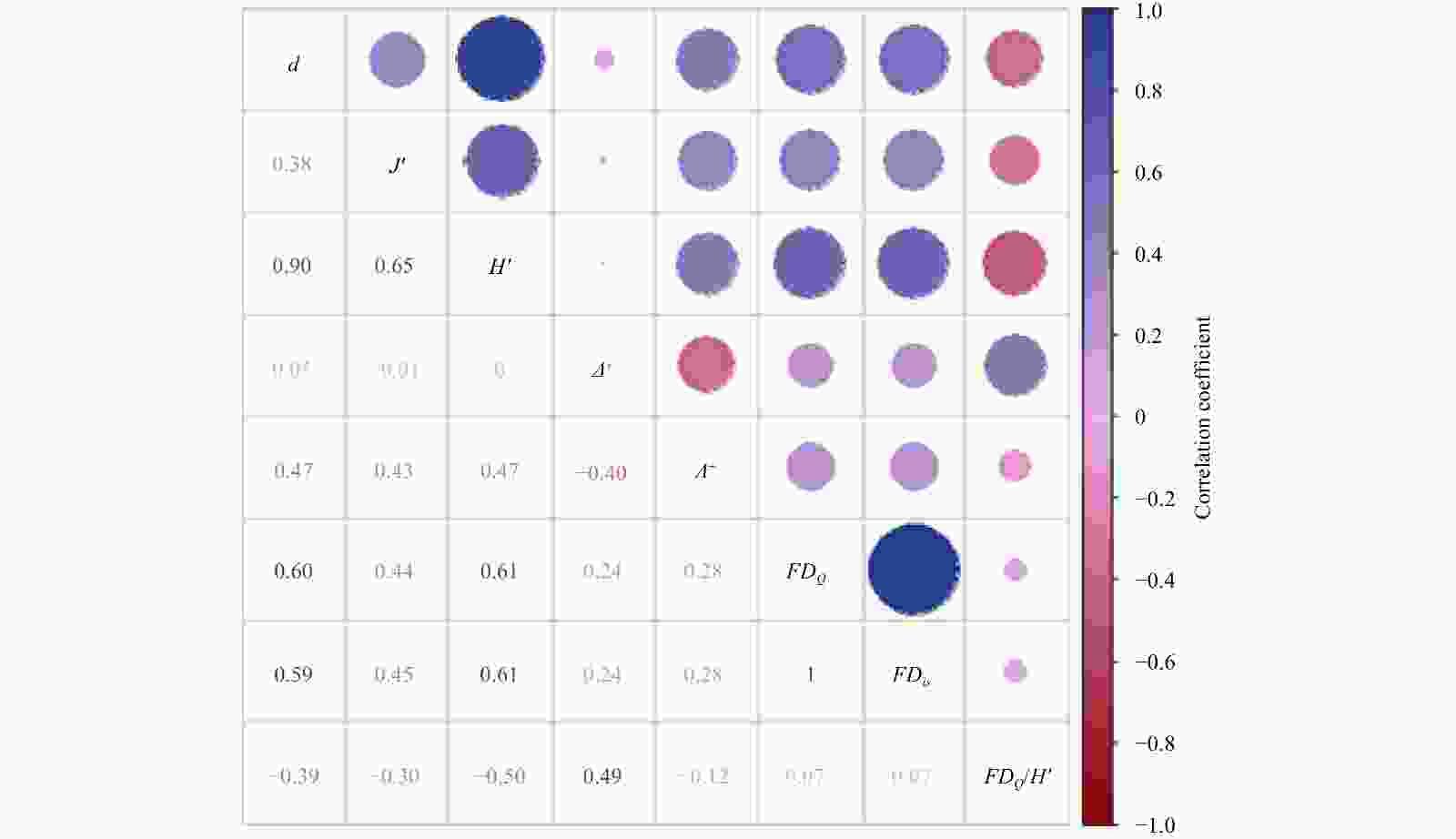
Figure 3. The correlation matrix of the macrobenthic diversity index in Chongming Dongtan wetland from 2019 to 2020. The d is the Margalef species richness index; J′, Pielou species evenness index; H', Shannon-Wiener index; Δ+, average taxonomic distinctness; Λ+, variation in taxonomic distinctness; FDQ, functional diversity index; FDis, functional dispersion; and FDQ/H', functional redundancy. Species diversity includes d, J' and H'; taxonomic diversity, Δ+ and Λ+; functional diversity, FDQ and FDis; Functional redundancy, FD/H'.
Table 1. The relationship between AMBI and M-AMBI and ecological quality status/environmental disturbance
Ecological quality/Disturbance classification AMBI M-AMBI High/undisturbed (0, 1.2] >0.77 Good/slightly disturbed (1.2, 3.3] (0.53, 0.77] Moderate/moderately disturbed (3.3, 5.0] (0.38, 0.53] Poor/heavily disturbed (5.0, 6.0] (0.20, 0.38] Bad/extremely disturbed >6.0 (0, 0.20] Note: AMBI is the abbreviation of AZTI’s Marine Biotic Index; and M-AMBI, multivariate AZTI’s Marine Biotic Index. Table 2. The biodiversity index of macrobenthos in the Chongming Dongtan wetland, Shanghai from 2019 to 2020
Transect N3 Transect N4 Site S1 Site S1A Site S2 Site S2E Site S3 DO concentration/(mg·L−1) 7.95±2.72 7.89±4.54 8.40±3.50 10.09±4.92 11.45±3.84 8.63 ± 2.69 10.49 ± 2.61 pH 8.14±0.47 7.88±0.52 8.02±0.49 8.32±0.29 8.36±0.49 7.96±0.75 8.09±0.50 Water temperature/°C 20.72±10.11 20.30±10.04 19.73±7.77 19.82±8.41 20.49±8.13 19.71±8.38 20.52±8.64 Salinity 8.33±1.91b 8.77±2.27b 3.52±2.65a 3.46±2.67a 1.37±2.07a 3.11±1.97a 4.37±1.96a d 2.18±0.59c 1.85±0.59bc 0.94±0.42ab 1.67±0.87bc 0.19±0.26a 1.44±0.60bc 1.23±0.74b J' 0.62±0.15ab 0.65±0.14b 0.70±0.15b 0.82±0.10b 0.18±0.29a 0.60±0.19ab 0.77±0.15b H' 2.36±0.65b 2.31±0.59b 1.62±0.39b 2.54±0.81b 0.31±0.59a 1.86±0.72b 2.01±1.00b Δ+ 88.33±3.73b 83.43±14.02b 84.74±9.01b 82.47±9.55b 48.26±51.67a 85.24±2.70b 90.13±6.84b $\varLambda $+ 437.13±108.99b 362.08±65.10ab 331.40±166.21ab 533.50±414.53b 51.12±121.58a 521.72±113.81b 332.89±234.43ab FDQ 42.56±3.20b 44.97±4.10b 37.81±7.68b 41.88±6.15b 11.99±13.81a 38.92±6.67b 39.23±11.46b FDis 6.42±0.25b 6.60±0.33b 6.01±0.69b 6.39±0.49b 2.20±2.47a 6.15±0.55b 6.09±1.09b FDQ/H' 19.38±6.34 20.86±7.37 24.49±7.44 17.89±5.95 39.50±53.30 25.03±12.74 24.54±14.46 Note: d is the Margalef species richness index; J', Pielou species evenness index; H', Shannon-Wiener index; Δ+, average taxonomic distinctness; $\varLambda $+, variation in taxonomic distinctness; FDQ, functional diversity index; FDis, functional dispersion; and FDQ/H', functional redundancy. Different letters indicate significant differences among sites. Table 3.
AMBI and M-AMBI of 7 habitats in Chongming Dongtan wetland from 2019 to 2020 Sampling
areaAMBI Disturbance classification M-AMBI Ecological
qualityN3 2.210 slightly disturbed 0.83 high N4 1.514 slightly disturbed 0.95 high S1 1.474 slightly disturbed 0.82 high S1A 1.453 slightly disturbed 0.99 high S2 2.863 slightly disturbed 0.35 poor S2E 3.014 slightly disturbed 0.69 good S3 2.543 slightly disturbed 0.77 high Note: AMBI is the abbreviation of AZTI’s Marine Biotic Index; and M-AMBI, multivariate AZTI’s Marine Biotic Index. Table 4.
Comparison of community characteristics before and after reclamation in Chongming Dongtan wetland Variable 2007−2008 2019−2020 High and middle marsh Low marsh Semi-closed restoration area Natural tidal flat area Average number of species 15 19 23 33 Average density/(ind.·m−2) 672.75 1866.5 1304.8 4078.5 d 2.054 2.461 3.063 3.851 J' 0.514 0.584 0.587 0.634 H' 1.946 2.502 2.707 3.195 Note: d is the Margalef species richness index; J', Pielou species evenness index; H', Shannon-Wiener index. -
Adler P B, Bradford J B. 2002. Compensation: an alternative method for analyzing diversity-productivity experiments. Oikos, 96(3): 411–420. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0706.2002.960303.x Barbier E B, Hacker S D, Kennedy C, et al. 2011. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecological Monographs, 81(2): 169–193. doi: 10.1890/10-1510.1 Bertness M D, Ewanchuk P J, Silliman B R. 2002. Anthropogenic modification of New England salt marsh landscapes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(3): 1395–1398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.022447299 Borja A, Dauer D M, Díaz R, et al. 2008. Assessing estuarine benthic quality conditions in Chesapeake Bay: A comparison of three indices. Ecological Indicators, 8(4): 395–403. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2007.05.003 Borja Á, Dauer D M, Grémare A. 2012. The importance of setting targets and reference conditions in assessing marine ecosystem quality. Ecological Indicators, 12(1): 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.06.018 Borja A, Franco J, Pérez V. 2000. A marine Biotic Index to establish the ecological quality of soft-bottom benthos within European estuarine and coastal environments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(12): 1100–1114. doi: 10.1016/s0025-326x(00)00061-8 Borja Á, Marín S L, Muxika I, et al. 2015. Is there a possibility of ranking benthic quality assessment indices to select the most responsive to different human pressures?. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 97(1–2): 85–94, Chen Zhongbing, Guo Li, Jin Binsong, et al. 2009. Effect of the exotic plant Spartina alterniflora on macrobenthos communities in salt marshes of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 82(2): 265–272, Chen Jing, Jiang Wanxiang, He Shishui, et al. 2018. Study of macroinvertebrate species and functional diversity in the New Xue River, Shandong Province, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(9): 3328–3336 Christianen M J A, Middelburg J J, Holthuijsen S J, et al. 2017. Benthic primary producers are key to sustain the Wadden Sea food web: stable carbon isotope analysis at landscape scale. Ecology, 98(6): 1498–1512. doi: 10.1002/ecy.1837 Crain C M, Silliman BR, Bertness S L, et al. 2004. Physical and biotic drivers of plant distribution across estuarine salinity gradients. Ecology, 85(9): 2539–2549. doi: 10.1890/03-0745 Forde James, O’Beirn Francis X, O’Carroll Jack P J, et al. 2015. Impact of intertidal oyster trestle cultivation on the ecological status of benthic habitats. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 95(1): 223–233. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.04.013 Gao Yu, Lin Guanghui. 2018. Algal diversity and their importance in ecological processes in typical mangrove ecosystems. Biodiversity Science, 26(11): 1223–1235. doi: 10.17520/biods.2018080 Gao Z G, Zhang L Q. 2006. Multi-seasonal spectral characteristics analysis of coastal salt marsh vegetation in Shanghai, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 69(1–2): 217–224, Han Taotao, Tang Xuan, Ren Hai, et al. 2021. Community/ecosystem functional diversity: measurements and development. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(8): 3286–3295 Herman P M J, Middelburg J J, Van De Koppel J, et al. 1999. Ecology of estuarine macrobenthos. In: Nedwell D B, Raffaelli D G, eds. Advances in Ecological Research. Academic Press, 29: 195–240 Huang Yinying, Li Yiming, Chen Qiang, et al. 2021. Effects of reclamation methods and habitats on macrobenthic communities and ecological health in estuarine coastal wetlands. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 168: 112420. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112420 Korb S K, Bolshakov L V, Fric Z F, et al. 2016. Cluster biodiversity as a multidimensional structure evolution strategy: checkerspot butterflies of the group Euphydryas aurinia (Rottemburg, 1775) (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Systematic Entomology, 41(2): 441–457. doi: 10.1111/syen.12167 Laursen A E, Seitzinger S P, Dekorsey R, et al. 2002. Multiple stressors in an estuarine system: Effects of nutrients, trace elements, and trophic complexity on benthic photosynthesis and respiration. Estuaries, 25(1): 57–69. doi: 10.1007/BF02696049 Leung J Y S. 2015. Habitat heterogeneity affects ecological functions of macrobenthic communities in a mangrove: Implication for the impact of restoration and afforestation. Global Ecology and Conservation, 4: 423–433. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2015.08.005 Levins R. 1970. An introduction to mathematical ecology. Evolution, 24(2): 482 Li Xiaoxiao, Yang Wei, Sun Tao, et al. 2019. Framework of multidimensional macrobenthos biodiversity to evaluate ecological restoration in wetlands. Environmental Research Letters, 14(5): 054003. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab142c Liu Zhiquan, Chen Minghai, Li Yiming, et al. 2018a. Different effects of reclamation methods on macrobenthos community structure in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 127: 429–436. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.12.038 Liu Zhiquan, Fan Bin, Huang Youhui, et al. 2019. Assessing the ecological health of the Chongming Dongtan Nature Reserve, China, using different benthic biotic indices. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 146: 76–84. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.06.006 Liu Zhiquan, Yu Ping, Chen Minghai, et al. 2018b. Macrobenthic community characteristics and ecological health of a constructed intertidal oyster reef in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 135: 95–104. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.019 Luo Xianxiang, Sun Kaijing, Yang Jianqiang, et al. 2016. A comparison of the applicability of the Shannon-Wiener index, AMBI and M-AMBI indices for assessing benthic habitat health in the Huanghe (Yellow River) Estuary and adjacent areas. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(6): 50–58. doi: 10.1007/s13131-016-0842-9 Lv Weiwei, Huang Youhui, Liu Zhiquan, et al. 2016a. Application of macrobenthic diversity to estimate ecological health of artificial oyster reef in Yangtze Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 103(1–2): 137–143, Lv Weiwei, Liu Zhiquan, Yang Yang, et al. 2016b. Loss and self-restoration of macrobenthic diversity in reclamation habitats of estuarine islands in Yangtze Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 103(1–2): 128–136, Lv Weiwei, Zhou Wenzong, Zhao Yunlong. 2019. Effect of freshwater inflow on self-restoration of macrobenthic diversity in seaward intertidal wetlands influenced by reclamation projects in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 138: 177–186. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.11.044 Ma Qiang, Wu Wei, Tang Chendong, et al. 2017. Effects of habitat restoration on the diversity of bird and marcobenthos in the Chongming Dongtan wetland. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 41(1): 9–14 Margalef R. 1969. Diversity and stability: a practical proposal and a model of interdependence. Brookhaven Symposia in Biology, 22: 25–37 Martinez-Haro M, Beiras R, Bellas J, et al. 2015. A review on the ecological quality status assessment in aquatic systems using community based indicators and ecotoxicological tools: what might be the added value of their combination?. Ecological Indicators, 48: 8–16. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.07.024 Mascaro J, Hughes R F, Schnitzer S A. 2012. Novel forests maintain ecosystem processes after the decline of native tree species. Ecological Monographs, 82(2): 221–228. doi: 10.1890/11-1014.1 Mor J R, Ruhí A, Tornés E, et al. 2018. Dam regulation and riverine food-web structure in a Mediterranean river. Science of the Total Environment, 625: 301–310. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.296 Muxika I, Borja Á, Bald J. 2007. Using historical data, expert judgement and multivariate analysis in assessing reference conditions and benthic ecological status, according to the European Water Framework Directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 55(1–6): 16–29, Nie Minghua, Yan Caixia, Dong Wenbo, et al. 2015. Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of estrogens in surface water, suspended particulate matter, and sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Chemosphere, 127: 109–116. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.021 Nishijima W, Nakano Y, Nakai S, et al. 2014. Macrobenthic succession and characteristics of a man-made intertidal sandflat constructed in the diversion channel of the Ohta River Estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 82(1–2): 101–108, Nunes M, Coelho J P, Cardoso P G, et al. 2008. The macrobenthic community along a mercury contamination in a temperate estuarine system (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Science of The Total Environment, 405(1–3): 186–194, Petchey O L. 2003. Integrating methods that investigate how complementarity influences ecosystem functioning. Oikos, 101(2): 323–330. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0706.2003.11828.x Petchey O L, Gaston K J. 2002. Functional diversity (FD), species richness and community composition. Ecology Letters, 5(3): 402–411. doi: 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2002.00339.x Petchey O L, Gaston K J. 2006. Functional diversity: back to basics and looking forward. Ecology Letters, 9(6): 741–758. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00924.x Peterson C H, Lipcius R N. 2003. Conceptual progress towards predicting quantitative ecosystem benefits of ecological restorations. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 264: 297–307. doi: 10.3354/meps264297 Piló D, Ben-Hamadou R, Pereira F, et al. 2016. How functional traits of estuarine macrobenthic assemblages respond to metal contamination?. Ecological Indicators, 71: 645–659. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.07.019 Poos M S, Walker S C, Jackson D A. 2009. Functional-diversity indices can be driven by methodological choices and species richness. Ecology, 90(2): 341–347. doi: 10.1890/08-1638.1 Ren Zhonghua, Li Fan, Wei Jiali, et al. 2016. Community characteristics of macrobenthos in the Huanghe (Yellow River) Estuary during water and sediment discharge regulation. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(8): 74–81. doi: 10.1007/s13131-016-0881-2 Rosenfeld J S. 2002. Functional redundancy in ecology and conservation. Oikos, 98(1): 156–162. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0706.2002.980116.x Sakamaki T, Richardson J S. 2009. Dietary responses of tidal flat macrobenthos to reduction of benthic microalgae: a test for potential use of allochthonous organic matter. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 386: 107–113. doi: 10.3354/meps08094 Salas F, Marcos C, Neto J M, et al. 2006. User-friendly guide for using benthic ecological indicators in coastal and marine quality assessment. Ocean & Coastal Management, 49(5–6): 308–331, Schmera D, Erős T, Podani J. 2009. A measure for assessing functional diversity in ecological communities. Aquatic Ecology, 43(1): 157–167. doi: 10.1007/s10452-007-9152-9 Seitzinger S. 2008. Out of reach. Nature, 452(7184): 162–163. doi: 10.1038/452162a Shannon C E, Weaver W. 1962. The Mathematical Theory of Communication. Urbana: University of Illinois Press Tang Chendong. 2016. Ecological control of Spartina alternilfora and improvement of birds habitats in Chongming Dongtan Wetland, Shanghai. Wetland Science & Management, 12(3): 4–8 Tian Bo, Zhou Yunxuan, Zhang Liquan, et al. 2008. Analyzing the habitat suitability for migratory birds at the Chongming Dongtan Nature Reserve in Shanghai, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 80(2): 296–302, Tilman D, Reich P B, Knops J, et al. 2001. Diversity and productivity in a long-term grassland experiment. Science, 294(5543): 843–845. doi: 10.1126/science.1060391 Usseglio-Polatera P, Bournaud M, Richoux P, et al. 2000. Biological and ecological traits of benthic freshwater macroinvertebrates: relationships and definition of groups with similar traits. Freshwater Biology, 43(2): 175–205. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2427.2000.00535.x van der Linden P, Patrício J, Marchini A, et al. 2012. A biological trait approach to assess the functional composition of subtidal benthic communities in an estuarine ecosystem. Ecological Indicators, 20: 121–133. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.02.004 Voß K, Schäfer R B. 2017. Taxonomic and functional diversity of stream invertebrates along an environmental stress gradient. Ecological Indicators, 81: 235–242. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.05.072 Wang Ruizhao, Yuan Lin, Zhang Liquan. 2010. Impacts of Spartina alterniflora invasion on the benthic communities of salt marshes in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Ecological Engineering, 36(6): 799–806. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.02.005 Wang Xuejing, Zhang Yan, Luo Manhua, et al. 2021. Radium and nitrogen isotopes tracing fluxes and sources of submarine groundwater discharge driven nitrate in an urbanized coastal area. Science of the Total Environment, 763: 144616. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144616 Warwick R M. 1986. A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities. Marine Biology, 92(4): 557–562. doi: 10.1007/BF00392515 Warwick R M, Clarke K R. 1994. Relearning the ABC: taxonomic changes and abundance/biomass relationships in disturbed benthic communities. Marine Biology, 118(4): 739–744. doi: 10.1007/BF00347523 Witman J D, Cusson M, Archambault P, et al. 2008. The relation between productivity and species diversity in temperate-arctic marine ecosystems. Ecology, 89(S11): S66–S80. doi: 10.1890/07-1201.1 Wong M C, Dowd M. 2015. Patterns in taxonomic and functional diversity of macrobenthic invertebrates across seagrass habitats: a case study in Atlantic Canada. Estuaries and Coasts, 38(6): 2323–2336. doi: 10.1007/s12237-015-9967-x Yang Wei, Li Ming, Sun Tao, et al. 2017. The joint effect of tidal barrier construction and freshwater releases on the macrobenthos community in the northern Yellow River Delta (China). Ocean & Coastal Management, 136: 83–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2016.11.024 Zhong Xin, Qiu Baochao, Liu Xiaoshou. 2020. Functional diversity patterns of macrofauna in the adjacent waters of the Yangtze River Estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 154: 111032. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111032 Zhou Zhengquan, Li Xiaojing, Chen Linlin, et al. 2018. Macrobenthic assemblage characteristics under stressed waters and ecological health assessment using AMBI and M-AMBI: a case study at the Xin’an River Estuary, Yantai, China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 37(5): 77–86. doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1180-x Zhu Xiaofen, Chen Bin, Yu Weiwei, et al. 2018. Discussion on taxonomic diversity indices and taxonomic sufficiency for macrobenthos in Xiamen Bay. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(15): 5554–5565 -




 下载:
下载: