Spatiotemporal distribution patterns of macrobenthic communities and their relationship with environmental factors in the Shengsi Archipelago (Zhejiang, China)
-
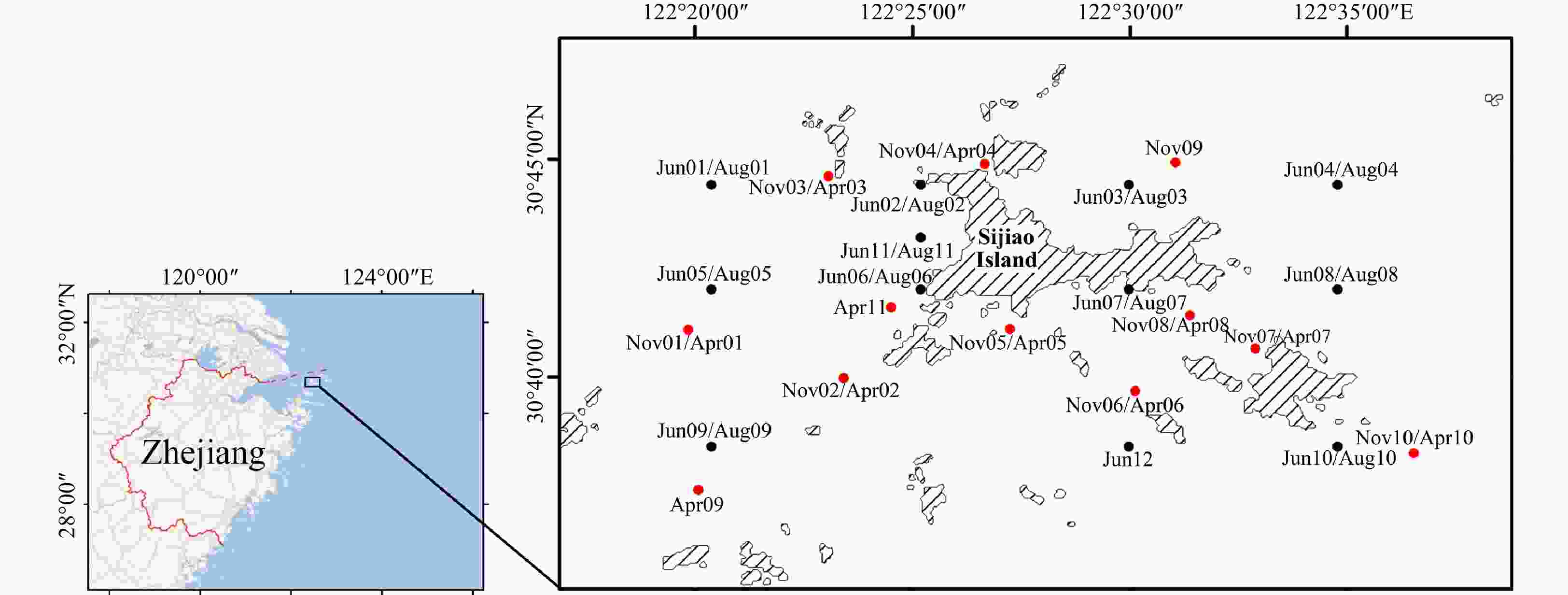
Abstract: Macrobenthic organisms are commonly employed as biomonitors for environmental risk assessment. In this study, we aimed to investigate the spatial and temporal patterns of the macrobenthic community, which is influenced by environmental factors of sediments and bottom water layer. We sampled a total of 12, 11, 10, and 11 stations in the Shengsi Archipelago during June 2010, August 2010, November 2020, and April 2021 respectively. A total of 124 species of macrobenthos were identified, with polychaetes being the dominant group. The abundance, biomass, and diversity indices exhibited no significant temporal differences. Similarly, biodiversity did not exhibit a clear spatial gradient, likely due to the small study area and the absence of significant differences in key factors such as depth. However, the stations with the lowest biodiversity values consistently appeared in the southwest region, possibly due to the impact of human activities. Significant differences in the macrobenthic community were observed between all months except between June and August, and mollusk Endopleura lubrica and polychaete Sigambra hanaokai were important contributors to these differences according to the results of the Similarity Percentages analysis. Suspended particulate matter (SPM) was identified as the primary driving factors of macrobenthic variability. In summary, the community structure underwent temporal changes influenced by complex current patterns, while biodiversity remained relatively stable. This study contributes to our understanding of the key environmental factors affecting macrobenthic communities and biodiversity. It also provides valuable data support for the long-term monitoring of macrobenthos and the environment in the Shengsi Archipelago.
-
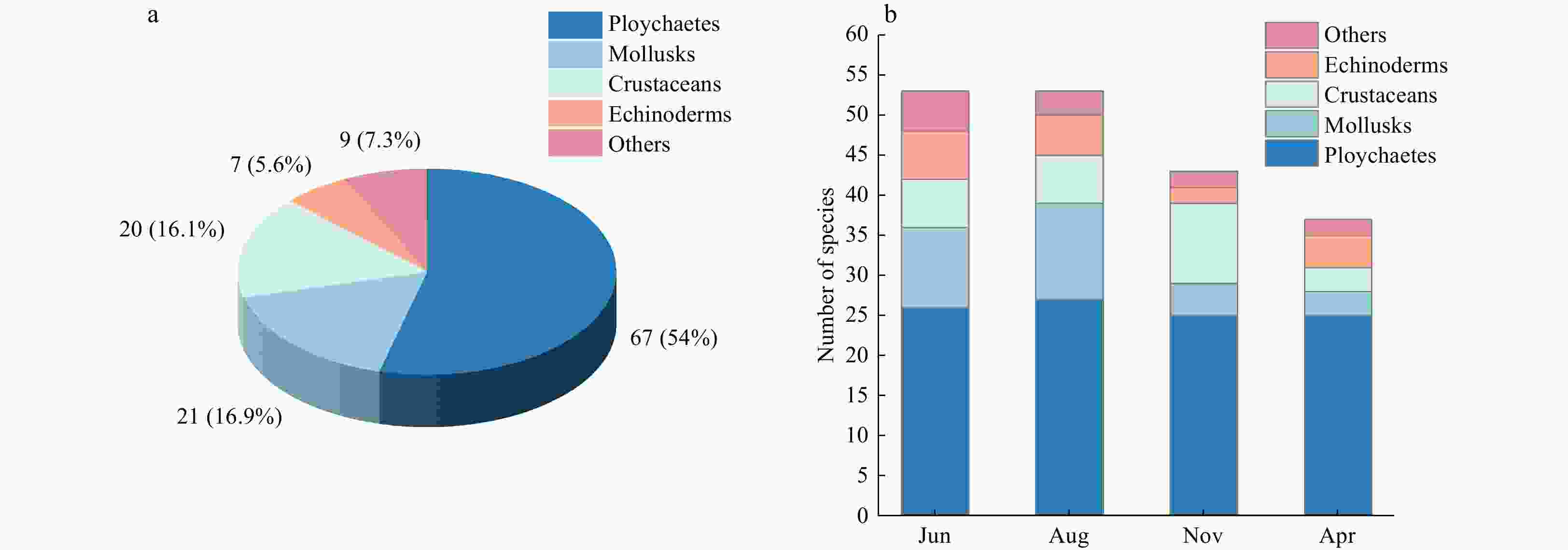
Figure 2. Species richness (S) and their assemblage composition in Shengsi Archipelago. a. Macrobenthic assemblage composition in general. b. Temporal variation in macrobenthos diversity and assemblage composition. The 'others' category classification includes nemerteans, echiurans, and fish. Jun, Aug, Nov, and Apr represent different sampling times (June 2010, August 2010, November 2020 and April 2021, respectively).
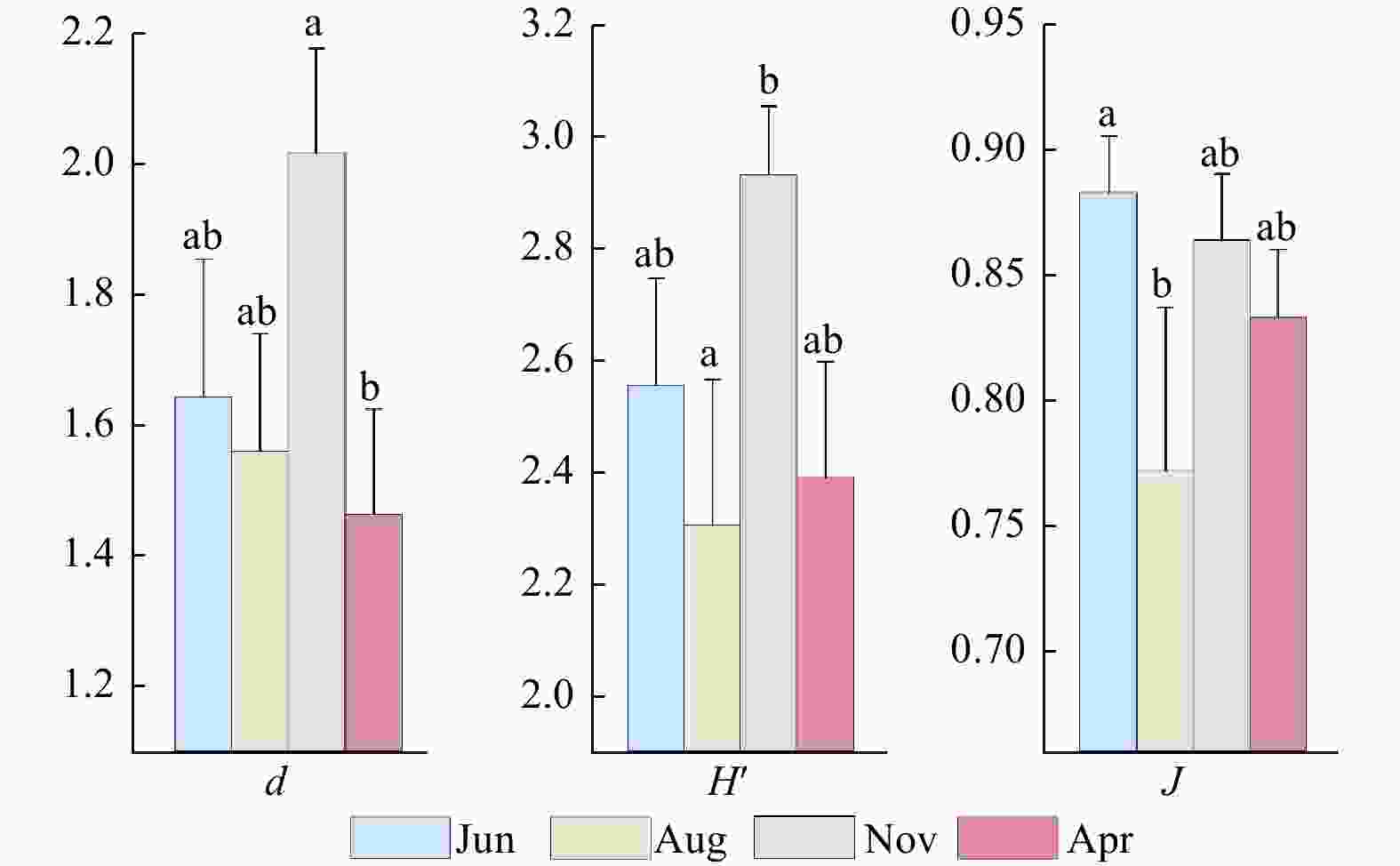
Figure 4. Temporal variation in diversity indices of microbenthic community in the Shengsi Archipelago. Jun, Aug, Nov, and Apr represent different sampling times (June 2010, August 2010, November 2020, and April 2021, respectively). d, H' and J represent the Margalef richness index, Shannon-Wiener diversity index, and Pielou evenness index, respectively. Different letters (a, b) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in these indices between different months.
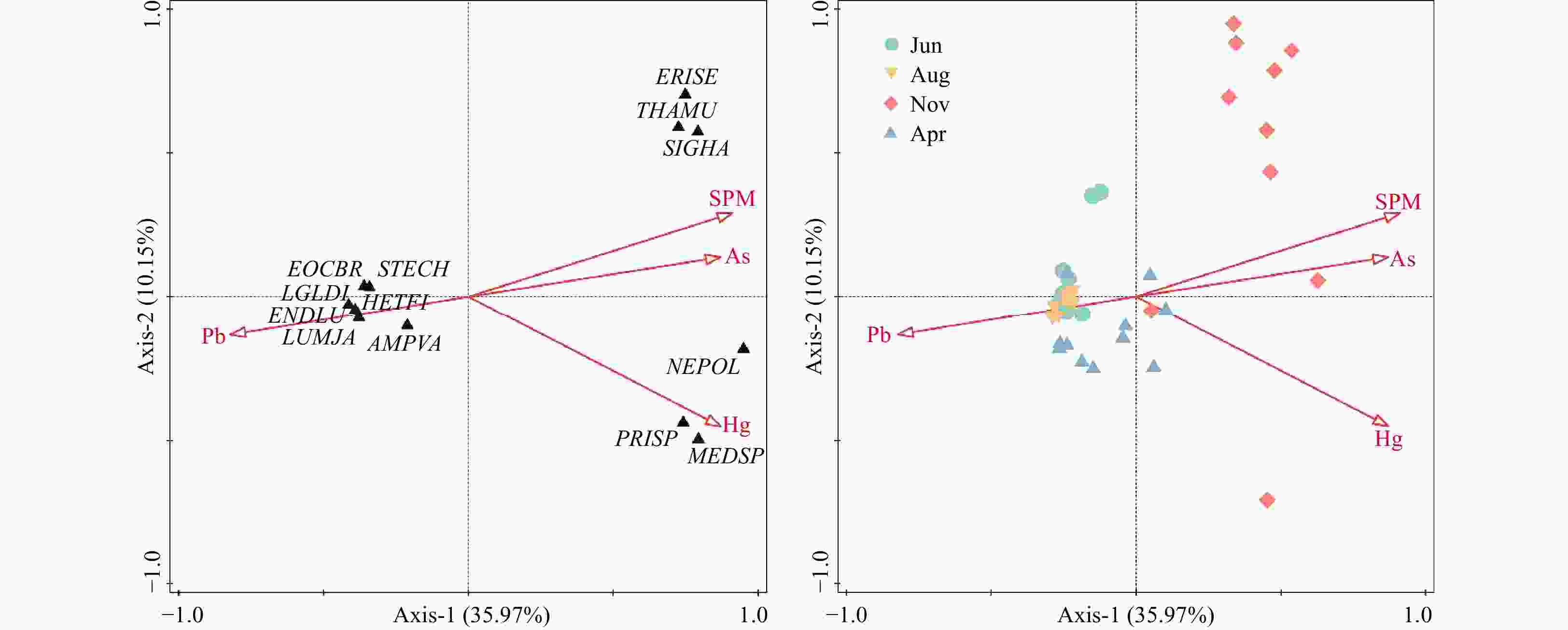
Figure 5. CCA Analysis Results for community-environment correlation. The abundance of dominant species in the stations of Jun11, Aug02, Aug05 and Aug11 was 0. Therefore, these stations were omitted from the analysis. The abbreviations in the figure were formed using the first three letters of the genus name and the first two letters of the specific epithet. Polychaete Sternaspis chinensis is abbreviated as STECH, polychaete Aglaophamus dibranchis as AGLDI, mollusk Eocylichna braunsi as EOCBR, mollusk Endopleura lubrica as ENDLU, polychaete Tharyx multifilis as THAMU, polychaete Nephtys oligobranchia as NEPOL, polychaete Sigambra hanaokai as SIGHA, polychaete Prionospio sp. as PRISP, polychaete Mediomastus sp. as MEDSP, crustacean Eriopisella sechellensis as ERISE, echinoderm Amphiura vadicola as AMPVA, polychaete Heteromastus filiformis as HETFI, and polychaete Lumbrineris japonica as LUMJA.
Table 1. Temporal variations of environmental variables in the waters of Shengsi Archipelago
Environmental Variables June August November April Hg/mg·kg–1 0.020 (0.001) a 0.020 (0.001) a 0.077 (0.014) b No data Pb/mg·kg–1 25.4 (0.6) a 24.7 (0.6) a 19.9 (0.4) b No data As/mg·kg–1 5.5 (0.1) a 5.6 (0.2) a 9.5 (0.6) b No data D/um 9.8 (0.4) a 12.7 (0.8) b 11.6 (0.7) ab No data Depth/m 13.2 (1.8) a 17.5 (6.0) a 13.3 (1.9) a 13.7 (2.7) a Temperature/℃ 19.4 (0.1) a 25.1 (0.3) b 20.2 (0.1) c 16.3 (0.2) d Salinity/‰ 20.6 (0.8) a 21.9 (0.7) a 27.2 (0.7) b 28.3 (0.7) b SPM/mg·L–1 40 (15) a 18 (2) a 235 (43) b 604 (90) c Chl a/μg·L–1 3.23 (0.77) a 15.61 (4.01) b No data No data The standard error for each value is indicated in brackets. Superscripts (a, b, c, d) are used to indicate whether there is a significant difference in the environmental variables among different months. Superscripts with the same letter indicate non-significant differences (p > 0.05), whereas different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). Table 2. Temporal variation in the average abundance of dominant species in Shengsi Archipelago
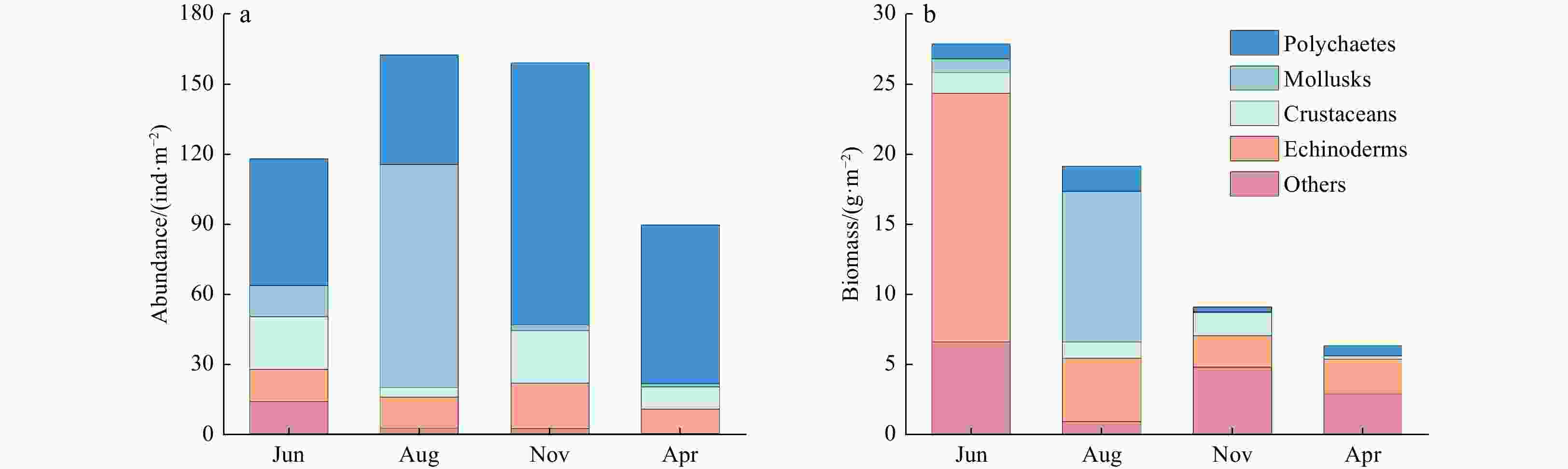
Dominant Species June August November April Aglaophamus dibranchis/ind.·m–² 6.7 (3.1)* 8.2 (4.2)* 0 0 Sternaspis chinensis/ind.·m–² 23.8 (7.9)* 14.5 (5.8)* 8.0 (2.7)* 9.1 (3.4)* Eocylichna braunsi/ind.·m–² 5.8 (2.2)* 6.4 (3.2) 0.5 (0.5) 0.5 (0.5) Endopleura lubrica/ind.·m–² 2.9 (1.1) 79.1 (54.2)* 0 0 Tharyx multifilis/ind.·m–² 0 0 11 (3.4)* 0 Nephtys oligobranchia/ind.·m–² 0 0 10.5 (3.7)* 5.9 (2.5)* Sigambra hanaokai/ind.·m–² 0 0 29.5 (7.3)* 0.9 (0.6) Prionospio sp. /ind.·m–² 0 0 14.0 (4.8)* 0 Mediomastus sp./ind.·m–² 0 0 12.0 (5.6)* 0 Eriopisella sechellensis/ind.·m–² 0 0 10.0 (5.8)* 0 Amphiura vadicola/ind.·m–² 4.5 (1.8) 4.1 (2.4) 19.0 (15.8)* 8.6 (3.1)* Lumbrineris japonica/ind.·m–² 0 0 0 4.5 (1.6)* Dentinephtys glabra/ind.·m–² 0 0 0 9.5 (4.4)* Heteromastus filiformis/ind.·m–² 0.8 (0.8) 0 0 11.8 (5.7)* The standard error for each value is indicated in brackets. The dominant species in the corresponding month are marked with *. Table 3. Average dissimilarity and ANOSIM analysis results of macrobenthic communities in the Shengsi Archipelago between different months
Groups Average dissimilarity (%) R p value Jun&Aug 83.37 −0.003 0.468 Jun&Nov 93.68 0.658 0.001*** Jun&Apr 90.54 0.401 0.001*** Aug&Nov 95.29 0.660 0.001*** Aug&Apr 93.03 0.456 0.001*** Nov&Apr 88.48 0.662 0.001*** Jun, Aug, Nov, and Apr represent different sampling times (June 2010, August 2010, November 2020, and April 2021, respectively). *p < 0.05 (significantly different); **p < 0.01 (very significant); ***p < 0.001 (extremely significant). Table 4. SIMPER analysis results: key differentiating species and their contribution rates
Key differentiating species Jun&Aug Jun&Nov Jun&Apr Aug&Nov Aug&Apr Nov&Apr Endopleura lubrica/% 9.7 1.91 2.48 7.31 9.07 0 Sternaspis chinensis/% 7.68 5.75 7.5 4.56 5.91 4.03 Amphiura vadicola/% 4.39 4.31 5.17 4.21 5.07 5.56 Heteromastus filiformis/% 0.4 0.32 5.44 0 5.03 4.44 Sigambra hanaokai/% 0 9.05 0.77 8.55 0.72 9.06 Prionospio sp./% 0 4.93 0 4.68 0 5.3 Tharyx multifilis/% 0 4.79 0 4.52 0 5.14 Only species with contributions ≥ 4% in any given month are listed. Jun, Aug, Nov, and Apr represent different sampling times (June 2010, August 2010, November 2020, and April 2021, respectively). -
Armonies W, Buschbaum C, Mielck F, et al. 2023. Mollusc shell detritus affects benthic subtidal community dynamics in the Northern Wadden Sea. Marine Biodiversity, 53(1): 2, doi: 10.1007/s12526-022-01301-4 Brey T. 2012. A multi-parameter artificial neural network model to estimate macrobenthic invertebrate productivity and production. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 10(8): 581–589, doi: 10.4319/lom.2012.10.581 Buchman M F, 2008. Screening Quick Reference Tables (SQuiRTs). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Office of Response and Restoration Chen Yaqu, Xu zhaoli, Wang Yunlong, et al. 1995. An ecological study on zooplankton in plume front zone of Changjiang (Yangtze) river estuaring area I biomass distribution of dominant species. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (in Chinese), 2(1): 49–58 Ding Yanlong, Gao Yong, Meng Zhongju, et al. 2016. Particle size characteristics of wind erosion surface soil in the Desert Steppe. Soils (in Chinese), 48(4): 803–812 Fan Liming, Liu Pengxia, Gu Yanzhen, et al. 2020. Hydrological characteristics in the Zhoushan sea area in summer. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (in Chinese), 59(S1): 1–11 Fukumori K, Oi M, Doi H, et al. 2008. Bivalve tissue as a carbon and nitrogen isotope baseline indicator in coastal ecosystems. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 79(1): 45–50, doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2008.03.004 Gao Fengming, Zhang Shuhua, Wang Xinyuan, et al. 1980. Study of the determination of ammonianitrogen in sea water with the sodium hypobromite oxidation method. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology (in Chinese), (4): 45–51 Goh Chin-Ping, Lim Poh-Eng. 2017. Potassium permanganate as oxidant in the COD test for saline water samples. ASEAN Journal on Science and Technology for Development, 25(2): 383–393, doi: 10.29037/ajstd.269 He Qiqi. 2017. Research on summertime Zhoushan coastal upwelling based on satellite remote sensing and numerical modelling (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Hu Mingna, Zhao Chaofang. 2007. Long-time observation of upwelling in the Zhoushan Islands and adjacent eeas during the summer season. Periodical of Ocean University of China (in Chinese), 37(S1): 235–240 Huang Haiping, Sun Yuanmin, Yu Weiwei, et al. 2020. Analysis of the characteristics of Eco-Exergy-based indices and diversity indices in the Zhoushan Archipelago, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(30): 37278–37285, doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07544-2 Ji Liqiang, et al. 2023. China Checklist of Animals (in Chinese). Beijing: Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences Jia Haibo, Cao Liuyan, Chai Xiaoping. 2022. The changes of macrobenthic community structure and cause analysis in the Yangtze Estuary during summer from 2016 to 2019. Marine Environmental Science (in Chinese), 41(2): 180–186 Jia Haibo, Hu Haoyan, Tang Jingliang, et al. 2012. Ecological characteristics of macrobenthos community in Zhoushan sea area in spring of 2009. Journal of Marine Sciences (in Chinese), 30(1): 27–33 Jia Haibo, Hu Haoyan, Tang Jingliang, et al. 2011. Effects of terrigenous organic pollution on distribution of macrobenthos in Zhoushan Sea. Environmental Monitoring in China (in Chinese), 27(5): 65–69 Jia Shenghua, Liao Yibo, Zeng jiangning, et al. 2017. Secondary productivity of macrobenthos in typical coastal ecosystems: Oujiang River estuary and Dongtou Islands as examples. Acta Ecologica Sinica (in Chinese), 37(21): 7140–7151 Jiang QiaoLi, Xu YongJiu, Zheng Ji, et al. 2021. Niches and interspecific association of major shrimp and crab species in Pishan waters of Zhejiang Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (in Chinese), 32(7): 2604–2614 Jin Yanjian, Zhuo Lifei. 2017. A space-time distribution of Chl-a and its correlation analysis with water quality factors in Zhoushan region. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science) (in Chinese), 36(5): 389–395 Jing Zhiyou, Qi Yiquang, Hua Zulin. 2007. Numerical study on upwelling and its seasonal variation along Fujian and Zhejiang coast. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences) (in Chinese), 35(4): 464–470 Jung Y, Park H, Yoon K, et al. 2017. Long-term changes in rocky intertidal macrobenthos during the five years after the Hebei Spirit oil spill, Taean, Korea. Ocean Science Journal, 52(1): 103–112, doi: 10.1007/s12601-017-0008-5 Lai Jiangshan. 2013. Canoco 5: a new version of an ecological multivariate data ordination program. Biodiversity Science (in Chinese), 21(6): 765–768 Lang B J, Caballes C F, Uthicke S, et al. 2023. Impacts of ocean warming on the settlement success and post-settlement survival of Pacific crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster cf. solaris). Coral Reefs, 42(1): 143–155, doi: 10.1007/s00338-022-02314-y Laudien J, Rojo M E, Oliva M E, et al. 2007. Sublittoral soft bottom communities and diversity of Mejillones Bay in northern Chile (Humboldt Current upwelling system). Helgoland Marine Research, 61(2): 103–116, doi: 10.1007/s10152-007-0057-8 Lemanowicz J, Brzezińska M, Siwik-Ziomek A, et al. 2020. Activity of selected enzymes and phosphorus content in soils of former sulphur mines. Science of The Total Environment, 708: 134545, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134545 Li Jingyi, Jia Xinmiao, Tian Yansheng. 2017. Environmental restoration of marine benthic animals. Journal Of Marine Information Technology And Application (in Chinese), (3): 41–47 Li Xinzheng. 2011. An overview of studies on marine macrobenthic biodiversity from Chinese waters: principally from the Yellow Sea. Biodiversity Science (in Chinese), 19(6): 676–684 Li Xuemei, Liu Lu, Gong Sensen, et al. 2023. Seasonal variation and driving factors of primary productivity of phytoplankton in Lake Changhu, Jianghan Plain. Journal of Lake Sciences (in Chinese), 35(3): 833–843, doi: 10.18307/2023.0307 Li Zhuo, Wang Yan, Kong Jin. 2008. Discussion and research of the determination of soil redox potentials. Environmental Science and Management (in Chinese), 33(10): 172–174 Liao Weimin, Long Ju. 2021. Current status of ocean ecological environment near Majishan Island in Zhejiang province. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences (in Chinese), 49(14): 69–71,75 Liu Qinghe, Ma Lin, Li Xinzheng. 2020. The communities of meiofauna in the northern East China Sea and their responses to runoff and the intrusion of Kuroshio Current. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 42(2): 52–64 Liu Ruiyu. 2008. Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 430–431 Liu Ruiyu, Cui Yuheng, Xu Fengshan, et al. 1986. Ecological characteristics of macrobenthos of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. Studia Marina Sinica (in Chinese), (27): 153–173 Macdonald D D, Carr R S, Calder F D, et al. 1996. Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology, 5: 253–278, doi: 10.1007/BF00118995 Mao Hanlee, Ren Yunwu, Wan Koumin. 1964. A preliminary investigation on the application of using T-S diagrams for a quantitative analysis of the watermasses in the shallow water area. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 6(1): 1–22 Nicholls P, Hewitt J, Halliday J. 2003. Effects of Suspended Sediment Concentrations on Suspension and Deposit Feeding Marine Macrofauna. Hamilton: National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research Ltd (NIWA Ning Xiuren, Shi Junxian, Cai Yuming, et al. 2004. Biological productivity front in the Changjiang Estuary and the Hangzhou Bay and its ecological effects. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 26(6): 96–106 Peng Songyao, Li Xinzheng, Wang Hongfa, et al. 2014. Macrobenthic community structure and species composition in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in jellyfish bloom. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 32(3): 576–594, doi: 10.1007/s00343-014-3068-8 Pielou E C. 1966. Species-diversity and pattern-diversity in the study of ecological succession. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 10(2): 370–383, doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90133-0 Qin Mingli, Wang Qiong, Ge Chunying, et al. 2013. Water quality assessment of Shang-Chuan-Shan Sea Dumping Site for dredged material in Shengsi. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science) (in Chinese), 32(6): 527–531 Santos S L, Bloom S A. 1983. Evaluation of succession in an estuarine macrobenthic soft-bottom community near Tampa, Florida. Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie, 68(5): 617–632, doi: 10.1002/iroh.3510680503 Shannon C E. 1997. The mathematical theory of communication. 1963. M. D. Computing : Computers in Medical Practice, 14(4): 306–317 Shen Meng, Miao Mingfang, Wang Shuyu, et al. 2020. Analysis of upwelling characteristics and formation mechanism in the Zhoushan coastal region in the summer of 2018. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (in Chinese), 59(S1): 18–23 Shi Xiaoyong, Wang Xiulin, Han Xiurong, et al. 2003. Nutrient distribution and its controlling mechanism in the adjacent area of Changjiang River estuary. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14(7): 1086–1092 Shou Lu, Zeng Jiangning, Liao Yibo, et al. 2012. Seasonal distribution of macrozoobenthos in relation to environmental factors in Hangzhou Bay. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 34(6): 151–159 Song Chen, Xu Liting, Wang XIaobo, et al. 2022a. Composition and main environmental factors of macrobenthos community in sea area of Zhoushan Islands, Zhejiang. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 53(6): 1585–1597 Song Xuanli, Xu Yongjiu, Yu Cungen, et al. 2022b. Diurnal variation and influence factors of chlorophyll-a in Changjiang River estuary in summer of 2017. Fisheries Science (in Chinese), 41(1): 52–61 Su Jilan, Pan Yuqiu. 1989. A preliminary study on the circulation dynamics of the continental shelf north of Taiwan. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 11(1): 1–14 Sun Yuyang. 2021. Changes of zooplankton and macrobenthic community structure and these relationship with environment factors in the Yushan sea (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Ningbo: Ningbo University Tang Yanbin, Liu Qiang, Liao Yibo, et al. 2021. Responses of macrobenthic communities to patchy distributions of heavy metals and petroleum hydrocarbons in sediments: A study in China’s Zhoushan Archipelago. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 40(9): 117–125, doi: 10.1007/s13131-021-1892-1 ter Braak C J F , Smilauer P. 2012. Canoco Reference Manual and User's Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0. Ithaca, USA: Microcomputer Power Thiel H. 1978. Benthos in Upwelling Regions. In: Boje R, Tomczak M, eds. Upwelling Ecosystems. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 124–138 Tian Shengyan, Zhang Wenliang, Zhang Rui. 2009. Role of macrobenthos in marine ecosystem. Journal of Saly and Chemical Industry (in Chinese), 38(2): 50–54 Tian Wei, Xu Zhaoli. 2015. Distribution of quantity and diversity of macrobenthos in the Jiaojiang Estuary. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology (in Chinese), 21(2): 358–365 Wu Wei, Lai Xiaochen, Liu Ling, et al. 2023. Research progress of soil sulfide determination methods. Contemporary Chemical Industry (in Chinese), 52(2): 497–500,504 Wu Xuwen, Salazar-Vallejo S I, Xu Kuidong. 2015. Two new species of Sternaspis Otto, 1821 (Polychaeta: Sternaspidae) from China seas. Zootaxa, 4052(3): 373–382 Xie Jianming. 2019. Factors regulating plankton communitty respiration in the Pearl River estuary (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Xiamen: Jimei University Xie Yuhuan, Gan Jie. 2010. Determination the oil class in offshore sediment in accelerated solvent extraction by fluorescence spectrophotomentric method. Environmental Science and Management (in Chinese), 35(9): 142–144 Xu Jianping, Cao Xinzhong, Pan Yuqiu. 1983. Evidence for the coastal upwelling off Zhejiang. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology (in Chinese), (4): 17–25 Xu Mingben, Zhang Rongcan, Jiang Fajun, et al. 2022. Spatiotemporal variation in phytoplankton and physiochemical factors during Phaeocystis globosa red-tide blooms in the Northern Beibu Gulf of China. Water, 14(7): 1099, doi: 10.3390/w14071099 Xu Yong. 2017. Variations of macrofaunal diversity in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea and the influence of Kuroshio Current (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences Xu Yong, Li Xinzheng, Wang Hongfa, et al. 2016. Seasonal and spatial variations of macrobenthic community structure and diversity in the South Yellow Sea. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 19(1): 92–100 Xu Yong, Sui Jixing, Ma Lin, et al. 2020. Temporal variation of macrobenthic community zonation over nearly 60 years and the effects of latitude and depth in the southern Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Science of The Total Environment, 739: 139760, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139760 Xu Yong, Yu Fei, Li Xinzheng, et al. 2018. Spatiotemporal patterns of the macrofaunal community structure in the East China Sea, off the coast of Zhejiang, China, and the impact of the Kuroshio Branch Current. PLoS One, 13(1): e0192023, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192023 Xue Biying, Wang Houjie, Zhang Yong, et al. 2018. Seasonal variations of suspended sediments in transport and flux in the coastal area of the northern Fujian Province. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 38(5): 30–40 Yan Runxuan, Feng Ming, Wang Xiaobo, et al. 2020. Temporal and spatial distribution of dominant macrozoobenthos species in the sea area off northern Zhejiang province. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 51(5): 1162–1174 Yang Dezhou, Yin Baoshu, Sun Junchuan, et al. 2013. Numerical study on the origins and the forcing mechanism of the phosphate in upwelling areas off the coast of Zhejiang province, China in summer. Journal of Marine Systems, 123-124: 1–18, doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.04.002 Yang Lei, Huang Ruihuan, LU Zhanhui, et al. 2017. The distribution of macrobenthos and the relationship with environmental factors in the waters around Jintang Island. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science) (in Chinese), 36(4): 295–301,307 Yang Wei, Huang Ju, Yu Tan. 2020. Impact of typhoon on the upwelling and chlorophyll distribution in the Zhoushan sea area. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (in Chinese), 59(S1): 24–31 Ye Lin'an, Wang Libo, Jiang Zhifa, et al. 2017. Seasonal variations of distribution characteristics of nutrients in the East China Sea in 2015. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University (in Chinese), 26(3): 432–439 Zeng Dingyong, Ni Xiaobo, Huang Daji. 2012. Temporal and spatial variability of the ZheMin Coastal Current and the Taiwan Warm Current in winter in the southern Zhejiang coastal sea. Scientia Sinica Terrae (in Chinese), 42(7): 1123–1134, doi: 10.1360/zd-2012-42-7-1123 Zhang Dongrong, Xu Zhaoli, Gao Qian, et al. 2016. Effects of tide and water masses on the distribution of zooplankton in different parts of Hangzhou Bay. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(3): 133–140, doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2015.12.007 Zhang Feijun, Liu Tao, Ying Yue, et al. 2017. Biodiversity of macrobenthos of sea area in Daishan. Ocean Development and Management (in Chinese), 34(9): 120–124 Zhang J, Liu S M, Ren J L, et al. 2007a. Nutrient gradients from the eutrophic Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary to the oligotrophic Kuroshio waters and re-evaluation of budgets for the East China Sea Shelf. Progress in Oceanography, 74(4): 449–478, doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2007.04.019 Zhang Qilong, Wang Fan. 2004. Climatological analysis of water masses in Zhoushan fishing ground and adjacent region. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 35(1): 48–54 Zhang Qilong, Wang Fan, Zhao Weihong, et al. 2007b. Seasonal characteristics in the water masses in Zhoushan fishing ground and adjacent region. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 29(5): 1–9 Zhang Yang, Chai Fei, Zhang J, et al. 2022. Numerical investigation of the control factors driving Zhe-Min Coastal Current. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 41(2): 127–138, doi: 10.1007/s13131-021-1849-4 Zhang Yurong, Guo Yuanming, Li Tiejun, et al. 2014. Present marine environment situation investigation of Sijiao Island. Guangzhou Chemical Industry (in Chinese), 42(9): 131–132,147 Zhao Baoren. 1993. Upwelling phenomenon outside the Yangtze Estuary. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 15(2): 108–114 Zhao Zhengjia, Liu Qiang, Liao Yibo, et al. 2023. Ecological risk assessment of trace metals in sediments and their effect on benthic organisms from the south coast of Zhejiang province, China. Marine pollution bulletin, 187: 114529, doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114529 Zheng Zhenming, Jin Haiyan, Chen Fajin, et al. 2022. Distribution characteristics of chlorophyll a and the exploration of its influencing factors in Beibu Gulf, August-September 2021. Journal of Marine Sciences (in Chinese), 40(3): 142–152 Zhou Hong, Zhang Zhinan. 2003. Rationale of the multivariate statistical software PRIMER and its application in benthic community ecology. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao (in Chinese), 33(1): 58–64 Zhou Hongli, Zhu Jianhua, Han Bing, et al. 2004. Research on the key technique of the analysis of suspended matter by weighting method. Journal of Ocean Technology (in Chinese), 23(3): 15–20 Zhou Nan. 2021. Study on the spatio-temporal variations and the causes of the upwelling in Zhoushan sea area (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University Zhu Dedi, Lu Douding, Wang Yunfeng, et al. 2009. The low temperature characteristics in Zhejiang coastal region in the early spring of 2005 and its influence on harmful algae bloom occurrence of Prorocentrum donghaiense. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 31(06): 31–39 Zhu Zhiqing, Ye Linan, Zhang Zining, et al. 2020. Analysis of the impact of dumping site on the environment in the nearby sea area: a case study of Shengsi Shangchuanshan Sea. Ocean Development and Management (in Chinese), 37(5): 52–56 Zou Li, Yao Xiao, Yamaguchi H, et al. 2018. Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Macro Benthos in the Intertidal Mudflat of Southern Yellow River Delta, China in 2007/2008. Journal of Ocean University of China, 17(2): 437–444, doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3313-4 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 266
- HTML全文浏览量: 91
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: