Differential scavenging behavior of anthropogenic Pb revealed by sediment traps in the northern South China Sea basin
-
Abstract: Trace metals emitted from human activities may have penetrated into the deep seas, and the underlying control mechanisms remain poorly understood. Sinking particles collected by moored time-series sediment traps from the northern South China Sea (NSCS) basin showed significant enrichment of anthropogenic aerosol Pb relative to lithogenic Fe. Total mass flux was primarily driven by seasonal primary production, and significant positive correlations were found between Pb/Fe flux and major biogenic components, indicating the crucial role of the biological pump in Pb/Fe scavenging in the water column. Notably, Pb exhibited 30−50 times higher affinity to biogenic components than Fe. A comparison was made between the enrichment factors of Fe and Pb in aerosols, euphotic particles, and sinking particles, which revealed that Pb exhibited significantly higher particle reactivity than Fe. This higher particle reactivity may encompass processes such as adsorption/desorption, bioaccumulation and decomposition release. The differential scavenging behavior of Pb suggested that the majority of Pb was rapidly scavenged in the euphotic zone and was preferentially released for accumulation in the twilight zone. This accumulation may further outflow through the Luzon Strait and result in the high dissolved Pb concentration observed in the subsurface water columns in both the NSCS and western Pacific Ocean. The rest of anthropogenic Pb in sinking particles tended to penetrate into deeper water layers and continue to be released below the twilight zone. These findings provide new insights into the biogeochemical cycling of trace metals originating from anthropogenic aerosols in marginal seas and serve as an example of the fate of other anthropogenic atmospheric pollutants.
-
Key words:
- anthropogenic aerosol /
- Pb /
- sinking particle /
- biological pump /
- northern South China Sea
-
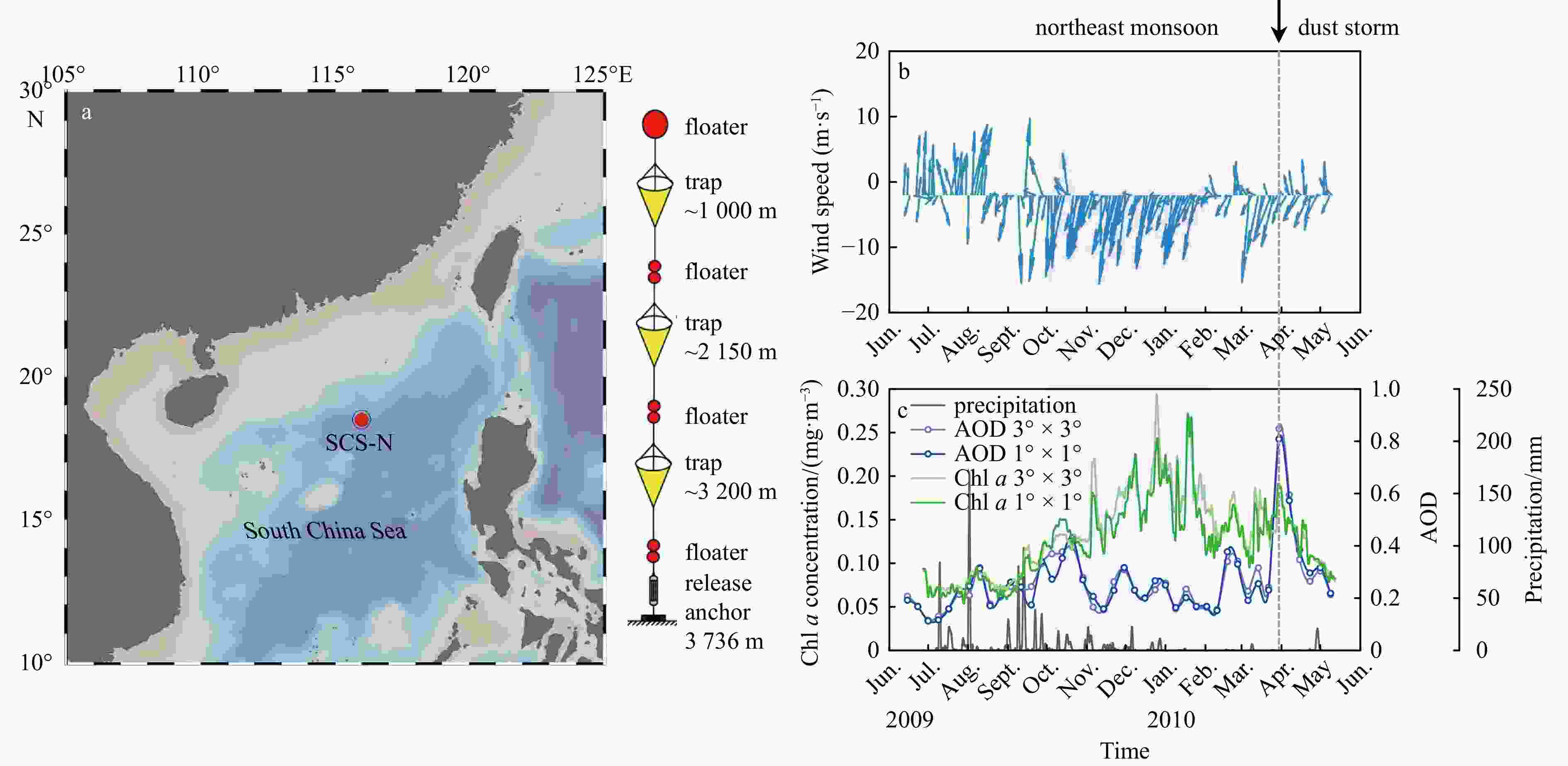
Figure 1. The location of the SCS-N (18.5°N, 116°E, water depth
3736 m) sediment trap mooring station in the northern South China Sea with the diagram of the three synchronized traps array structure to the right (a). The time-series of wind (b), 8-day average AOD, daily precipitation and surface Chl a data (c) at the SCS-N station during June 2009 to May 2010. Blue shade in b and c indicates northeast monsoon, the grey dashed line denotes the dust storm event in 19−21 March 2010.Figure 2. The temporal variations of total mass flux (TMF) (a), Al flux (b), Fe flux (c), Pb flux (d), EFFe (e) and EFPb (f) of sinking particles. The date labels on the x-axis indicate the mid date of each sampling period. For all depths full and hollow symbol denote, respectively, the low and high particle flux period. The arrow with numbers 1, 2 and 3 represent the three uncommon samples with abnormal biogenic relationships.
Figure 3. The vertical distribution of EFFe (a), EFPb (b) and POC : Al molar concentration ratio (c). Full and hollow symbol stand, respectively, for the low and high particle flux period. The reference values of EFFe and EFPb were calculated by dividing the reported trace metal to Al ratios in aerosols, 30−160 m sinking particles and sediments by the trace metal to Al ratios in the average crustal abundance (Table S3). The reference values of POC : Al molar concentration ratio in 30−160 m sinking particles and sediments were also listed in Table S3. Dissolved Pb concentration data in b were collected from Kuroshio transect (Chen et al., 2023b).
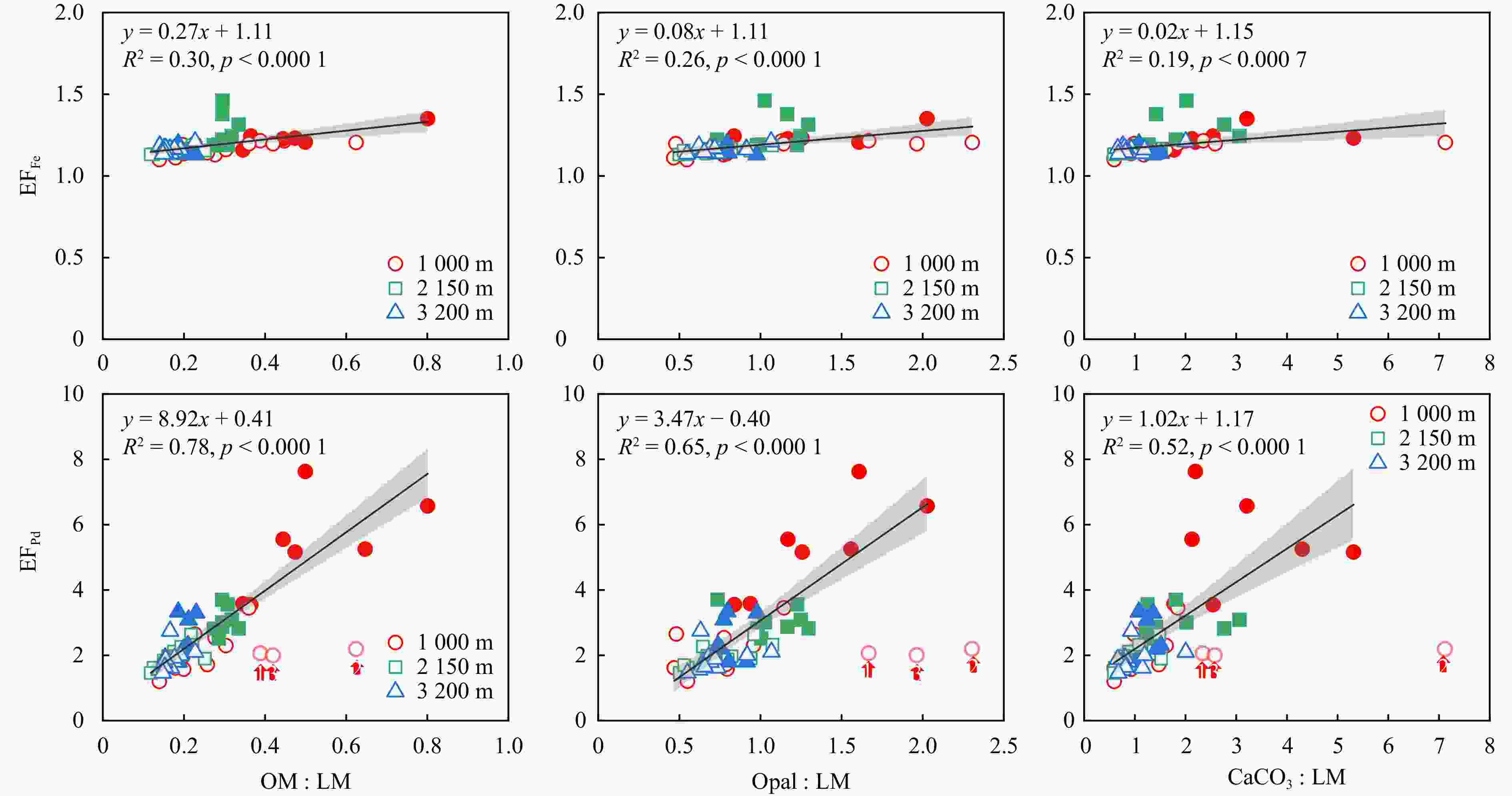
Figure 4. Correlation between the EFFe, EFPb and the ratios of OM : LM, Opal : LM, and CaCO3 : LM, respectively. OM and LM represent organic matter and lithogenic matter, respectively. Full and hollow symbol denote, respectively, the low and high particle flux period. The arrow numbers 1, 2 and 3 represent the three uncommon samples with abnormal biogenic relationships. Shades of dark grey and light grey represent 95% confidence band and prediction band, respectively.
-
Chen Mengli, Boyle E A, Jiang Shuo, et al. 2023b. Dissolved Lead (Pb) concentrations and pb isotope ratios along the East China Sea and Kuroshio transect—evidence for isopycnal transport and particle exchange. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 128(2): e2022JC019423, doi: 10.1029/2022JC019423 Chen Jie, Zhu Wenyue, Liu Qiang, et al. 2023a. Temporal evolution and regional properties of aerosol over the South China Sea. Remote Sensing, 15(2): 501, doi: 10.3390/rs15020501 Conte M H, Carter A M, Koweek D A, et al. 2019. The elemental composition of the deep particle flux in the Sargasso Sea. Chemical Geology, 511: 279–313, doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.11.001 Dai Minhan, Meng Feifei, Tang Tiantian, et al. 2009. Excess total organic carbon in the intermediate water of the South China Sea and its export to the North Pacific. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 10(12): Q12002 Gamo T. 2020. Anthropogenic lead pollution in the ocean. In: Himiyama Y, Satake K, Oki T, eds. Human Geoscience. Singapore: Springer, 295–306 Ho Tung-Youan, Chou Wenchen, Lin Huiling, et al. 2011. Trace metal cycling in the deep water of the South China Sea: the composition, sources, and fluxes of sinking particles. Limnology and Oceanography, 56(4): 1225–1243, doi: 10.4319/lo.2011.56.4.1225 Ho Tung-Youan, Chou Wenchen, Wei Ching-Ling, et al. 2010. Trace metal cycling in the surface water of the South China Sea: vertical fluxes, composition, and sources. Limnology and Oceanography, 55(5): 1807–1820, doi: 10.4319/lo.2010.55.5.1807 Ho Tung-Youan, Wen Liang-Saw, You Chen-Feng, et al. 2007. The trace metal composition of size-fractionated plankton in the South China Sea: biotic versus abiotic sources. Limnology and Oceanography, 52(5): 1776–1788, doi: 10.4319/lo.2007.52.5.1776 Ho Tung-Youan, You Chen-Feng, Chou Wen-Chen, et al. 2009. Cadmium and phosphorus cycling in the water column of the South China Sea: the roles of biotic and abiotic particles. Marine Chemistry, 115(1–2): 125–133, doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2009.07.005 Honjo S. 1996. Fluxes of particles to the interior of the open oceans. In: Ittekkot V, Schaefer P, Honjo S, et al., eds. Particle Flux in the Ocean. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 372 Hsu Shih-Chieh, Wong George T F, Gong Gwo-Ching, et al. 2010. Sources, solubility, and dry deposition of aerosol trace elements over the East China Sea. Marine Chemistry, 120(1–4): 116–127, doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2008.10.003 Hu Zhaochu, Gao Shan. 2008. Upper crustal abundances of trace elements: a revision and update. Chemical Geology, 253(3–4): 205–221, doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.05.010 Huang S, Conte M H. 2009. Source/process apportionment of major and trace elements in sinking particles in the Sargasso Sea. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(1): 65–90, doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.08.023 Jickells T D, Deuser W G, Fleer A, et al. 1990. Variability of some elemental fluxes in the western tropical Atlantic Ocean. Oceanologica Acta, 13: 291–298 Jickells T D, Deuser W G, Knap A H. 1984. The sedimentation rates of trace elements in the Sargasso Sea measured by sediment trap. Deep-Sea Research Part A: Oceanographic Research Papers, 31(10): 1169–1178 Kim M, Hwang J, Eglinton T I, et al. 2020. Lateral particle supply as a key vector in the oceanic carbon cycle. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 34(9): e2020GB006544, doi: 10.1029/2020GB006544 Lahajnar N, Wiesner M G, Gaye B. 2007. Fluxes of amino acids and hexosamines to the deep South China Sea. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 54(12): 2120–2144, doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2007.08.009 Lam P J, Marchal O. 2015. Insights into particle cycling from thorium and particle data. Annual Review of Marine Science, 7: 159–184, doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-015623 Lamborg C H, Buesseler K O, Lam P J. 2008. Sinking fluxes of minor and trace elements in the North Pacific Ocean measured during the VERTIGO program. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 55(14–15): 1564–1577, doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2008.04.012 Lanning N T, Jiang Shuo, Amaral V J, et al. 2023. Isotopes illustrate vertical transport of anthropogenic Pb by reversible scavenging within Pacific Ocean particle veils. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 120(23): e2219688120 Li Qian, Cheng Hongguang, Zhou Tan, et al. 2012. The estimated atmospheric lead emissions in China, 1990–2009. Atmospheric Environment, 60: 1–8, doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.06.025 Li Hongliang, Wiesner M G, Chen Jianfang, et al. 2017. Long-term variation of mesopelagic biogenic flux in the central South China Sea: impact of monsoonal seasonality and mesoscale eddy. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 126: 62–72, doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2017.05.012 Liao Wen-Hsuan, Ho Tung-Yuan. 2018. Particulate trace metal composition and sources in the Kuroshio adjacent to the East China Sea: the importance of aerosol deposition. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(9): 6207–6223, doi: 10.1029/2018JC014113 Liao Wen-Hsuan, Takano S, Tian Hung-An, et al. 2021. Zn elemental and isotopic features in sinking particles of the South China Sea: implications for its sources and sinks. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 314: 68–84, doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.09.013 Lin I I, Wong George T F, Lien Chun-Chi, et al. 2009. Aerosol impact on the South China Sea biogeochemistry: an early assessment from remote sensing. Geophysical Research Letters, 36(17): L17605 Liu Jianguo, Clift P D, Yan Wen, et al. 2014. Modern transport and deposition of settling particles in the northern South China Sea: sediment trap evidence adjacent to Xisha Trough. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 93: 145–155, doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2014.08.005 Müller P J, Suess E, AndréUngerer C. 1986. Amino acids and amino sugars of surface particulate and sediment trap material from waters of the Scotia Sea. Deep-Sea Research Part A: Oceanographic Research Papers, 33(6): 819–838 Mahowald N M, Hamilton D S, Mackey K R M, et al. 2018. Aerosol trace metal leaching and impacts on marine microorganisms. Nature Communications, 9(1): 2614, doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04970-7 Nakaguchi Y, Ikeda Y, Sakamoto A, et al. 2021. Distribution and stoichiometry of Al, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in the East China Sea. Journal of Oceanography, 77(3): 463–485, doi: 10.1007/s10872-020-00577-z Noriki S, Ishimori N, Harada K, et al. 1985. Removal of trace metals from seawater during a phytoplankton bloom as studied with sediment traps in Funka Bay, Japan. Marine Chemistry, 17(1): 75–89, doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(85)90037-4 Pinedo-González P, Hawco N J, Bundy R M, et al. 2020. Anthropogenic Asian aerosols provide Fe to the North Pacific Ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(45): 27862–27868 Pohl C, Löffler A, Hennings U. 2004. A sediment trap flux study for trace metals under seasonal aspects in the stratified Baltic Sea (Gotland Basin; 57°19.20′N; 20°03.00′E). Marine Chemistry, 84(3–4): 143–160, doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2003.07.002 Pullwer J, Waniek J J. 2020. Particulate trace metal fluxes in the center of an oceanic desert: Northeast Atlantic subtropical gyre. Journal of Marine Systems, 212: 103447, doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2020.103447 Ran Lihua, Chen Jianfang, Wiesner M G, et al. 2015. Variability in the abundance and species composition of diatoms in sinking particles in the northern South China Sea: results from time-series moored sediment traps. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 122: 15–24, doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.07.004 Takano S, Liao Wen-Hsuan, Tian Hung-An, et al. 2020. Sources of particulate Ni and Cu in the water column of the northern South China Sea: evidence from elemental and isotope ratios in aerosols and sinking particles. Marine Chemistry, 219: 103751, doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2020.103751 Tan Shiru, Zhang Jingjing, Li Hongliang, et al. 2020. Deep ocean particle flux in the Northern South China Sea: variability on intra-seasonal to seasonal timescales. Frontiers in Earth Science, 8: 74, doi: 10.3389/feart.2020.00074 Traill C D, Weis J, Wynn-Edwards C, et al. 2022. Lithogenic particle flux to the subantarctic Southern Ocean: a multi-tracer estimate using sediment trap samples. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 36(9): e2022GB007391, doi: 10.1029/2022GB007391 Wang Sheng-Hsiang, Christina Hsu N, Tsay S C, et al. 2012. Can Asian dust trigger phytoplankton blooms in the oligotrophic northern South China Sea?. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(5): L05811 Wang Dongxiao, Wang Qiang, Cai Shuqun, et al. 2019. Advances in research of the mid-deep South China Sea circulation. Science China: Earth Sciences, 62(12): 1992–2004, doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9546-3 Wu Yunchao, Zhang Jingping, Ni Zhixin, et al. 2018. Atmospheric deposition of trace elements to Daya Bay, South China Sea: fluxes and sources. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 127: 672–683, doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.12.046 Xie Sirong, Jiang Wei, Sun Yinan, et al. 2022. Interannual variation and sources identification of heavy metals in seawater near shipping lanes: evidence from a coral record from the northern South China Sea. Science of the Total Environment, 854: 158755 Xu Fangjian, Tian Xu, Yin Feng, et al. 2016. Heavy metals in the surface sediments of the northern portion of the South China Sea shelf: distribution, contamination, and sources. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(9): 8940–8950, doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6151-1 Zhang Jingjing, Li Hongliang, Wiesner M G, et al. 2022a. Carbon isotopic constraints on basin-scale vertical and lateral particulate organic carbon dynamics in the northern South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 127(8): e2022JC018830, doi: 10.1029/2022JC018830 Zhang Jingjing, Li Hongliang, Xuan Jiliang, et al. 2019. Enhancement of mesopelagic sinking particle fluxes due to upwelling, aerosol deposition, and monsoonal influences in the Northwestern South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(1): 99–112, doi: 10.1029/2018JC014704 Zhang Ruifeng, Ren Jingling, Zhang Zhaoru, et al. 2022b. Distribution patterns of dissolved trace metals (Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb) in China marginal seas during the GEOTRACES GP06-CN cruise. Chemical Geology, 604: 120948, doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2022.120948 Zhu Chuanyong, Tian Hezhong, Hao Jiming. 2020. Global anthropogenic atmospheric emission inventory of twelve typical hazardous trace elements, 1995–2012. Atmospheric Environment, 220: 117061, doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.117061 -




 下载:
下载: