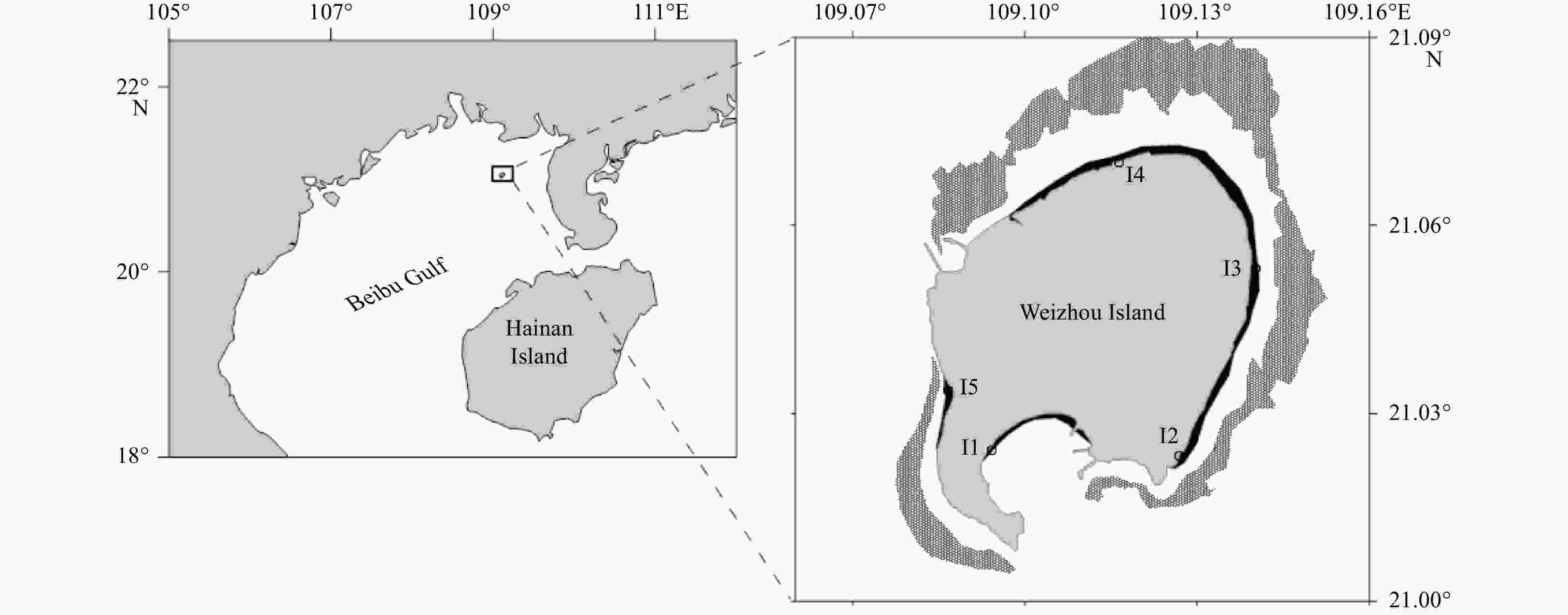
Sedimentary nitrogen dynamics in a coastal reef area with relatively high nitrogen concentration
-
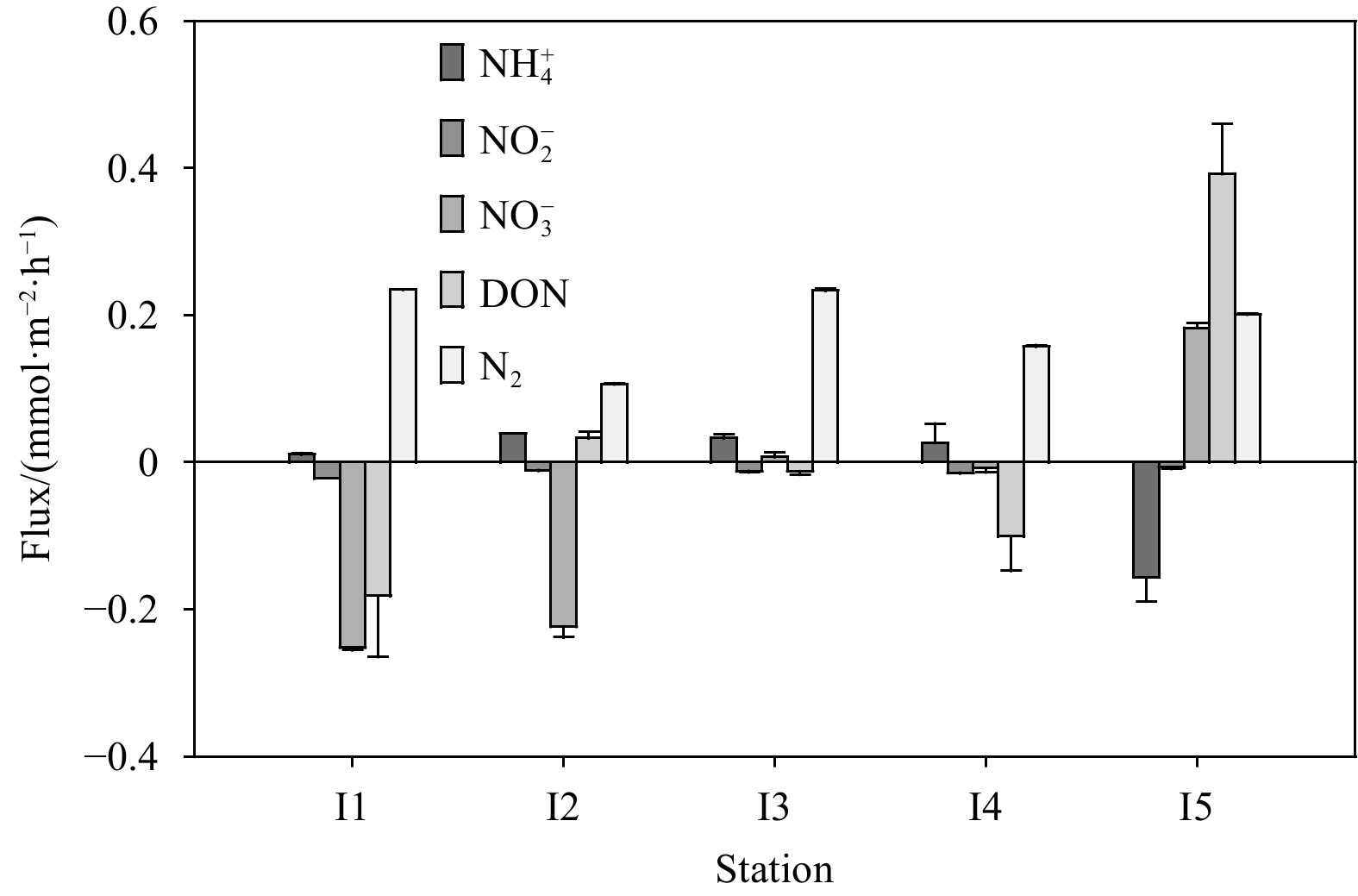
Abstract: The migration and transformation of nitrogen (N) in sediments play an important role in regulating the N concentration and nutrient structures in shallow seas. However, studies of sedimentary N dynamics are rarely focused on carbonate sediments, although these account for about 40% of the continental shelf area. Thus, the regulation mechanisms of the N dynamics in the carbonate sands of coral reefs are not clear. Taking the coral reef area of Weizhou Island, which has a relatively high N concentration, as the research object, we conducted a series of flow-through reactor experiments to investigate the fluxes of different N forms at the interface of sediment and seawater and their regulation mechanism by environmental factors. The fluxes of dissolved inorganic and organic N (DIN and DON) at different stations were −0.39–0.12 mmol/(m2·h) and −0.18–0.39 mmol/(m2·h), respectively. Denitrification (0.11–0.25 mmol/(m2·h)) was closely coupled to nitrification, which was limited by the availability of organic matter and its degradation product (i.e.,
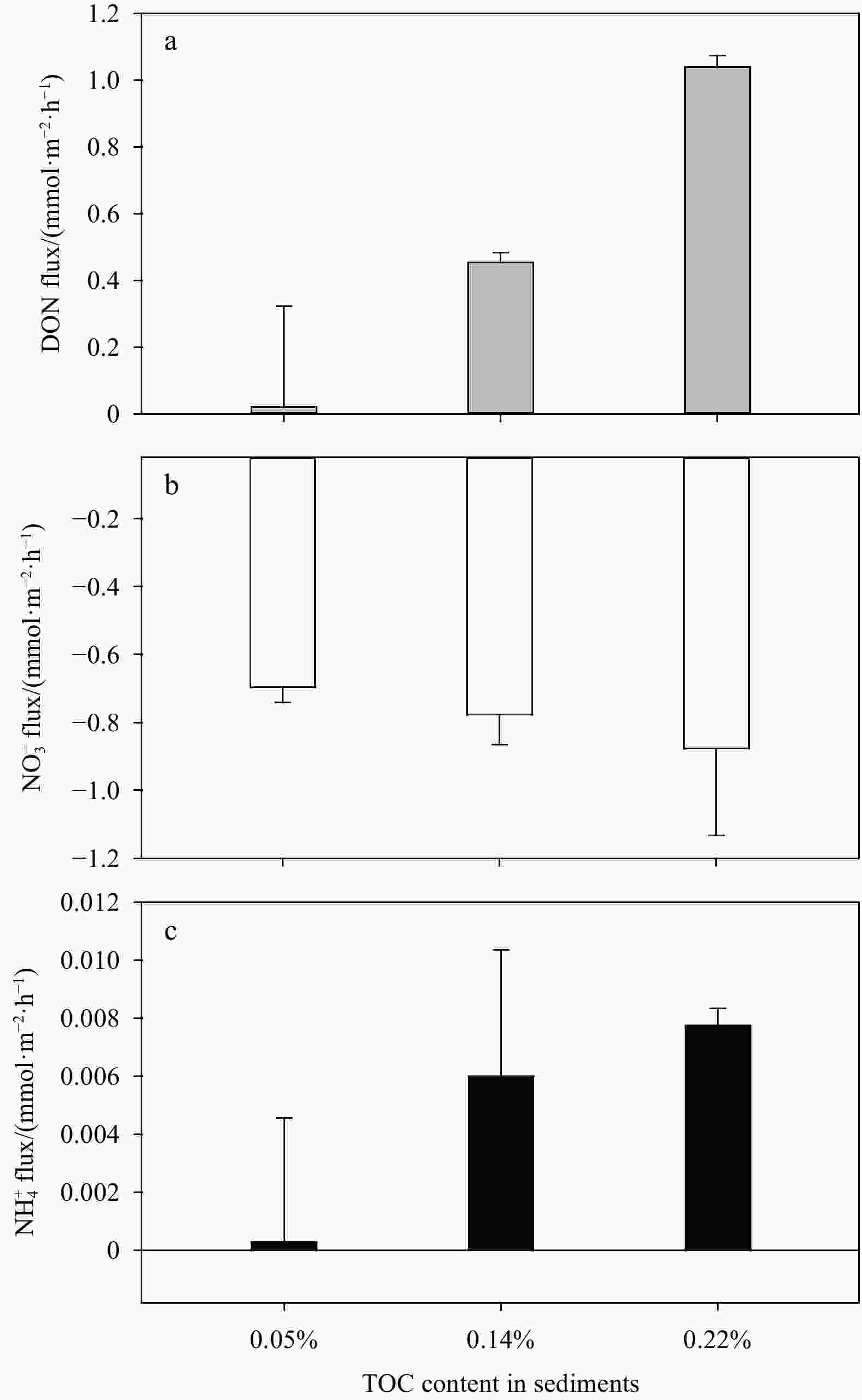
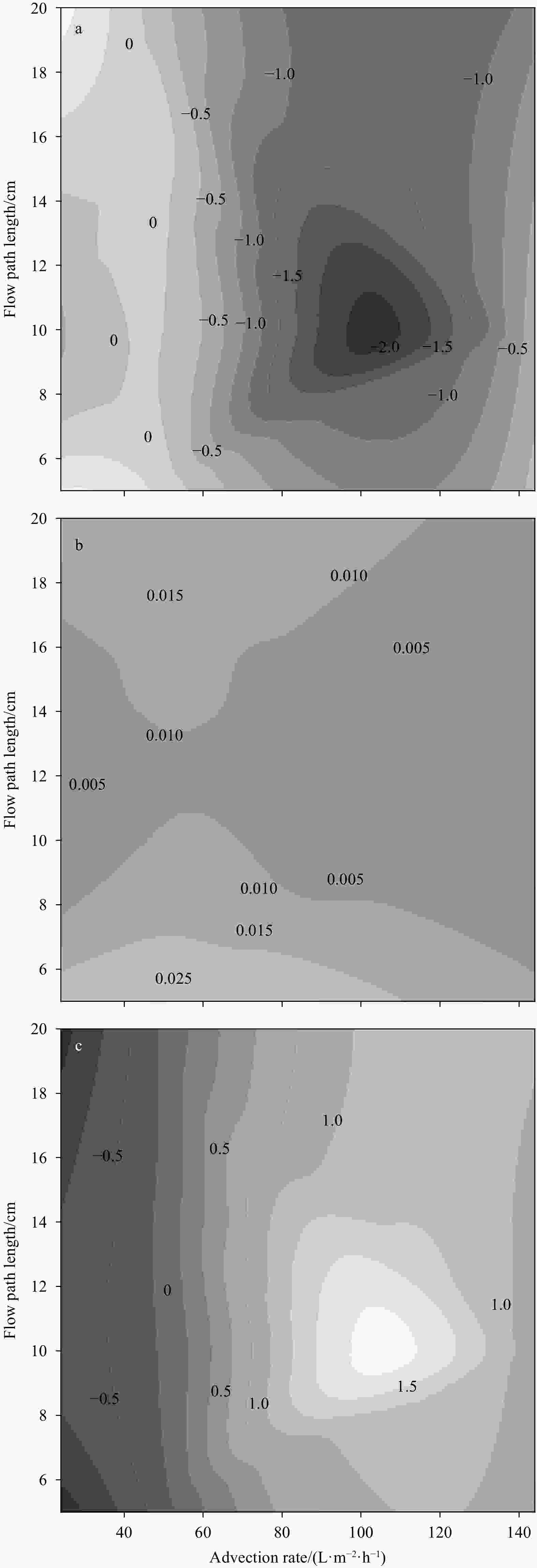
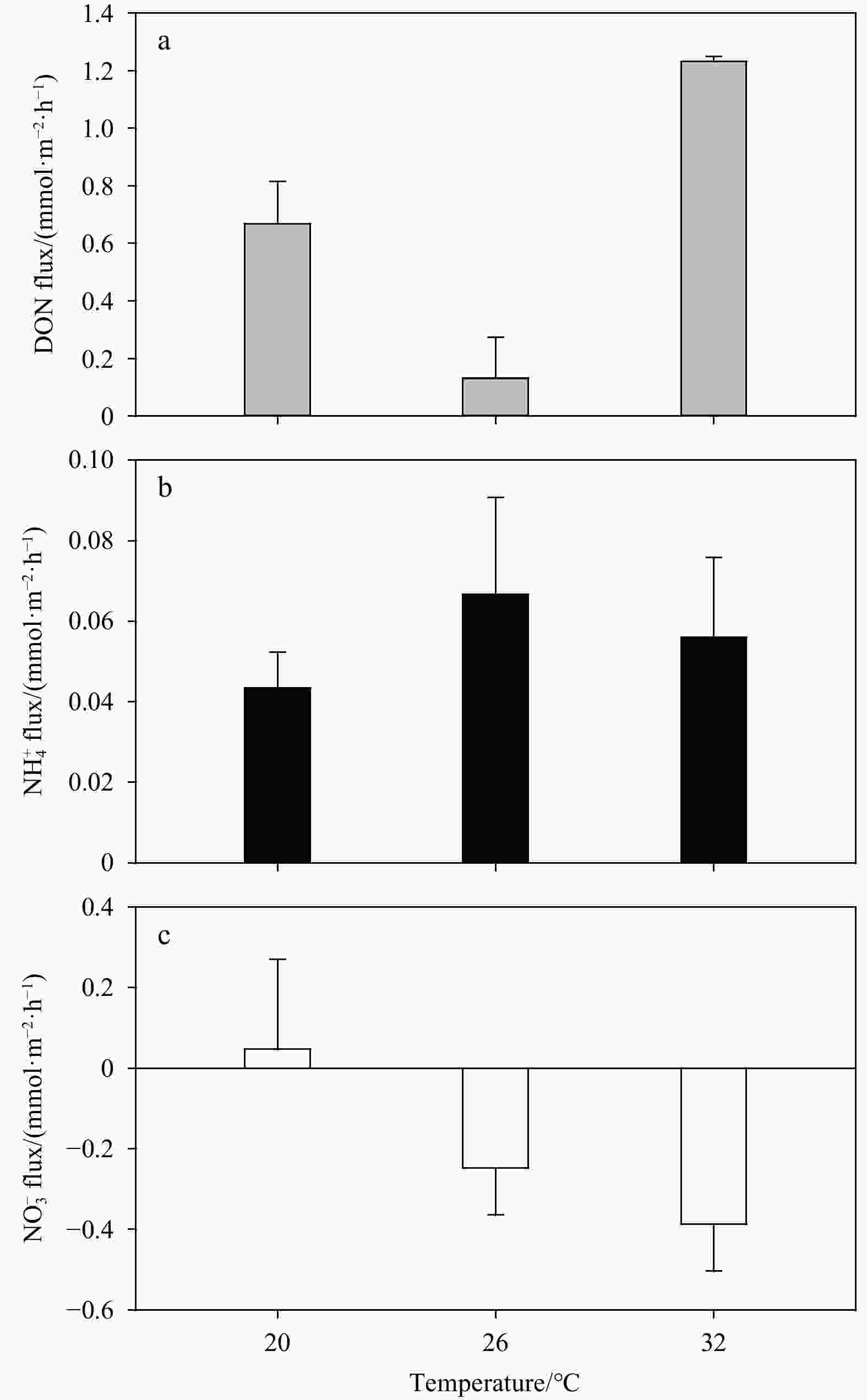
${\rm{NH}}_4^+ $ ). Thus, the excessive${\rm{NO}}_3^– $ might be reduced to${\rm{NH}}_4^+ $ by dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium, rather than to N2 by denitrification.${\rm{NO}}_3^– $ reduction peaked at intermediate advection rates (96 L/(m2·h)) and flow path lengths (10 cm), but the release of DON also peaked at the same condition. In addition, climate warming would significantly affect sedimentary N dynamics at Weizhou Island. These results may help address the broader issue of the N cycle in coral reef ecosystems under the dual pressure of climate warming and anthropogenic activities, and these results are beneficial to coral reef protection and local ecological management.-
Key words:
- nitrogen dynamics /
- sediments /
- coral reefs /
- Weizhou Island
-
Table 1. Summary of conditions in flow-through reactor experiment
Experiment Temperature/℃ ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $/(μmol·L–1) TOC content Advection rate/(mL·min–1) Column length/cm 1− Station 26 see Table 2 0.03%±0.01% 1 10 2− ${\rm{NO} }_3^- $ concentration 26 1, 4, 10, 30, 45 0.05% 1 10 3− TOC concentration 26 25±5 0.05%, 0.14%, 0.22% 1 10 4− Advection rate and flow path length 26 45±5 0.05% 0.5, 1, 2, 3 5, 10, 15, 20 5− Temperature 20, 26, 32 10±5 0.05% 1 10 Note: The variable parameters are indicated in bold. Table 2. Nutrient concentrations in overlying seawater and porewater in sediments, and total nitrogen (TN) content in bulk sediments
Station Seawater Porewater Sediment ${{\rm {NH}}_4^+} $/ (μmol·L−1) ${{\rm {NO}}_2^-} $/ (μmol·L−1) ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $/ (μmol·L−1) DIP/ (μmol·L−1) ${\rm{NH}}_4^+ $/ (μmol·L−1) ${\rm{NO}}_2^- $/ (μmol·L−1) ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $/ (μmol·L−1) DIP/ (μmol·L−1) TN (dry weight)/ (μmol·g−1) I1 0.70 0.33 4.36 0.02 6.72 3.16 6.76 0.46 2.90 I2 0.81 0.33 9.95 0.08 8.64 2.54 214.03 0.54 3.34 I3 1.14 0.30 1.44 0.08 113.28 0.81 0.43 0.54 4.28 I4 1.27 0.32 5.04 0.15 14.75 3.94 48.80 0.50 1.25 I5 2.02 0.46 9.28 0.43 156.03 1.29 0.56 0.69 2.47 Table 3. Correlation analysis results for
${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ and DIP concentrations in seawater and the TN in sediments and fluxes of DO, N2, DIN, and DON obtained from the first FTR experiment${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ concentration DIP concentration TN concentration DO flux N2 flux DIN flux DIP concentration 0.23 TN concentration 0.22 −0.02 DO flux −0.05 0.13 −0.45* N2 flux −0.72* 0.01 0.05 −0.04 DIN flux −0.65* 0.34 −0.06 0.18 0.47* DON flux 0.34 0.92* 0.00 0.17 −0.20 0.34 Note: * correlation is significant at the 0.05 level, n=20. -
Alongi D M, Trott L A, Pfitzner J. 2008. Biogeochemistry of inter-reef sediments on the northern and central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs, 27(2): 407–420. doi: 10.1007/s00338-007-0347-2 Baird M E, Mongin M, Rizwi F, et al. 2021. The effect of natural and anthropogenic nutrient and sediment loads on coral oxidative stress on runoff-exposed reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 168: 112409. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112409 Canion A, Kostka J E, Gihring T M, et al. 2014. Temperature response of denitrification and anammox reveals the adaptation of microbial communities to in situ temperatures in permeable marine sediments that span 50° in latitude. Biogeosciences, 11(2): 309–320. doi: 10.5194/bg-11-309-2014 Cook P L M, Kessler A J, Eyre B D. 2017. Does denitrification occur within porous carbonate sand grains?. Biogeosciences, 14(18): 4061–4069 Deek A, Emeis K, van Beusekom J. 2012. Nitrogen removal in coastal sediments of the German Wadden Sea. Biogeochemistry, 108(1–3): 467–483 Eakin C M, Sweatman H P A, Brainard R E. 2019. The 2014–2017 global-scale coral bleaching event: insights and impacts. Coral Reefs, 38(4): 539–545. doi: 10.1007/s00338-019-01844-2 El-Khaled Y C, Roth F, Rädecker N, et al. 2021. Nitrogen fixation and denitrification activity differ between coral- and algae-dominated Red Sea reefs. Scientific Reports, 11(1): 11820. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90204-8 Erler D V, Santos I R, Eyre B D. 2014. Inorganic nitrogen transformations within permeable carbonate sands. Continental Shelf Research, 77: 69–80. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.02.002 Eyre B D, Glud R N, Patten N. 2008. Mass coral spawning: a natural large-scale nutrient addition experiment. Limnology and Oceanography, 53(3): 997–1013. doi: 10.4319/lo.2008.53.3.0997 Guo Jing, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. 2019. Potential impacts of anthropogenic nutrient enrichment on coral reefs in the South China Sea: evidence from nutrient and chlorophyll a levels in seawater. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 21(10): 1745–1753 Hughes T P, Baird A H, Bellwood D R, et al. 2003. Climate change, human impacts, and the resilience of coral reefs. Science, 301(5635): 929–933. doi: 10.1126/science.1085046 Hughes T P, Kerry J T, Álvarez-Noriega M, et al. 2017. Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature, 543(7645): 373–377. doi: 10.1038/nature21707 Jäntti H, Stange F, Leskinen E, et al. 2011. Seasonal variation in nitrification and nitrate-reduction pathways in coastal sediments in the Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 63(2): 171–181. doi: 10.3354/ame01492 Jiang Shan, Kavanagh M, Ibánhez J S P, et al. 2021. Denitrification-nitrification process in permeable coastal sediments: an investigation on the effect of salinity and nitrate availability using flow-through reactors. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 40(9): 1–12. doi: 10.1007/s13131-021-1811-5 Kawasaki N, Benner R. 2006. Bacterial release of dissolved organic matter during cell growth and decline: molecular origin and composition. Limnology and Oceanography, 51(5): 2170–2180. doi: 10.4319/lo.2006.51.5.2170 Kessler A J, Cardenas M B, Santos I R, et al. 2014. Enhancement of denitrification in permeable carbonate sediment due to intra-granular porosity: a multi-scale modelling analysis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 141: 440–453. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.06.028 Lapointe B E, Brewton R A, Herren L W, et al. 2019. Nitrogen enrichment, altered stoichiometry, and coral reef decline at Looe Key, Florida Keys, USA: a 3-decade study. Marine Biology, 166(8): 108. doi: 10.1007/s00227-019-3538-9 Lu Dongliang, Kang Zhenjun, Yang Bin, et al. 2020. Compositions and spatio-temporal distributions of different nitrogen species and lability of dissolved organic nitrogen from the Dafengjiang River to the Sanniang Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 156: 111205. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111205 Mackin J E, Aller R C. 1984. Ammonium adsorption in marine sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 29(2): 250–257. doi: 10.4319/lo.1984.29.2.0250 Marchant H K, Holtappels M, Lavik G, et al. 2016. Coupled nitrification-denitrification leads to extensive N loss in subtidal permeable sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 61(3): 1033–1048. doi: 10.1002/lno.10271 Morris L A, Voolstra C R, Quigley K M, et al. 2019. Nutrient availability and metabolism affect the stability of coral–symbiodiniaceae symbioses. Trends in Microbiology, 27(8): 678–689. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2019.03.004 Muta N, Umezawa Y, Yamaguchi A, et al. 2020. Estimation of spatiotemporal variations in nutrient fluxes from sediments in the seasonally hypoxic Omura Bay, Japan. Limnology, 21(3): 341–356. doi: 10.1007/s10201-019-00591-1 Ning Zhiming, Fang Cao, Yu Kefu, et al. 2020. Influences of phosphorus concentration and porewater advection on phosphorus dynamics in carbonate sands around the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 160: 111668. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111668 Ning Zhiming, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. 2019. Carbon and nutrient dynamics of permeable carbonate and silicate sands adjacent to coral reefs around Weizhou Island in the northern South China Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 225: 106229 Ning Zhiming, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. 2022. Effects of nutrient enrichment and skewed N: P ratios on physiology of scleractinian corals from Weizhou Island in the northern South China Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 682: 111–122. doi: 10.3354/meps13933 Pan Ke, Zheng Xinqing, Liu Xinming, et al. 2021. Nitrogen cycling in a tropical coral reef ecosystem under severe anthropogenic disturbance in summer: insights from isotopic compositions. Water Research, 207: 117824. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117824 Rahman M, Grace M R, Roberts K L, et al. 2019. Effect of temperature and drying-rewetting of sediments on the partitioning between denitrification and DNRA in constructed urban stormwater wetlands. Ecological Engineering, 140: 105586. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105586 Rao A M F, McCarthy M J, Gardner W S, et al. 2007. Respiration and denitrification in permeable continental shelf deposits on the South Atlantic Bight: Rates of carbon and nitrogen cycling from sediment column experiments. Continental Shelf Research, 27: 1801–1819. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2007.03.001 Rasheed M, Badran M I, Huettel M. 2003. Particulate matter filtration and seasonal nutrient dynamics in permeable carbonate and silicate sands of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Coral Reefs, 22(2): 167–177. doi: 10.1007/s00338-003-0300-y Robertson E K, Bartoli M, Brüchert V, et al. 2019. Application of the isotope pairing technique in sediments: use, challenges, and new directions. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 17(2): 112–136. doi: 10.1002/lom3.10303 Rosset S, Wiedenmann J, Reed A J, et al. 2017. Phosphate deficiency promotes coral bleaching and is reflected by the ultrastructure of symbiotic dinoflagellates. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 118(1–2): 180–187 Rysgaard S, Risgaard-Petersen N, Niels Peter S, et al. 1994. Oxygen regulation of nitrification and denitrification in sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 39(7): 1643–1652. doi: 10.4319/lo.1994.39.7.1643 Santos I R, Eyre B D, Glud R N. 2012. Influence of porewater advection on denitrification in carbonate sands: evidence from repacked sediment column experiments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 96: 247–258. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.08.018 Tan Ehui, Zou Wenbin, Zheng Zhenzhen, et al. 2020. Warming stimulates sediment denitrification at the expense of anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Nature Climate Change, 10(4): 349–355. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0723-2 Wang Weilei, Moore J K, Martiny A C, et al. 2019. Convergent estimates of marine nitrogen fixation. Nature, 566(7743): 205–211. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0911-2 Wang Weibo, Wang Xu, Shu Xiao, et al. 2021. Denitrification of permeable sand sediment in a headwater river is mainly influenced by water chemistry, rather than sediment particle size and heterogeneity. Microorganisms, 9(11): 2202. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112202 Wiedenmann J, D’Angelo C, Smith E G, et al. 2013. Nutrient enrichment can increase the susceptibility of reef corals to bleaching. Nature Climate Change, 3(2): 160–164. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1661 Wild C, Rasheed M, Jantzen C, et al. 2005. Benthic metabolism and degradation of natural particulate organic matter in carbonate and silicate reef sands of the northern Red Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 298: 69–78. doi: 10.3354/meps298069 Xie Lei, Gao Xuelu, Liu Yongliang, et al. 2021. Perpetual atmospheric dry deposition exacerbates the unbalance of dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus in coastal waters: a case study on a mariculture site in North China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 172: 112866. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112866 Yang S, Gruber N. 2016. The anthropogenic perturbation of the marine nitrogen cycle by atmospheric deposition: nitrogen cycle feedbacks and the 15N Haber-Bosch effect. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 30(10): 1418–1440. doi: 10.1002/2016GB005421 Yu Wanjun, Wang Wenhuan, Yu Kefu, et al. 2019. Rapid decline of a relatively high latitude coral assemblage at Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea. Biodiversity and Conservation, 28(14): 3925–3949. doi: 10.1007/s10531-019-01858-w Zhang Zengyu, Furman A. 2021. Redox dynamics at a dynamic capillary fringe for nitrogen cycling in a sandy column. Journal of Hydrology, 603: 126899. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126899 -






 下载:
下载: