Sedimentary characteristics and genetic mechanism of the giant ancient pockmarks in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea
-
Abstract: In the late Miocene, giant ancient pockmarks, which are fairly rare globally, developed in the Qiongdongnan Basin. In this paper, to determine the sedimentary characteristics and genetic mechanism of these giant ancient pockmarks in the Yinggehai Formation of the Qiongdongnan Basin, based on high-resolution 3D seismic data and multiattribute fusion technologies, we analyzed the planar distribution and seismic facies of the ancient pockmarks and compared the characteristics of the ancient pockmarks with those of channels, craters, and hydrate pits. Moreover, we also discussed the implications of the fluid escape system and paleo-bottom current activity in the ancient pockmark development area and analyzed the influence of the ancient pockmarks on the paleoclimate in this region. Finally, an evolutionary model was proposed for the giant ancient pockmarks. This model shows that the giant ancient pockmarks in the southern Qiongdongnan Basin were affected by both deep fluid escape and lateral transformation of paleobottom currents. In addition, the giant ancient pockmarks contributed to the atmospheric CO2 concentration in the late Miocene and played a great role in the contemporary evaluation of deepwater petroleum exploration.
-
Key words:
- giant ancient pockmark /
- bottom current /
- fluid escape /
- Yinggehai Formation /
- Qiongdongnan Basin
-
Figure 1. Location of the study area (red rectangle) in the Qiongdongnan Basin (black dashed line boundary), northern South China Sea (insert) (modified from Lei and Ren (2016), Cao et al. (2015) and Jiang et al. (2013)). The elevation data were derived from Tozer et al. (2019). Moreover, the deep-water well data were derived from Lei and Ren (2016).
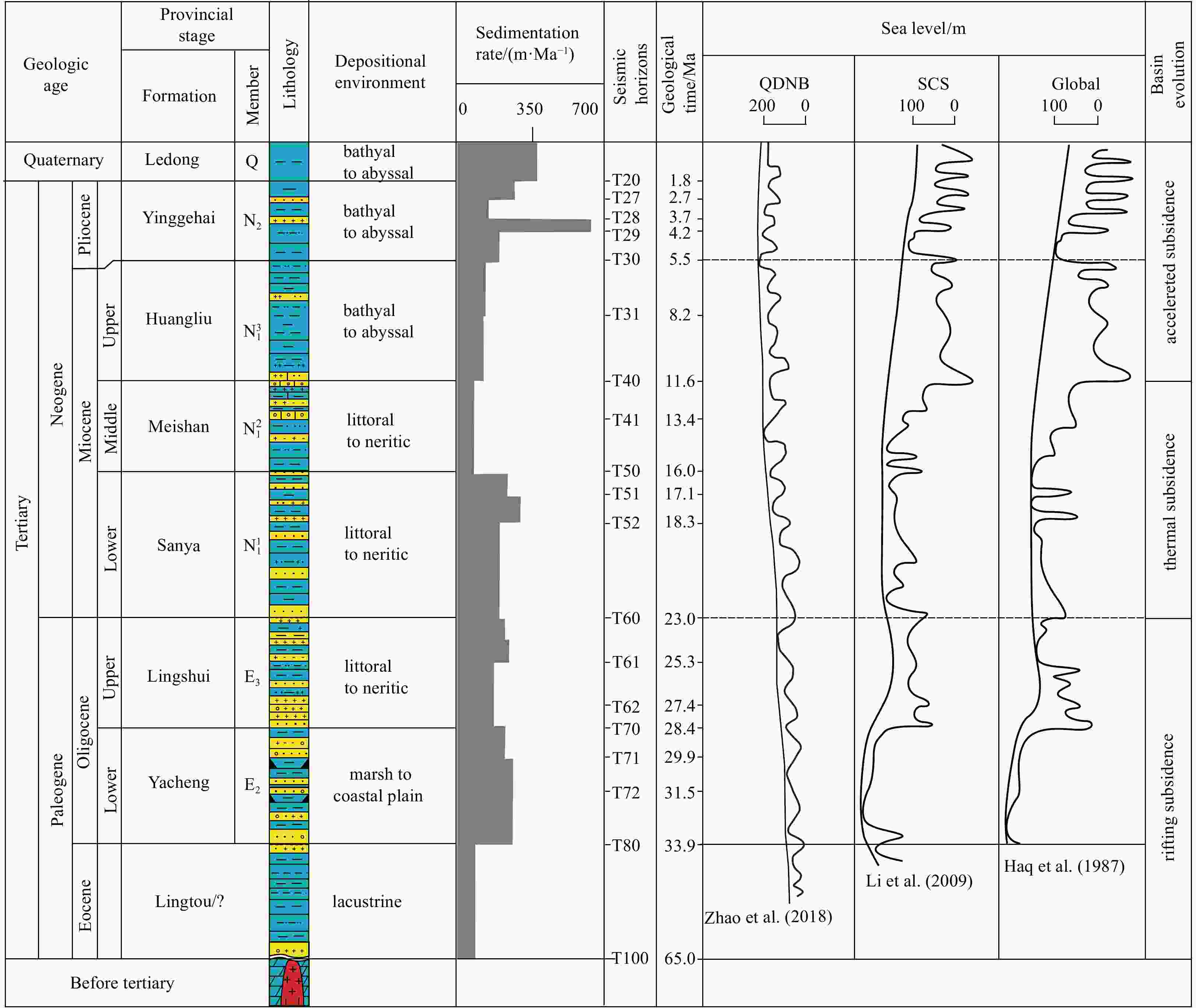
Figure 2. Simplified stratigraphic, age, and lithological column information characterizing the Qiongdongnan Basin (modified from Jiang et al. (2013) and Cheng et al. (2021)). The sedimentation rate series was derived from Zhao et al. (2018). The sea level curves were derived from Zhao et al. (2018), Li (2009) and Haq et al. (1987).
Figure 3. Sequential stratigraphy of the Qiongdongnan Basin, modified from Cheng et al. (2021) (the section location is shown in Fig. 1).
Figure 5. Time structure diagram of the T30 Interface. Bottom current direction modified from Li et al. (2018c).
Figure 7. Root mean square (RMS) amplitude map between Horizon T27 and 40 ms above Horizon T27 (a); RMS amplitude map between Horizon T40 and 40 ms above Horizon T40 (b); paleo-topographic map of Horizon T40 (c) (source direction from Xiong et al. (2021)); planar distributions of sedimentary systems between Horizons T27 and T20 (d) (source direction modified from Cheng et al. (2022)); characteristics of the Late Middle Miocene on the seismic profiles (e). See d for the location of e. MTDs: mass-transport deposits.
Figure 8. Typical section structures of meteorite craters (a, b) (modified from Keerthy et al. (2019)); Xiuyan meteorite craters (c) (modified from Wang et al. (2013)); typical channel section structures (d, e) (modified from Tian et al. (2017)); and high-curvature channel deposits (f) (modified from Mayall et al. (2006)).
Figure 9. The evolution model of the giant ancient pockmarks in the Qiongdongnan Basin. Overpressure built up, and deep fluids accumulated in the channel sands (a); the fluid in the channel sands escaped following accumulation, forming near-circular ancient pockmarks on the seafloor (b); affected by bottom-current erosion, these ancient pockmarks were transformed into different shapes (c); and the overlying effective capping prevented the ancient pockmarks from developing in multiple stages, causing the pockmarks to be buried in the stratum (d).
Figure 10. Slight leakage of deep-formation fluids, most of which reacted with seabed sediments to form carbonate precipitation, while a few reacted with seawater and failed to break through the hydrosphere (a); intense deep-formation fluid leakage, most of which broke through the hydrosphere and entered the atmosphere, while a small part reacted with the seawater and seafloor sediments (b) (redrawn after Katz et al. (1999) and Dickens (2003)).
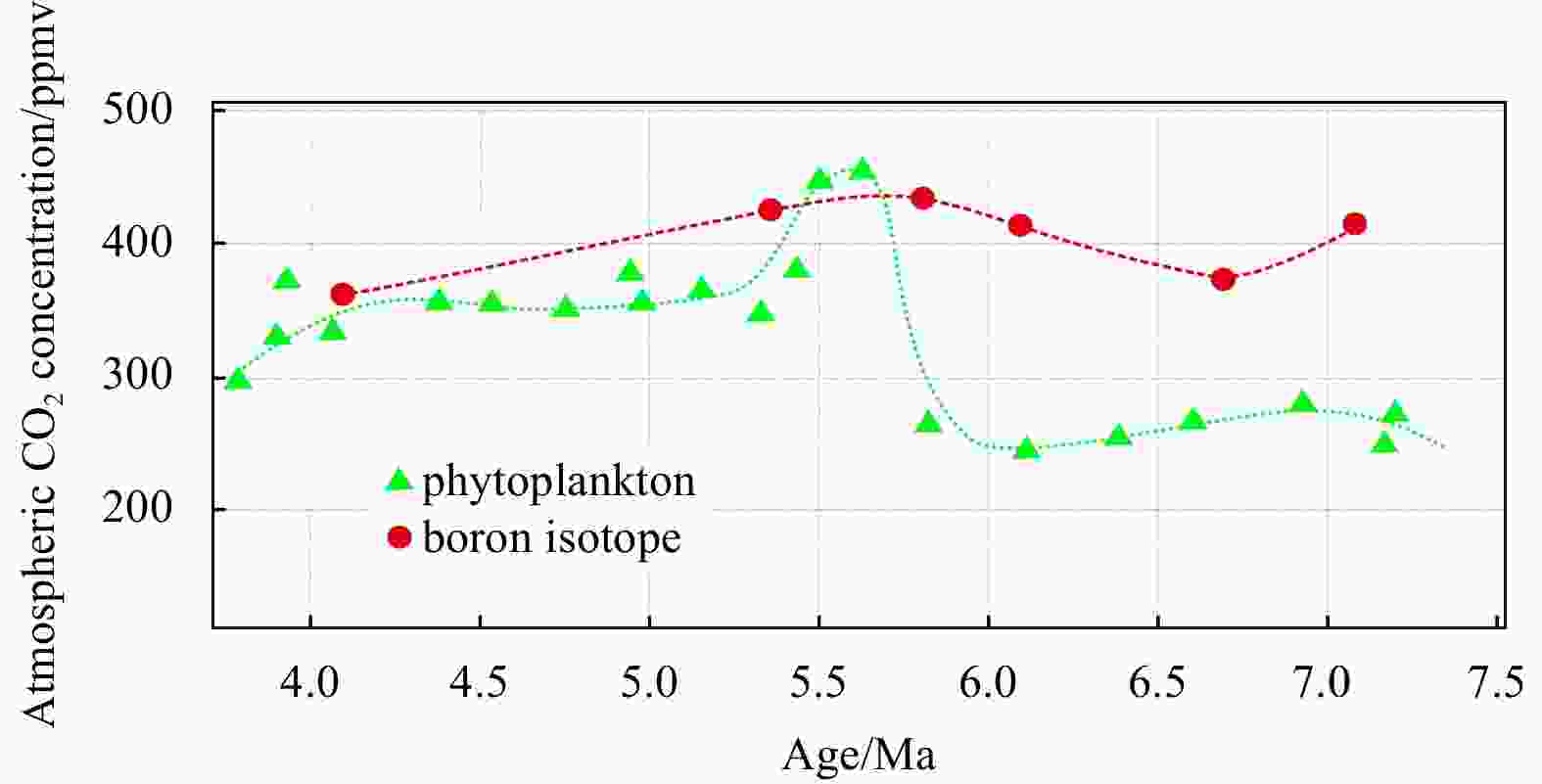
Figure 11. Reconstructed records of atmospheric CO2 concentrations from different metrics ranging from 7.5 Ma to 4.0 Ma (redrawn after Wei and Tian (2022); dates are referenced from Sosdian et al. (2018) and Breecker and Retallack. (2014)).
Table 1. Summary of ancient pockmark characteristics in the study area
Number Long axis/km Short axis/km Depth/km Dip angle of the long axis/(°) Trend Profile shape Planar shape 1 4.95 2.21 0.34 7.87 near NE U oval 2 2.29 1.25 0.43 21.52 near NE U oval 3 4.54 2.44 0.40 10.10 near NE W oval 4 4.18 1.56 0.36 9.87 near EW U crescent 5 2.75 1.68 0.60 25.00 near EW U oval 6 4.67 2.01 0.33 8.10 near NE U oval 7 12.04 10.66 1.03 9.80 near EW V chain 8 14.63 10.22 1.17 9.16 near EW V chain 9 9.16 7.38 1.25 15.64 near EW W oval Note: The information provided for ancient Pockmarks 7, 8, and 9 comprises only the data collected within the research area, although these pockmarks extend past the study area. -
Bai Yang, Song Haibin, Guan Yongxian, et al. 2014. Structural characteristics and genesis of pockmarks in the northwest of the South China Sea derived from reflective seismic and multibeam data. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 57(7): 2208–2222 Böttner C, Berndt C, Reinardy B T I, et al. 2019. Pockmarks in the Witch Ground Basin, Central North Sea. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 20(4): 1698–1719, Breecker D O, Retallack G J. 2014. Refining the pedogenic carbonate atmospheric CO2 proxy and application to Miocene CO2. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 406: 1–8, Brook E J, Sowers J, Orchardo J. 1996. Rapid variations in atmospheric methane concentration during the past 110, 000 years. Science, 273(5278): 1087–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5278.1087 Cao Licheng, Jiang Tao, Wang Zhenfeng, et al. 2015. Provenance of Upper Miocene sediments in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basins, northwestern South China Sea: Evidence from REE, heavy minerals and zircon U–Pb ages. Marine Geology, 361: 136–146. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.01.007 Chen Jiangxin, Song Haibin, Guan Yongxian, et al. 2015. Morphologies, classification and genesis of pockmarks, mud volcanoes and associated fluid escape features in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 122: 106–117. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.11.007 Chen Jiangxin, Song Haibin, Guan Yongxian, et al. 2018. Geological and oceanographic controls on seabed fluid escape structures in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 168: 38–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.04.027 Chen Hui, Xie Xinong, Van Rooij D, et al. 2014. Depositional characteristics and processes of alongslope currents related to a seamount on the northwestern margin of the Northwest Sub-Basin, South China Sea. Marine Geology, 355: 36–53. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.05.008 Chen Hui, Xie Xinong, Zhang Wenyan, et al. 2016. Deep-water sedimentary systems and their relationship with bottom currents at the intersection of Xisha Trough and Northwest Sub-Basin, South China Sea. Marine Geology, 378: 101–113. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.11.002 Cheng Cong, Jiang Tao, Kuang Zenggui, et al. 2021. Seismic characteristics and distributions of Quaternary mass transport deposits in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 129: 105118. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105118 Cheng Cong, Kuang Zenggui, Jiang Tao, et al. 2022. Source of the sand-rich gas hydrate reservoir in the northern South China Sea: Insights from detrital zircon U–Pb geochronology and seismic geomorphology. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 145: 105904. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2022.105904 Dandapath S, Chakraborty B, Karisiddaiah S M, et al. 2010. Morphology of pockmarks along the western continental margin of India: Employing multibeam bathymetry and backscatter data. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 27(10): 2107–2117. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.09.005 Davy B, Pecher I, Wood R, et al. 2010. Gas escape features off New Zealand: Evidence of massive release of methane from hydrates. Geophysical Research Letters, 37(21): L21309. doi: 10.1029/2010GL045184 Dickens G R. 2003. Rethinking the global carbon cycle with a large, dynamic and microbially mediated gas hydrate capacitor. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 213(3–4): 169–183, Fang Yunxin, Wei Jianggong, Lu Hailong, et al. 2019. Chemical and structural characteristics of gas hydrates from the Haima cold seeps in the Qiongdongnan Basin of the South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 182: 103924. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.103924 Geng Minghui, Song Haibin, Guan Yongxian, et al. 2017. Characteristics and generation mechanism of gullies and mega-pockmarks in the Zhongjiannan Basin, western South China Sea. Interpretation, 5(3): SM49–SM59. doi: 10.1190/INT-2016-0216.1 Gong Chenglin, Wang Yingmin, Zheng Rongcai, et al. 2016. Middle Miocene reworked turbidites in the Baiyun Sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea margin: Processes, genesis, and implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 128: 116–129. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.06.025 Guan Yongxian, Luo Min, Chen Linying, et al. 2014. Tracing study on the activity of mega-pockmarks in southwestern Xisha Uplift, South China Sea. Geochimica, 43(6): 628–639. doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.2014.06.007 Haq B U, Hardenbol J, Vail P R. 1987. Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic. Science, 235(4793): 1156–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4793.1156 Hassan M A, Church M, Lisle T E, et al. 2005. Sediment transport and channel morphology of small, forested streams. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 41(4): 853–876. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.2005.tb03774.x Hovland M, Gardner J V, Judd A G. 2002. The significance of pockmarks to understanding fluid flow processes and geohazards. Geofluids, 2(2): 127–136. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2002.00028.x Hovland M, Sommerville J H. 1985. Characteristics of two natural gas seepages in the North Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2(4): 319–326. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(85)90027-3 Hovland M, Svensen H. 2006. Submarine pingoes: Indicators of shallow gas hydrates in a pockmark at Nyegga, Norwegian Sea. Marine Geology, 228(1–4): 15–23, Huang Heting, Huang Baojia, Huang Yiwen, et al. 2017. Condensate origin and hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism of the deepwater giant gas field in western South China Sea: A case study of Lingshui 17–2 gas field in Qiongdongnan Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 44(3): 409–417. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30047-2 Huang Baojia, Tian Hui, Li Xushen, et al. 2016. Geochemistry, origin and accumulation of natural gases in the deepwater area of the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 72: 254–267. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.02.007 Jiang Tao, Xie Xinong, Wang Zhenfeng, et al. 2013. Seismic features and origin of sediment waves in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Marine Geophysical Research, 34(3–4): 281–294, Judd A, Hovland M. 2007. Seabed Fluid Flow: The Impact on Geology, Biology and the Marine Environment. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 408–409 Judd A G, Hovland M, Dimitrov L I, et al. 2002. The geological methane budget at Continental Margins and its influence on climate change. Geofluids, 2(2): 109–126. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2002.00027.x Katz M E, Pak D K, Dickens G R, et al. 1999. The source and fate of massive carbon input during the Latest Paleocene thermal maximum. Science, 286(5444): 1531–1533. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5444.1531 Keerthy S, Vishnu C L, Li Shanshan, et al. 2019. Reconstructing the dimension of Dhala Impact Crater, Central India, through integrated geographic information system and geological records. Planetary and Space Science, 177: 104691. doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2019.07.006 King L H, Maclean B. 1970. Pockmarks on the Scotian Shelf. GSA Bulletin, 81(10): 3141–3148. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1970)81[3141:Potss]2.0.Co;2 Lai C C A. 2007. Effects of gas hydrates on the chemical and physical properties of seawater. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 56(1–3): 47–53, Lai Hongfei, Fang Yunxin, Kuang Zenggui, et al. 2021. Geochemistry, origin and accumulation of natural gas hydrates in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea: Implications from site GMGS5-W08. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 123: 104774. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104774 Lei Chao, Ren Jianye. 2016. Hyper-extended rift systems in the Xisha Trough, northwestern South China Sea: Implications for extreme crustal thinning ahead of a propagating ocean. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 77(33): 846–864. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.07.022 Li Qianyu. 2009. The South China Sea: Paleoceanography and Sedimentology. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 75–170. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-9745-4_3 Li Na. 2013. The sedimentary paleoenvironment and provenance analysis in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin since Oligocene (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, Li Shanshan, Keerthy S, Santosh M, et al. 2018a. Anatomy of impactites and shocked zircon grains from Dhala reveals Paleoproterozoic meteorite impact in the Archean basement rocks of Central India. Gondwana Research, 54: 81–101. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.10.006 Li Yufeng, Pu Renhai, Qu Hongjun, et al. 2018b. Distribution of bottom current channels and mounds controlled by Paleo-Morphology in Mid-Miocene in Beijiao Sag of Qiongdongnan Basin. Geological Science and Technology Information (in Chinese), 37(2): 1–8. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0201 Li Yufeng, Pu Renhai, Zhang Gongcheng. 2018c. Direction and deposition/erosion characteristics of the bottom currents in the QDNB, northwestern South China Sea. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 33(6): 2546–2554. doi: 10.6038/pg2018BB0567 Li Yufeng, Pu Renhai, Zhang Gongcheng, et al. 2021. Characteristics and origins of ridges and troughs on the top of the middle Miocene strata in the Beijiao Sag of the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Interpretation, 9(2): SB1–SB15. doi: 10.1190/INT-2020-0109.1 Liang Jinqiang, Fu Shaoying, Chen Fang, et al. 2017. Characteristics of methane seepage and gas hydrate reservoir in the northeastern slope of South China Sea. Natural Gas Geoscience (in Chinese), 28(5): 761–770. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2017.02.006 Lin Meihua. 1995. Submarine geomorphology of the eastern continental shelf of the Hainan Island. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 4(4): 37–46. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1995.04.004 Liu Xingjian, Tang Dehao, Yan Pin, et al. 2017. Characteristics of authigenic carbonates from a mega-pockmark on the eastern side of Baiyun Sag, South China Sea and their geological significance. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 37(6): 119–127. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2017.06.013 Lu Yintao, Luan Xiwu, Lu Fuliang, et al. 2017. Seismic evidence and formation mechanism of gas hydrates in the Zhongjiannan Basin, western margin of the South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 84: 274–288. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.04.005 Luo Min, Wu Lushan, Chen Duofu. 2012. Research status and progress of seabed pockmarks. Marine Geology Frontiers (in Chinese), 28(5): 33–42. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2012.05.009 Masoumi S, Reuning L, Back S, et al. 2014. Buried pockmarks on the Top Chalk surface of the Danish North Sea and their potential significance for interpreting palaeocirculation patterns. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 103(2): 563–578. doi: 10.1007/s00531-013-0977-2 Mayall M, Jones E, Casey M. 2006. Turbidite channel reservoirs—Key elements in facies prediction and effective development. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 23(8): 821–841. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.08.001 Palamenghi L, Keil H, Spiess V. 2015. Sequence stratigraphic framework of a mixed turbidite-contourite depositional system along the NW slope of the South China Sea. Geo-Marine Letters, 35(1): 1–21. doi: 10.1007/s00367-014-0385-z Pilcher R, Argent J. 2007. Mega-pockmarks and linear pockmark trains on the West African continental margin. Marine Geology, 244(1–4): 15–32, Ren Jinfeng, Cheng Cong, Xiong Pengfei, et al. 2022. Sand-rich gas hydrate and shallow gas systems in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 215: 110630. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110630 Ren Jianye, Lei Chao. 2011. Tectonic stratigraphic framework of Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basins and its implication for tectonic province division in South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 54(12): 3303–3314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.028 Selim E S I. 2012. The use of seismic interpretation for delineating the characteristic features of Messinian channels in the north Nile Delta, Egypt. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 5(4): 713–722. doi: 10.1007/s12517-010-0248-5 Sosdian S M, Greenop R, Hain M P, et al. 2018. Constraining the evolution of Neogene ocean carbonate chemistry using the boron isotope pH proxy. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 498: 362–376. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2018.06.017 Su Ming, Li Junliang, Jiang Tao, et al. 2009. Morphological features and formation mechanism of Central Canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 29(4): 85–93. doi: 10.3724/sp.J.1140.2009.04085 Sun Qiliang, Cartwright J, Lüdmann T, et al. 2017. Three-dimensional seismic characterization of a complex sediment drift in the South China Sea: Evidence for unsteady flow regime. Sedimentology, 64(3): 832–853. doi: 10.1111/sed.12330 Sun Zhen, Wang Zhenfeng, Sun Zhipeng, et al. 2015. Structure and kinematic analysis of the deepwater area of the Qiongdongnan Basin through a seismic interpretation and analogue modeling experiments. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(4): 32–40. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0585-z Sun Qiliang, Wu Shiguo, Hovland M, et al. 2011. The morphologies and genesis of mega-pockmarks near the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 28(6): 1146–1156. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.03.003 Sun Qiliang, Wu Shiguo, Lü Fuliang, et al. 2010. Polygonal faults and their implications for hydrocarbon reservoirs in the southern Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 39(5): 470–479. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.002 Sun Tiantian, Wu Daidai, Pan Mengdi, et al. 2018. Geochemical characteristics of surface sediments in the southern Qiongdongnan Basin of the northern South China Sea and its implication for sedimentary environment. Journal of Tropical Oceanography (in Chinese), 37(4): 70–80. doi: 10.11978/2017091 Tian Dongmei, Jiang Tao, Zhang Daojun, et al. 2017. Genesis mechanism and characteristics of submarine channel: A case study of the first member of Yinggehai Formation in Ledong area of Yinggehai Basin. Earth Science (in Chinese), 42(1): 130–141. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.010 Tian Jie, Wu Shiguo, Lv Fuliang, et al. 2015. Middle Miocene mound-shaped sediment packages on the slope of the Xisha carbonate platforms, South China Sea: Combined result of gravity flow and bottom current. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 122: 172–184. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.06.016 Tozer B, Sandwell D T, Smith W H F, et al. 2019. Global bathymetry and topography at 15 arc sec: SRTM15+. Earth and Space Science, 6(10): 1847–1864. doi: 10.1029/2019EA000658 Wang Xinyuan, Luo Lei, Guo Huadong, et al. 2013. Cratering process and morphological features of the Xiuyan impact crater in Northeast China. Science China Earth Sciences, 56(10): 1629–1638. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4695-1 Wang Xiujuan, Wu Shiguo, Dong Dongdong, et al. 2011. Control of mass transport deposits over the occurrence of gas hydrate in Qiongdongnan Basin. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 31(1): 109–118. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1140.2011.01109 Wei Sihua, Tian Jun. 2022. Mechanisms of greenhouse climate at low atmospheric CO2 levels in the Late Miocene. Advances in Earth Science (in Chinese), 37(4): 417–428. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2021.116 Wei Jiangong, Wu Tingting, Zhu Linqi, et al. 2021. Mixed gas sources induced co-existence of sI and sII gas hydrates in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 128: 105024. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105024 Wu Xiaochuan, Pu Renhai, Chen Ying, et al. 2018. Seismic analysis of early-mid Miocene carbonate platform in the southern Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 37(2): 54–65. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1128-6 Xie Yuhong, Li Xushen, Fan Caiwei, et al. 2016. The axial channel provenance system and natural gas accumulation of the Upper Miocene Huangliu Formation in Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 43(4): 570–578. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(16)30067-2 Xie Xinong, Li Sitian, Ge Ligang, et al. 1996. Internal Achitectures and evoluting model of Bay Fan Delta System in Yanan Sag of Qiongdongnan Basin. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica (in Chinese), 41(3): 66–73 Xiong Pengfei, Jiang Tao, Kuang Zenggui, et al. 2021. Sedimentary characteristics and origin of moundes in Meishan Formation, southern Qiongdongnan Basin. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology (in Chinese), 40(4): 11–21. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0427 Yang Jiayan, Wu Dexing, Lin Xiaopei. 2008. On the dynamics of the South China Sea Warm Current. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 113(C8): C08003. doi: 10.1029/2007JC004427 Ye Jianliang, Qin Xuwen, Qiu Haijun, et al. 2018. Data Report: Molecular and isotopic compositions of the extracted gas from China’s first offshore natural gas hydrate production test in South China Sea. Energies, English,11(10): 2793. doi: 10.3390/en11102793 Yu Kaiqi, Miramontes E, Alves T M, et al. 2021. Incision of submarine channels over pockmark trains in the South China Sea. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(24): e2021GL092861. doi: 10.1029/2021GL092861 Zhai Puqiang, Chen Honghan, Xie Yuhong, et al. 2013. Modelling of evolution of overpressure system and hydrocarbon migration in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology) (in Chinese), 44(10): 4187–4201 Zhang Kun, Guan Yongxian, Song Haibin, et al. 2020. A preliminary study on morphology and genesis of giant and mega pockmarks near Andu Seamount, Nansha Region (South China Sea). Marine Geophysical Research, 41(1): 2. doi: 10.1007/s11001-020-09404-y Zhang Tiansheng, Wu Ziyin, Zhao Dineng, et al. 2019. The morphologies and genesis of pockmarks in the Reed Basin, South China Sea. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 41(3): 106–120 Zhao Chengbin, Liu Mingjun, Fan Jichang, et al. 2011. High-resolution seismic exploration of Xiuyan impact crater structures. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 54(6): 1559–1565 Zhao Zhongxian, Sun Zhen, Sun Longtao, et al. 2018. Cenozoic tectonic subsidence in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Basin Research, 30(S1): 269–288. doi: 10.1111/bre.12220 Zhu Song, Li Xuejie, Zhang Huodai, et al. 2021. Types, characteristics, distribution, and genesis of pockmarks in the South China Sea: insights from high-resolution multibeam bathymetric and multichannel seismic data. International Geology Review, 63(13): 1682–1702. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2020.1848645 -





 下载:
下载: